Abstract
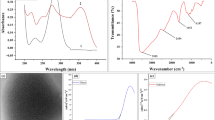
This work present a highly sensitive fluorescence method for auramine O (AO) detection in food and drug samples based on carbon nanodots (CDs). The AO can effectively diminish the emission of CDs based on an integrated quenching mechanism of inner filter effect (IFE) and dynamic reaction. The CDs were prepared via a one-step hydrothermal method with citric acid and o-phenylenediamine as precursors. The good selectivity and high sensitivity feature of the proposed method for AO detection were validated. The fluorescence signals were linearly correlated with AO concentration over a range of 0.01‒10.0 µM with a detection limit of 36.3 nM was obtained. The proposed method was finally used for AO determination in traditional Chinese medicine, curry power, bean curb and candy samples with high accuracy. The recoveries ranged from 95.5 to 107.2% and relative standard deviations (RSDs) were less than 3.39%. This work provided a new insight and an operational access to AO detection in food and drug colorants monitoring. Thus, the CDs-based sensor demonstrated feasibility of rapid AO detection considering its appealing simplicity, rapidity and high sensitivity features.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Dixit, S.K. Khanna, M. Das, A simple method for simultaneous determination of basic dyes encountered in food preparations by reversed-phase hplc. J. AOAC Int. 94, 1874–1881 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.10-450
J. Li, X.M. Ding, D.D. Liu, F. Guo, Y. Chen, Y.B. Zhang, H.M. Liu, Simultaneous determination of eight illegal dyes in chili products by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 942–943, 46–52 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.10.010
T. Tabanligil Calam, G. Taskin, Cakici, Optimization of square wave voltammetry parameters by response surface methodology for the determination of sunset yellow using an electrochemical sensor based on purpald(r). Food Chem. 404, 134412 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134412
S. Parodi, L. Santi, P. Russo, A. Albini, D. Vecchio, M. Pala, L. Ottaggio, A. Carbone, DNA damage induced by auramine o in liver, kidney, and bone marrow of rats and mice, and in a human cell line (alkaline elution assay and sce induction). Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 9, 941–952 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1080/15287398209530216
C.C. de Jesus Azevedo, R. de Oliveira, P. Suares-Rocha, D. Sousa-Moura, A.T. Li, C.K. Grisolia, G. de Aragao, C.C. Umbuzeiro, Montagner, Auramine dyes induce toxic effects to aquatic organisms from different trophic levels: an application of predicted non-effect concentration (pnec). Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. Int. 28, 1866–1877 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10462-3
J.C. Tung, W.C. Huang, J.C. Yang, G.Y. Chen, C.C. Fan, Y.C. Chien, P.S. Lin, S.C. Candice Lung, W.C. Chang, Auramine o, an incense smoke ingredient, promotes lung cancer malignancy. Environ. Toxicol. 32, 2379–2391 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22451
I. A. F. R. O. J. B. J. o. C. Some aromatic amines and related nitro compounds-hair dyes, colouring agents and miscellaneous industrial chemicals. J. Med. Entomol. 39, 209–210 (1978). doi: 978–92–832–1216–4.
T. Nguyen Thi Kim, T.T. Bui, A.T. Pham, V.T. Duong, T.H.G. Le, Fast determination of auramine o in food by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. J Anal Methods Chem 2019, 8639528 (2019). doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8639528
A. Martelli, G.B. Campart, R. Canonero, R. Carrozzino, F. Mattioli, L. Robbiano, M.J.M.R.G.T. Cavanna, E. Mutagenesis, Evaluation of auramine genotoxicity in primary rat and human hepatocytes and in the intact rat. MUTAT. RES-GEN TOX EN. 414, 37–47 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1383-5718(98)00037-0
L. Gagliardi, D.D. Orsi, G. Cavazzutti, G. Multari, D.J.C. Tonelli, Hplc determination of rhodamine b (c.I. 45170) in cosmetic products. Chromatographia. 43, 76–78 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02272825
C. Tatebe, X. Zhong, T. Ohtsuki, H. Kubota, K. Sato, H. Akiyama, A simple and rapid chromatographic method to determine unauthorized basic colorants (rhodamine b, auramine o, and pararosaniline) in processed foods. Food Sci. Nutr. 2, 547–556 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.127
D.T.N. Hoa, T.T.T. Toan, T.X. Mau, N.T.V. Hoan, T.T.N. Tram, T.D. Manh, V.T. Nguyen, V.T. Duyen, P.L.M. Thong, D.Q. Khieu, Voltammetric determination of auramine o with zif-67/fe2o3/g-c3n4-modified electrode. J. MATER. SCI. 31, 19741–19755 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04499-w
C. Zhao, W. Rao, L.J.C.J. o., P.A. Mo, Hplc determination of auramine o added in pollen typhae. J. Pharm. Anal. 27, 1956–1958 (2007). https://doi.org/10.16155/j.0254-1793.2007.12.020
T.K. Thuong Nguyen, T.H. Giang Le, V.T. Duong, T.A.J.A. Pham, B. ELECTROCHEMISTRY, Electrochemical study of auramine o at glassy carbon electrode and its determination in food by differential pulse adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Anal. Bioanal Electrochem. 11, 000466569300006 (2019)
T.T. Tran-Lam, M.B.T. Hong, G.T. Le, P.D. Luu, Auramine o in foods and spices determined by an uplc-ms/ms method. Food Addit. Contam. Part. B 13, 171–176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/19393210.2020.1742208
R.F. Straub, R.D. Voyksner, J.T.J.A.C. Keever, Determination of aromatic amines originating from azo dyes by hydrogen-palladium reduction combined with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 65, 2131–2136 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00063a034
M.S. Narvekar, A.K.J.C. Srivastava, Separation of banned amine isomers in relation to german ban on azo dyes by derivatization on gc-ms. Chromatographia. 55, 729–735 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02491789
H. Zhai, L.I. Jiangmeia, Z. Chen, Q. Zhou, J. o. A. C. Pan, Rapid determination of auramine o in yellow croaker by microchip capillary electrophoresis. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 30, 481 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1095.2013.20273
J. Li, H. Zhai, Z. Chen, Q. Zhou, Z. Liu, Z. Su, Preparation and evaluation of a novel molecularly imprinted spe monolithic capillary column for the determination of auramine o in shrimp. J. Sep. Sci. 36, 3608–3614 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201300681
W. Zhang, H. Qin, Z. Liu, H. Du, H. Li, L. Fang, Z.J.A.L. Chen, Quantitative determination of auramine o in bean curd sheets by dispersive solid phase extraction with dynamic surfaced-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal. Lett. 53, 8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2019.1702669
D. Guner, B.B. Sener, C. Bayrac, Label free detection of auramine o by g-quadruplex-based fluorescent turn-on strategy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 267, 120532 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120532
J. Yan, X. Huang, S. Liu, J. Yang, Y. Yuan, R. Duan, H. Zhang, X. Hu, A simple and sensitive method for auramine o detection based on the binding interaction with bovin serum albumin. Anal. Sci. 32, 819–824 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.32.819
S. Han, Y. Wu, L. Yan, X.J.A.M. Chen, Determination of auramine o based on a carbon dot-enhanced chemiluminescence method. ANAL. METHODS. 8, 45 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY02572B
J.-H. Zhu, M.-M. Li, S.-P. Liu, Z.-F. Liu, Y.-F. Li, X.-L. Hu, Fluorescent carbon dots for auramine o determination and logic gate operation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 219, 261–267 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.05.032
D.A. Skoog, F.J. Holler, S.R. Crouch, Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 7 edn. (th Ed. (Brooks/Cole, 2017), pp. 361–362
L. Ðorđević, F. Arcudi, M. Cacioppo, M. Prato, A multifunctional chemical toolbox to engineer carbon dots for biomedical and energy applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 112–130 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-01051-7
D. Sun, R. Ban, P.H. Zhang, G.H. Wu, J.R. Zhang, J.J.J.C. Zhu, Hair fiber as a precursor for synthesizing of sulfur- and nitrogen-co-doped carbon dots with tunable luminescence properties. RSC Adv. 64, 424–434 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.07.095
L. Liu, H. Sun, L. Xiao, Z.Q. Yang, Q.J.A. Hu, B. Chemistry, Development of a highly sensitive fluorescence method for tartrazine determination in food matrices based on carbon dots. ANAL. BIOANAL CHEM. 413, 1485–1492 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03118-1
K. Hola, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, E.P. Giannelis, R. Zboril, A.L.J.N.T. Rogach, Carbon dots—emerging light emitters for bioimaging, cancer therapy and optoelectronics. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 9, 590–603 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2014.09.004
V. Sharma, P. Tiwari, S.M.J.J. o., M.C.B. Mobin, Sustainable carbon-dots: recent advances in green carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 45, 8904–8924 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB02484C
J. Xu, Y. Zhou, G. Cheng, M. Dong, S. Liu, C.J.L. Huang, Carbon dots as a luminescence sensor for ultrasensitive detection of phosphate and their bioimaging properties. J. LUMIN. 30, 411–415 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.2752
H. Ali, S. Ghosh, N.R. J. W. I., R.N. Jana, Nanobiotechnology, fluorescent carbon dots as intracellular imaging probes. J. NANOBIOTECHNOL. 12, 1617 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1617
H.J. Yu, R. Shi, Y.F. Zhao, G.I.N. Waterhouse, L.Z. Wu, C.H. Tung, T.R. Zhang, Smart utilization of carbon dots in semiconductor photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 28, 9454–9477 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201602581
A. Im, B. Sp, C. Mb, D. Sd, E. Ms, F. As, B.J.C.P.L. Tg, Effects of carbon quantum dots (cqd) on the energy storage capacity of a novel synthesized short-chain dyad. Chem. Phys Lett. 726, 1–6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2019.04.025
J. Gao, Q. Li, C. Wang, H. Tan, Copper (ii)-mediated fluorescence of lanthanide coordination polymers doped with carbon dots for ratiometric detection of hydrogen sulfide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 253, 27–33 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.092
J. Wang, D. Li, Y. Qiu, X. Liu, J.J.T. Hu, An europium functionalized carbon dot-based fluorescence test paper for visual and quantitative point-of-care testing of anthrax biomarker. Talanta. 220, 121377 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121377
J. Qian, K. Wang, C. Wang, C. Ren, Q. Liu, N. Hao, K. Wang, Ratiometric fluorescence nanosensor for selective and visual detection of cadmium ions using quencher displacement-induced fluorescence recovery of cdte quantum dots-based hybrid probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 241, 1153–1160 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.020
A. Hrha, B. Aih, B. Yfh, A.J.F.C. Ew, Colorimetric and fluorometric nanoprobe for selective and sensitive recognition of hazardous colorant indigo carmine in beverages based on ion pairing with nitrogen doped carbon dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 241, 1153–1160 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.020
Q. Hu, Y. Cui, L. Zhang, M. Qian, J.J.J. o., F.C. Han, Analysis, an ultrasensitive analytical strategy for malachite green determination in fish samples based on bright orange-emissive carbon dots. J. Food Compost Anal. 102, 104032 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104032
Q. Hu, H. Sun, L. Liu, L. Xiao, Z.Q. Yang, S. Rao, X. Gong, J. Han, Development of an ultrasensitive spectrophotometric method for carmine determination based on fluorescent carbon dots. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo Risk Assess. 38, 731–740 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2021.1889045
Q. Hu, W. Sun, L. Xiao, Z.-. Yang, M. Yang, X. Gong, J. Han, Ultrasensitive determination of allura red in food samples based on green-emissive carbon nanodots. J. FOOD MEAS. CHARACT. 16, 4716–4727 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-022-01564-2
Y. Zhang, Y. Sun, Z. Yang, S. Jin, L. Gao, L. He, X. Jiang, A simple one-step transferred sample preparation for effective purification and extraction of auramine o in bean product by combining air-assisted ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Microchem. J. 159 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105571
P. Anilkumar, X. Wang, L. Cao, S. Sahu, Y.P.J.N. Sun, Toward quantitatively fluorescent carbon-based “quantum’’ dots. Nanoscale. 3, 2023–2027 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NR00962H
J.E. Abraham, M. Balachandran, Fluorescent mechanism in zero-dimensional carbon nanomaterials: a review. J. Fluoresc. 32, 887–906 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-022-02915?4
Q. Hu, H. Sun, X. Zhou, X. Gong, L. Xiao, L. Liu, Z.Q. Yang, Bright-yellow-emissive nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots as a fluorescent nanoprobe for the straightforward detection of glutathione in food samples. Food Chem. 325, 126946 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126946
Y. Chen, H. Lian, Y. Wei, X. He, Concentration-induced multi-colored emissions in carbon dots: origination from triple fluorescent centers. Nanoscale. 10, 6734–6743 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr00204e
M. Syrjanpaa, E. Vuorinen, S. Kulmala, Q. Wang, H. Harma, K. Kopra, Qtr-fret: efficient background reduction technology in time-resolved forster resonance energy transfer assays. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1092, 93–101 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.045
Acknowledgements
The financial supports from Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20200949), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M671625), Postdoctoral Research Funding Program of Jiangsu Province (2021K249B), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21922202), Natural Science Fund for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province, China (19KJB150042) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.W., Q.H., Z.Y. and L.X. designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. X.G. and T. G. helped design the characterisation work. W.W., Q.H., and L.X. performed the experiments. W.W. and Q.H. analysed data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in their work.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Yang, Zq., Xiao, L. et al. Supersensitive detection of auramine O in food and drug samples by using carbon dots as sensing reagents. Food Measure 17, 5360–5370 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-02057-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-02057-6