Abstract
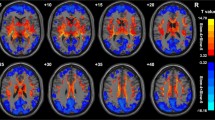
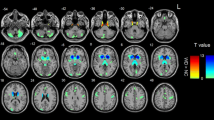
Resting state low-frequency brain activity may aid in our understanding of the mechanisms of aging-related cognitive decline. Our purpose was to explore the characteristics of the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF) in different frequency bands of fMRI to better understand cognitive aging. Thirty-seven cognitively normal older individuals underwent a battery of neuropsychological tests and MRI scans at baseline and four years later. ALFF from five different frequency bands (typical band, slow-5, slow-4, slow-3, and slow-2) were calculated and analyzed. A two-way ANOVA was used to explore the interaction effects in voxel-wise whole brain ALFF of the time and frequency bands. Paired-sample t-test was used to explore within-group changes over four years. Partial correlation analysis was performed to assess associations between the altered ALFF and cognitive function. Significant interaction effects of time × frequency were distributed over inferior frontal gyrus, superior frontal gyrus, right rolandic operculum, left thalamus, and right putamen. Significant ALFF reductions in all five frequency bands were mainly found in the right hemisphere and the posterior cerebellum; whereas localization of the significantly increased ALFF were mainly found in the cerebellum at typical band, slow-5 and slow-4 bands, and left hemisphere and the cerebellum at slow-3, slow-2 bands. In addition, ALFF changes showed frequency-specific correlations with changes in cognition. These results suggest that changes of local brain activity in cognitively normal aging should be investigated in multiple frequency bands. The association between ALFF changes and cognitive function can potentially aid better understanding of the mechanisms underlying normal cognitive aging.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Anderson, T. M., Sachdev, P. S., Brodaty, H., Trollor, J. N., & Andrews, G. (2007). Effects of sociodemographic and health variables on Mini-Mental State Exam scores in older Australians. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 15(6), 467–476. https://doi.org/10.1097/JGP.0b013e3180547053
Bai, F., Xie, C., Watson, D. R., Shi, Y., Yuan, Y., Wang, Y., . . . Zhang, Z. (2011). Aberrant hippocampal subregion networks associated with the classifications of aMCI subjects: a longitudinal resting-state study. PLoS One, 6(12), e29288. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029288
Beason-Held, L. L., Kraut, M. A., & Resnick, S. M. (2008). I. Longitudinal changes in aging brain function. Neurobiology of Aging, 29(4), 483–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.10.031
Benton, A. L., Sivan, A. B., & Spreen, O. (1996). Der Benton Test (7th ed.). Huber.
Bernard, J. A., & Seidler, R. D. (2014). Moving forward: Age effects on the cerebellum underlie cognitive and motor declines. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 42, 193–207.
Bernard, J. A., Seidler, R. D., Hassevoort, K. M., Benson, B. L., Welsh, R. C., Wiggins, J. L., … Peltier, S. J. (2012). Resting state cortico-cerebellar functional connectivity networks: a comparison of anatomical and self-organizing map approaches. Front Neuroanat, 6, 31. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2012.00031
Biswal, B., Zerrin Yetkin, F., Haughton, V. M., & Hyde, J. S. (1995). Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 34(4), 537–541.
Buzsáki, G., & Draguhn, A. (2004). Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science, 304(5679), 1926–1929.
Cao, W., Cao, X., Hou, C., Li, T., Cheng, Y., Jiang, L., … Yao, D. (2016). Effects of Cognitive Training on Resting-State Functional Connectivity of Default Mode, Salience, and Central Executive Networks. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 8(70). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00070
Cohen, A. D., Chang, C., & Wang, Y. (2021a). Using multiband multi-echo imaging to improve the robustness and repeatability of co-activation pattern analysis for dynamic functional connectivity. NeuroImage, 243, 118555.
Cohen, A. D., Yang, B., Fernandez, B., Banerjee, S., & Wang, Y. (2021b). Improved resting state functional connectivity sensitivity and reproducibility using a multiband multi-echo acquisition. NeuroImage, 225, 117461.
de Jong, L. W., van der Hiele, K., Veer, I. M., Houwing, J. J., Westendorp, R. G. J., Bollen, E. L. E. M., ... & van der Grond, J. (2008). Strongly reduced volumes of putamen and thalamus in Alzheimer's disease: an MRI study. Brain, 131(12), 3277–3285.
Diamond, A. (2013). Executive functions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 135–168. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750
Durrani, R., Friedrich, M. G., Schulze, K. M., Awadalla, P., Balasubramanian, K., Black, S. E., … Smith, E. E. (2021). Effect of Cognitive Reserve on the Association of Vascular Brain Injury With Cognition: Analysis of the PURE and CAHHM Studies. Neurology, 97(17), e1707–e1716. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000012765
Elliott, M. L., Knodt, A. R., & Hariri, A. R. (2021). Striving toward translation: Strategies for reliable fMRI measurement. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 25(9), 776–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2021.05.008
Fama, R., & Sullivan, E. V. (2015). Thalamic structures and associated cognitive functions: Relations with age and aging. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 54, 29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.03.008
Farfel, J. M., Nitrini, R., Suemoto, C. K., Grinberg, L. T., Ferretti, R. E. L., Leite, R. E. P., ... & Brazilian Aging Brain Study Group. (2013). Very low levels of education and cognitive reserve: a clinicopathologic study. Neurology, 81(7), 650–657.
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. (1975). “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12(3), 189–198.
Friston, K. J., Williams, S., Howard, R., Frackowiak, R. S., & Turner, R. (1996). Movement-related effects in fMRI time-series. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 35(3), 346–355. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.1910350312
Giménez, M., Guinea-Izquierdo, A., Villalta-Gil, V., Martínez-Zalacaín, I., Segalàs, C., Subirà, M., … behavior. (2017). Brain alterations in low-frequency fluctuations across multiple bands in obsessive compulsive disorder. Brain imaging behavior, 11(6), 1690–1706.
Gohel, S., Gallego, J. A., Robinson, D. G., DeRosse, P., Biswal, B., & Szeszko, P. R. (2018). Frequency specific resting state functional abnormalities in psychosis. Human Brain Mapping, 39(11), 4509–4518. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.24302
Gohel, S. R., & Biswal, B. B. (2015). Functional integration between brain regions at rest occurs in multiple-frequency bands. Brain Connectivity, 5(1), 23–34.
Habas, C., Kamdar, N., Nguyen, D., Prater, K., Beckmann, C. F., Menon, V., & Greicius, M. D. (2009). Distinct cerebellar contributions to intrinsic connectivity networks. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(26), 8586–8594.
Hamilton, O. K., Backhouse, E. V., Janssen, E., Jochems, A. C., Maher, C., Ritakari, T. E., ... & Wardlaw, J. M. (2021). Cognitive impairment in sporadic cerebral small vessel disease: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 17(4), 665–685.
Han, Y., Wang, J., Zhao, Z., Min, B., Lu, J., Li, K., … Jia, J. (2011). Frequency-dependent changes in the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a resting-state fMRI study. Neuroimage, 55(1), 287–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.11.059
Hazem, S. R., Awan, M., Lavrador, J. P., Patel, S., Wren, H. M., Lucena, O., … Vergani, F. (2021). Middle Frontal Gyrus and Area 55b: Perioperative Mapping and Language Outcomes. Front Neurol, 12(194), 646075. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.646075
Hu, S., Chao, H. H., Zhang, S., Ide, J. S., & Li, C. S. (2014). Changes in cerebral morphometry and amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations of BOLD signals during healthy aging: Correlation with inhibitory control. Brain Structure & Function, 219(3), 983–994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0548-0
Jacobs, H. I., Hopkins, D. A., Mayrhofer, H. C., Bruner, E., van Leeuwen, F. W., Raaijmakers, W., & Schmahmann, J. D. (2018). The cerebellum in Alzheimer’s disease: Evaluating its role in cognitive decline. Brain, 141(1), 37–47.
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage, 17(2), 825–841.
Jiao, F., Gao, Z., Shi, K., Jia, X., Wu, P., Jiang, C., . . . Shi, S. (2019). Frequency-dependent relationship between resting-state fMRI and glucose metabolism in the elderly. Frontiers in Neurology, 10, 566. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00566
La, C., Mossahebi, P., Nair, V. A., Young, B. M., Stamm, J., Birn, R., … Prabhakaran, V. (2016a). Differing Patterns of Altered Slow-5 Oscillations in Healthy Aging and Ischemic Stroke. Front Hum Neurosci, 10, 156. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00156
La, C., Nair, V. A., Mossahebi, P., Young, B. M., Chacon, M., Jensen, M., … Prabhakaran, V. (2016b). Implication of the Slow-5 Oscillations in the Disruption of the Default-Mode Network in Healthy Aging and Stroke. Brain Connect, 6(6), 482–495. https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2015.0375
Lee, H. L., Li, Z. M., Coulson, E. J., & Chuang, K. H. (2019). Ultrafast fMRI of the rodent brain using simultaneous multi-slice EPI. NeuroImage, 195, 48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.03.045
Li, Q., Dong, C., Liu, T., Chen, X., Perry, A., Jiang, J., … Wen, W. (2020). Longitudinal Changes in Whole-Brain Functional Connectivity Strength Patterns and the Relationship With the Global Cognitive Decline in Older Adults. Front Aging Neurosci, 12, 71. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2020.00071
Lin, F., Ren, P., Lo, R. Y., Chapman, B. P., Jacobs, A., Baran, T. M., … Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging, I. (2017). Insula and Inferior Frontal Gyrus' Activities Protect Memory Performance Against Alzheimer's Disease Pathology in Old Age. J Alzheimers Dis, 55(2), 669–678. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160715
Lin, X., Jia, X., Zang, Y. F., & Dong, G. (2015). Frequency-dependent changes in the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in internet gaming disorder. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1471. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01471
Lipnicki, D. M., Crawford, J. D., Dutta, R., Thalamuthu, A., Kochan, N. A., Andrews, G., . . . Matthews, F. E. (2017). Age-related cognitive decline and associations with sex, education and apolipoprotein E genotype across ethnocultural groups and geographic regions: a collaborative cohort study. PLoS Medicine, 14(3), e1002261. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002261
Liu, X., Chen, J., Shen, B., Wang, G., Li, J., Hou, H., . . . Mao, C. (2018). Altered Intrinsic Coupling between Functional Connectivity Density and Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation in Mild Cognitive Impairment with Depressive Symptoms. Neural plasticity, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1672708
Lv, H., Wang, Z., Tong, E., Williams, L. M., Zaharchuk, G., Zeineh, M., … Wintermark, M. (2018). Resting-State Functional MRI: Everything That Nonexperts Have Always Wanted to Know. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 39(8), 1390–1399. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5527
Lynch, C. J., Power, J. D., Scult, M. A., Dubin, M., Gunning, F. M., & Liston, C. (2020). Rapid Precision Functional Mapping of Individuals Using Multi-Echo fMRI. Cell Reports, 33(12), 108540. ARTN 108540.
Nugent, A. C., Martinez, A., D’alfonso, A., Zarate, C. A., & Theodore, W. H. (2015). The relationship between glucose metabolism, resting-state fMRI BOLD signal, and GABAA-binding potential: A preliminary study in healthy subjects and those with temporal lobe epilepsy. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 35(4), 583–591.
Park, D. C., Lautenschlager, G., Hedden, T., Davidson, N. S., Smith, A. D., & Smith, P. K. (2002). Models of visuospatial and verbal memory across the adult life span. Psychology and Aging, 17(2), 299–320.
Park, D. C., & Reuter-Lorenz, P. (2009). The adaptive brain: Aging and neurocognitive scaffolding. Annual Review of Psychology, 60, 173–196. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.59.103006.093656
Penny, W. D., Friston, K. J., Ashburner, J. T., Kiebel, S. J., & Nichols, T. E. (Eds.). (2011). Statistical parametric mapping: the analysis of functional brain images. Elsevier.
Pessoa, L., Gutierrez, E., Bandettini, P., & Ungerleider, L. (2002). Neural correlates of visual working memory: FMRI amplitude predicts task performance. Neuron, 35(5), 975–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00817-6
Ren, P., Lo, R. Y., Chapman, B. P., Mapstone, M., Porsteinsson, A., & Lin, F. (2016). Longitudinal alteration of intrinsic brain activity in the striatum in mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 54(1), 69–78.
Sachdev, P. S., Brodaty, H., Reppermund, S., Kochan, N. A., Trollor, J. N., Draper, B., … Broe, G. A. (2010). The Sydney Memory and Ageing Study (MAS): methodology and baseline medical and neuropsychiatric characteristics of an elderly epidemiological non-demented cohort of Australians aged 70–90 years. J International psychogeriatrics, 22(8), 1248–1264.
Schmahmann, J. D. (2004). Disorders of the cerebellum: Ataxia, dysmetria of thought, and the cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 16(3), 367–378.
Schmahmann, J. D., & Sherman, J. C. (1998). The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 121(4), 561–579.
Shea, T. B., & Remington, R. (2018). Apparent cognitive decline as revealed by an executive function test within a cohort of elderly individuals self-reporting normal cognitive performance. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 61(3), 913–915.
Singh-Manoux, A., Marmot, M. G., Glymour, M., Sabia, S., Kivimaki, M., & Dugravot, A. (2011). Does cognitive reserve shape cognitive decline? Annals of Neurology, 70(2), 296–304. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22391
Stoodley, C. J., & Schmahmann, J. D. (2009). The cerebellum and language: Evidence from patients with cerebellar degeneration. Brain and Language, 110(3), 149–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2009.07.006
Stoodley, C. J., Valera, E. M., & Schmahmann, J. D. (2012). Functional topography of the cerebellum for motor and cognitive tasks: An fMRI study. NeuroImage, 59(2), 1560–1570.
Strauss, E., Sherman, E. M., & Spreen, O. (2006). A compendium of neuropsychological tests: Administration, norms, and commentary. American Chemical Society.
Sun, Y., Dai, Z., Li, Y., Sheng, C., Li, H., Wang, X., … Han, Y. (2016). Subjective cognitive decline: mapping functional and structural brain changes—a combined resting-state functional and structural MR imaging study. Radiology, 281(1), 185–192.
Tombaugh, T. N. (2004). Trail Making Test A and B: Normative data stratified by age and education. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 19(2), 203–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0887-6177(03)00039-8
Veldsman, M., Egorova, N., Singh, B., Mungas, D., DeCarli, C., & Brodtmann, A. (2017). Low-frequency oscillations in default mode subnetworks are associated with episodic memory impairments in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 59, 98–106.
Wang, L., Kong, Q., Li, K., Su, Y., Zeng, Y., Zhang, Q., … Si, T. (2016). Frequency-dependent changes in amplitude of low-frequency oscillations in depression: A resting-state fMRI study. Neurosci Lett, 614, 105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.01.012
Wang, S., Rao, J., Yue, Y., Xue, C., Hu, G., Qi, W., … Chen, J. (2021). Altered Frequency-Dependent Brain Activation and White Matter Integrity Associated With Cognition in Characterizing Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease Stages. Front Hum Neurosci, 15(11), 625232. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2021.625232
Wang, X., Ren, P., Baran, T. M., Raizada, R. D., Mapstone, M., Lin, F., Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. (2019). Longitudinal functional brain mapping in Supernormals. Cerebral Cortex, 29(1), 242–252.
Wang, Z., Yan, C., Zhao, C., Qi, Z., Zhou, W., Lu, J., ... & Li, K. (2011). Spatial patterns of intrinsic brain activity in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: A resting‐state functional MRI study. Human brain mapping, 32(10), 1720–1740.
Wechsler, D. (1981). WAIS-R manual. The Psychological Corporation.
Wechsler, D. (1997a). Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-III. The Psychological Corporation.
Wechsler, D. (1997b). Wechsler Memory Scale. Third edition manual. The Psychological Corporation.
Wong, C. H., Liu, J., Lee, T. M., Tao, J., Wong, A. W., Chau, B. K., … Chan, C. C. (2020). Fronto-cerebellar connectivity mediating cognitive processing speed. Neuroimage, 226, 117556.
Wu, D., Zhao, H., Gu, H., Han, B., Wang, Q., Man, X., … Sun, J. (2021). The Effects of rs405509 on APOEepsilon4 Non-carriers in Non-demented Aging. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15, 677823. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.677823
Yan, C. G., Wang, X. D., Zuo, X. N., & Zang, Y. F. (2016). DPABI: Data Processing & Analysis for (Resting-State) Brain Imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14(3), 339–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-016-9299-4
Yan, L., Zhuo, Y., Wang, B., & Wang, D. J. (2011). Loss of Coherence of Low Frequency Fluctuations of BOLD FMRI in Visual Cortex of Healthy Aged Subjects. Open Neuroimag J, 5, 105–111. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874440001105010105
Yang, H., Long, X. Y., Yang, Y. H., Yan, H., Zhu, C. Z., Zhou, X. P., … Gong, Q. Y. (2007). Amplitude of low frequency fluctuation within visual areas revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Neuroimage, 36(1), 144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.01.054
Yu, R., Chien, Y. L., Wang, H. L. S., Liu, C. M., Liu, C. C., Hwang, T. J., … Tseng, W. Y. I. (2014). Frequency‐specific alternations in the amplitude of low‐frequency fluctuations in schizophrenia. Human Brain Mapping, 35(2), 627–637.
Zang, Y. F., He, Y., Zhu, C. Z., Cao, Q. J., Sui, M. Q., Liang, M., … Wang, Y. F. (2007). Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain and Development, 29(2), 83–91.
Zhang, H., Bai, X., & Diaz, M. T. (2021). The intensity and connectivity of spontaneous brain activity in a language network relate to aging and language. Neuropsychologia, 154, 107784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2021.107784
Zhang, Y., Zhu, C., Chen, H., Duan, X., Lu, F., Li, M., … Chen, H. (2015). Frequency-dependent alterations in the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in social anxiety disorder. J Affect Disord, 174, 329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2014.12.001
Zuo, X. N., Di Martino, A., Kelly, C., Shehzad, Z. E., Gee, D. G., Klein, D. F., … Milham, M. P. (2010). The oscillating brain: complex and reliable. Neuroimage, 49(2), 1432–1445.
Zuo, X. N., & Xing, X. X. (2014). Test-retest reliabilities of resting-state FMRI measurements in human brain functional connectomics: A systems neuroscience perspective. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 45, 100–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.05.009
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants and their informants for their time and generosity in contributing to this research. We also acknowledge the MAS research team.
Funding
This research received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81871434 and 61971017) and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. Z200016). MAS (The Sydney Memory and Ageing Study) cohort was supported by National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Australia Project Program Grants ID350833, ID568969 and ID1093083.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DF contributed to data analysis and the writing of the manuscript. NK, HB, PS, and WW contributed to the acquisition of data. TL and WL contributed to the study concept and design; WW and PS contributed to the critical revision of the report. JJ assisted with interpretation of findings. TL and PS assisted with funding and administration. All authors critically reviewed the first and final draft and approved final version for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent has been received from all participants in this study.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, D., Liu, T., Jiang, J. et al. Cognitive decline is associated with frequency-specific resting state functional changes in normal aging. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 2120–2132 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00682-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00682-1