Abstract
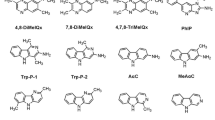
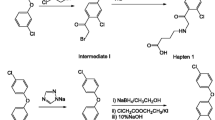
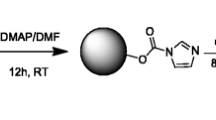
Based on the new hapten of fipronil, an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ic-ELISA) and time-resolved fluorescent immunochromatographic assay (TRFICA) for the determination of fipronil were developed. The sensitivity (IC50) of the ic-ELISA method was 2.33 ± 0.14 ng mL−1 (n = 3), and the limit of detection (LOD) (IC20) was 0.27 ± 0.02 ng mL−1 (n = 3). The cross-reaction rates of the three fipronil metabolites were all higher than 66.7%, and those of the three analogs were no more than 0.05%. The TRFICA was optimized with a handheld reader. The LOD was 0.862 ng mL−1 (n = 3). In this study, the pretreatment methods of samples such as Chinese cabbage, spinach, apple and egg, were explored. Methanol and acetonitrile were used to extract different food samples and the diluents were optimized. Three concentration levels in the spiked food samples were detected by the two methods. The range of recovery was 88.65–116.32% for ic-ELISA and 95.48–112.61% for TRFICA. In this study, the accuracy of the two methods was also judged by testing commercial quality control samples. The results showed that the accuracy was 83.75%–113.33% for ic-ELISA and 98.33–107.13% for TRFICA.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
S. Saini, M. Rani, B. Kumari, Environ. Monit. Assess. 186, 69 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3356-3
X. Li, W. Ma, H. Li, Q.H. Zhang, Z.Y. Ma, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 97, 185 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.018
N.S. Singh, R. Sharma, S.K. Singh, D.K. Singh, Environ. Res. 199, 111316 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111316
S. Amrith, T. Gunasekara, T. Truong, F. Spurlock, R.S. Tjeerdema, J. Pestic. Sci. 32, 189 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.R07-02
S. Gonçalves, M.W. Vasconcelos, T.F.M. Mota, J.M.H. Lopes, L.J. Guimaraes, K.S.B. Miglioranza, N.C. Ghisi, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 79111 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21135-8
R. An, The European Union RASFF reported that “poisonous eggs” had spread to 20 countries or regions (The foodmate net, 2017). http://news.foodmate.net/2017/08/439722.html. Accessed 14 Aug 2017
Z.L. He, X.H. Qi, Poisonous eggs were off the shelf in Taiwan. The residual excess of fluonitrile was up to 30 times as high as possible (The Paper, 2017). http://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_1771374. Accessed 22 Aug 2017
S. Hirashima, T. Amimoto, Y. Iwamoto, K. Takeda, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 89877 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28571-0
P. Bhatt, S. Gangola, S. Ramola, M. Bilal, K. Bhatt, Y. Huang, Z. Zhou, S. Chen, Microbiol. Res. 266, 127247 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2022.127247
Y.L. Zhou, S.W. Yue, B.W. Cheng, Q. Zhao, Food Chem. 377, 132021 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.132021
Y. Wei, H. Bao, Z. He, G. Huang, M. Feng, Z. Zhu, J. He, Chin. J. Chromatogr. 40, 206 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.1123.2021.04007
X.H. Wu, Y. Yu, J. Xu, F.S. Dong, X.A. Liu, P.Q. Du, D.M. Wei, Y.Q. Zheng, PLoS ONE 12, 0173690 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173690
R. Kaur, K. Mandal, R. Kumar, B. Singh, J. AOAC Int. 98, 464 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.13-066
A. Duhan, B. Kumari, S. Duhan, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 94, 260 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1447-7
T. Chen, J. Hu, Y. Chen, Y. Liu, Y. Li, H. Xu, Anal. Chim. Acta 1190, 339263 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339263
T.P. Ferreira, G.F. Bauerfeldt, R.N. Castro, V.S. Magalhães, M.C. Alves, F.B. Scott, Y.P. Cid, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 108, 225 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03369-3
S. Nagyová, P. Tölgyessy, S. Hrouzková, J. Chromatogr. A 1710, 464431 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2023.464431
S. Charernchai, M. Chikae, T.T. Phan, W. Wonsawat, D. Hirose, Y. Takamura, Anal. Chem 94, 5099 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c05401
F. Li, M.L. You, S.X. Li, J. Hu, C. Liu, Y. Gong, H.Y. Yang, X. Feng, Biotechnol. Adv. 39, 107442 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107442
S. Lv, X. Xu, L. Guo, L. Xu, L. Liu, H. Kuang, C. Xu, Analyst 148, 1703 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D3AN00084B
K.H. Wu, W.C. Huang, S.C. Chang, C.H. Kao, R.H. Shyu, Mater. Express 11, 63 (2021)
X.Q. Tao, Y.Y. Peng, J.W. Liu, J. Food Drug Anal. 28, 575 (2020). https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.1267
F. Yan, Z. Sun, H. Zhang, X. Sun, Y. Jiang, Z. Bai, Microchim. Acta 186, 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3688-y
Q.Y. Xie, Y.H. Wu, Q.R. Xiong, H.Y. Xu, Y.H. Xiong, K. Liu, J. Yong, W.H. Lai, Biosens. Bioelectron. 54, 262 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.11.002
X. Lu, J. Ji, M. Li, H.W. Xu, J.D. Sun, L.P. Wang, Y.Z. Zhang, X.L. Sun, Food Chem. 370, 131027 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131027
C. Song, A. Zhi, Q. Liu, J. Yang, G. Jia, J. Shervin, G. Zhang, Biosens. Bioelectron. 50, 62 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.06.022
M. Majdinasab, M. Sheikh-Zeinoddin, S. Soleimanian-Zad, P. Li, Q. Zhang, X. Li, J. Li, Food Control 47, 126 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.06.044
S. Wang, R.D. Allan, J.H. Skerritt, I.R.J. Kennedy, Agric. Food Chem. 46, 3330 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9800920
F. Xu, Z.Y. Jin, S.Y. Zou, C.Q. Chen, Q.F. Song, S.C. Deng, W. Xiao, X.L. Zhang, A.Q. Jia, Y. Tang, Talanta 214, 120865 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120865
Y. Zhang, J.W. Liu, W.J. Zheng, L. Wang, H.Y. Zhang, G.Z. Fang, S. Wang, J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 43, 127 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/03601230701795056
J. Yao, Z. Wang, L. Guo, X. Xu, L. Liu, H. Kuang, C. Xu, Food Chem. 356, 129710 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129710
L. Yin, X. Hu, M. Hao, J. Shi, X. Zou, K.D. Dusabe, J. Food Meas. Charact 17, 3125 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01849-0
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Project program of Tianjin Key Laboratory of Food Quality and Health, Tianjin University of Science and Technology, P. R. China (No. TJS202104) and the National Program on Key Research Project of China (No. 2018YFE0200402)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Junwei Liu: Conceptualization, methodology, project administration, writing—review and editing, resources; Yuqing Wu: Investigation, data curation, formal analysis, validation, writing—original draft, visualization; Chenchen Liu: Investigation, validation, formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft; Yan Cai: Methodology, validation, formal analysis; Yang Lu: Conceptualization, methodology, supervision, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of Tianjin University of Science and Technology for the use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Wu, Y., Liu, C. et al. Development of an ic-ELISA and a TRFICA for the detection of fipronil with a new hapten design. Food Measure 18, 2561–2572 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-02336-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-02336-2