Abstract
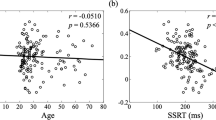
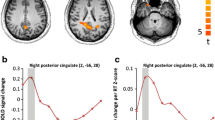
Aging is known to be associated with changes in cerebral morphometry and in regional activations during resting or cognitive challenges. Here, we investigated the effects of age on cerebral gray matter (GM) volumes and fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (fALFF) of blood oxygenation level-dependent signals in 111 healthy adults, 18–72 years of age. GM volumes were computed using voxel-based morphometry as implemented in Statistical Parametric Mapping, and fALFF maps were computed for task-residuals as described in Zhang and Li (Neuroimage 49:1911–1918, 2010) for individual participants. Across participants, a simple regression against age was performed for GM volumes and fALFF, respectively, with quantity of recent alcohol use as a covariate. At cluster level p < 0.05, corrected for family-wise error of multiple comparisons, GM volumes declined with age in prefrontal/frontal regions, bilateral insula, and left inferior parietal lobule (IPL), suggesting structural vulnerability of these areas to aging. FALFF was negatively correlated with age in the supplementary motor area (SMA), pre-SMA, anterior cingulate cortex, bilateral dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), right IPL, and posterior cingulate cortex, indicating that spontaneous neural activities in these areas during cognitive performance decrease with age. Notably, these age-related changes overlapped in the prefrontal/frontal regions including the pre-SMA, SMA, and DLPFC. Furthermore, GM volumes and fALFF of the pre-SMA/SMA were negatively correlated with the stop signal reaction time, in accord with our earlier work. Together, these results describe anatomical and functional changes in prefrontal/frontal regions and how these changes are associated with declining inhibitory control during aging.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (1999) Nonlinear spatial normalization using basis functions. Hum Brain Mapp 7:254–266
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry: the methods. Neuroimage 11:805–821
Bednarski SR, Erdman E, Luo X, Zhang S, Hu S, Li CSR (2012) Neural processes of an indirect analog of risk taking in young nondependent adult alcohol drinkers—an fMRI study of the stop signal task. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36:768–779
Bergfield KL, Hanson KD, Chen KW, Teipel SJ, Hampel H, Rapoport SI, Moeller JR, Alexander GE (2010) Age-related networks of regional covariance in MRI gray matter: reproducible multivariate patterns in healthy aging. Neuroimage. 49:1750–1759
Birn RM, Diamond JB, Smith MA, Bandettini PA (2006) Separating respiratory-variation-related neuronal-activity-related fluctuations in fluctuations from fMRI. Neuroimage 31:1536–1548
Birn RM, Smith MA, Jones TB, Bandettini PA (2008) The respiration response function: the temporal dynamics of fMRI signal fluctuations related to changes in respiration. Neuroimage 40:644–654
Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS (1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magnet Reson Med 34:537–541
Biswal BB, Mennes M, Zuo XN, Gohel S, Kelly C, Smith SM, Beckmann CF, Adelstein JS, Buckner RL, Colcombe S, Dogonowski AM, Ernst M, Fair D, Hampson M, Hoptman MJ, Hyde JS, Kiviniemi VJ, Kotter R, Li SJ, Lin CP, Lowe MJ, Mackay C, Madden DJ, Madsen KH, Margulies DS, Mayberg HS, McMahon K, Monk CS, Mostofsky SH, Nagel BJ, Pekar JJ, Peltier SJ, Petersen SE, Riedl V, Rombouts SARB, Rypma B, Schlaggar BL, Schmidt S, Seidler RD, Siegle GJ, Sorg C, Teng GJ, Veijola J, Villringer A, Walter M, Wang LH, Weng XC, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Williamson P, Windischberger C, Zang YF, Zhang HY, Castellanos FX, Milham MP (2010) Toward discovery science of human brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:4734–4739
Buckner RL (2004) Memory and executive function in aging and AD: multiple factors that cause decline and reserve factors that compensate. Neuron 44:195–208
Chang C, Glover GH (2009) Relationship between respiration, end-tidal CO2, and BOLD signals in resting-state fMRI. Neuroimage 47:1381–1393
Chang C, Cunningham JP, Glover GH (2009) Influence of heart rate on the BOLD signal: the cardiac response function. Neuroimage 44:857–869
Chao HH, Luo X, Chang JL, Li CS (2009) Activation of the pre-supplementary motor area but not inferior prefrontal cortex in association with short stop signal reaction time: an intra-subject analysis. BMC Neurosci 10:75
Chee MWL, Chen KHM, Zheng H, Chan KPL, Isaac V, Sim SKY, Chuah LYM, Schuchinsky M, Fischl B, Ng TP (2009) Cognitive function and brain structure correlations in healthy elderly East Asians. Neuroimage 46:257–269
Duann JR, Ide JS, Luo X, Li CS (2009) Functional connectivity delineates distinct roles of the inferior frontal cortex and presupplementary motor area in stop signal inhibition. J Neurosci 29:10171–10179
Eckert MA (2011) Slowing down: age-related neurobiological predictors of processing speed. Front Neurosci 5:25
Fair DA, Schlaggar BL, Cohen AL, Miezin FM, Dosenbach NUF, Wenger KK, Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Raichle ME, Petersen SE (2007) A method for using blocked and event-related fMRI data to study “resting state” functional connectivity. Neuroimage 35:396–405
Fellgiebel A, Yakushev I (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging of the hippocampus in MCI and early Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 26:257–262
First M, Spitzer R, Williams J, Gibbon M (1995) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV (SCID). American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Folstein M, Folstein S (2010) Functional expressions of the aging brain. Nutr Rev 68(Suppl 2):S70–S73
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, Mchugh PR (1975) Mini-mental state—practical method for grading cognitive state of patients for clinician. J Psychiat Res 12:189–198
Fox MD, Raichle ME (2007) Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:700–711
Friston K, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline JB, Frith CD, Frackowiak R (1995) Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Hum Brain Mapp 2:189–210
Giorgio A, Santelli L, Tomassini V, Bosnell R, Smith S, De Stefano N, Johansen-Berg H (2010) Age-related changes in grey and white matter structure throughout adulthood. Neuroimage 51:943–951
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RNA, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RSJ (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 14:21–36
Grieve SM, Clark CR, Williams LM, Peduto AJ, Gordon E (2005) Preservation of limbic and paralimbic structures in aging. Hum Brain Mapp 25:391–401
Han Y, Lui S, Kuang W, Lang Q, Zou L, Jia J (2012) Anatomical and functional deficits in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 7:e28664
Harper C (2007) The neurotoxicity of alcohol. Hum Exp Toxicol 26:251–257
Hu S, Li CS (2012) Neural processes of preparatory control for stop signal inhibition. Hum Brain Mapp 33:2785–2796
Hu S, Chao HH, Winkler AD, Li CS (2012) The effects of age on cerebral activations: internally versus externally driven processes. Front Aging Neurosci 4:4
Jernigan TL, Butters N, Ditraglia G, Schafer K, Smith T, Riwin M, Grant I, Schuckit M, Cermak LS (1991) Reduced cerebral gray-matter observed in alcoholics using magnetic-resonance-imaging. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 15:418–427
Jones DT, Machulda MM, Vemuri P, McDade EM, Zeng G, Senjem ML, Gunter JL, Przybelski SA, Avula RT, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Petersen RC, Jack CR (2011) Age-related changes in the default mode network are more advanced in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 77:1524–1531
Kantarci K, Jack CR (2003) Neuroimaging in Alzheimer disease: an evidence-based review. Neuroimag Clin N Am 13:197–203
Kramer JH, Mungas D, Reed BR, Wetzel ME, Burnett MM, Chui HC, Miller BL, Weiner MW (2007) Longitudinal MRI and cognitive change in healthy elderly. Neuropsychology 21:412–418
Kril JJ, Halliday GM, Svoboda MD, Cartwright H (1997) The cerebral cortex is damaged in chronic alcoholics. Neuroscience 79:983–998
Levitt H (1971) Transformed up-down methods in psychoacoustics. J Acoust Soc Am 49:467–477
Li CS, Krystal JH, Mathalon DH (2005) Fore-period effect and stop-signal reaction time. Exp Brain Res 167:305–309
Li CSR, Huang C, Constable RT, Sinha R (2006) Imaging response inhibition in a stop-signal task: neural correlates independent of signal monitoring and post-response processing. J Neurosci 26:186–192
Li CSR, Chao HHA, Lee TW (2009) Neural correlates of speeded as compared with delayed responses in a stop signal task: an indirect analog of risk taking and association with an anxiety trait. Cereb Cortex 19:839–848
Littow H, Elseound AA, Haapea M, Isohanni M et al (2010) Age-related differences in functional nodes of the brain cortex: a high model order group ICA study. Front Sys Neurosci 4:32
Logan GD, Cowan WB, Davis KA (1984) On the ability to inhibit simple and choice reaction-time responses: a model and a method. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 10:276–291
Long X, Liao W, Jiang C, Liang D, Qiu B, Zhang L (2012) Healthy aging: an automatic analysis of global and regional morphological alterations of human brain. Acad Radiol 19:785–793
Margulies DS, Bottger J, Long XY, Lv YT, Kelly C, Schafer A, Goldhahn D, Abbushi A, Milham MP, Lohmann G, Villringer A (2010) Resting developments: a review of fMRI post-processing methodologies for spontaneous brain activity. Magn Reson Mater Phy 23:289–307
Morris JC (2012) Revised criteria for mild cognitive impairment may compromise the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease dementia. Arch Neurol 69(6):700–708
Nagel IE, Preuschhof C, Li SC, Nyberg L, Backman L, Lindenberger U, Heekeren HR (2009) Performance level modulates adult age differences in brain activation during spatial working memory. P Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22552–22557
Nagel IE, Preuschhof C, Li SC, Nyberg L, Backman L, Lindenberger U, Heekeren HR (2011) Load modulation of BOLD response and connectivity predicts working memory performance in younger and older adults. J Cognitive Neurosci 23:2030–2045
Park DC, Polk TA, Park R, Minear M, Savage A, Smith MR (2004) Aging reduces neural specialization in ventral visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13091–13095
Paul RH, Haque O, Gunstad J, Tate DF, Grieve SM, Hoth K, Brickman AM, Cohen R, Lange K, Jefferson AL, MacGregor KL, Gordon E (2005) Subcortical hyperintensities impact cognitive function among a select subset of healthy elderly. Arch Clin Neuropsych 20:697–704
Power JD, Barnes KA, Snyder AZ, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE (2012) Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage 59:2142–2154
Raz N, Lindenberger U, Rodrigue KM, Kennedy KM, Head D, Williamson A, Dahle C, Gerstorf D, Acker JD (2005) Regional brain changes in aging healthy adults: general trends, individual differences and modifiers. Cereb Cortex 15:1676–1689
Reuter-Lorenz PA, Cappell KA (2008) Neurocognitive aging and the compensation hypothesis. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 17:177–182
Rosazza C, Minati L (2011) Resting-state brain networks: literature review and clinical applications. Neurol Sci 32:773–785
Seidler RD, Bernard JA, Burutolu TB, Fling BW, Gordon MT, Gwin JT, Kwak Y, Lipps DB (2010) Motor control and aging: links to age-related brain structural, functional, and biochemical effects. Neurosci Biobehav R 34:721–733
Sowell ER, Peterson BS, Thompson PM, Welcome SE, Henkenius AL, Toga AW (2003) Mapping cortical change across the human life span. Nat Neurosci 6:309–315
Su L, Wang L, Chen F, Shen H, Li B, Hu D (2012) Sparse representation of brain aging: extracting covariance patterns from structural MRI. PLoS ONE 7:e36147
Taki Y, Goto R, Evans A, Zijdenbos A, Neelin P, Lerch J, Sato K, Ono S, Kinomura S, Nakagawa M, Sugiura M, Watanabe J, Kawashima R, Fukuda H (2004) Voxel-based morphometry of human brain with age and cerebrovascular risk factors. Neurobiol Aging 25:455–463
Taki Y, Thyreau B, Kinomura S, Sato K, Goto R, Kawashima R, Fukuda H (2011) Correlations among brain gray matter volumes, age, gender, and hemisphere in healthy individuals. PLoS ONE 6:e22734
Taki Y, Hashizume H, Thyreau B, Sassa Y, Takeuchi H, Wu K, Kotozaki Y, Nouchi R, Asano M, Asano K, Fukuda H, Kawashima R (2012) Linear and curvilinear correlations of brain gray matter volume and density with age using voxel-based morphometry with the Akaike information criterion in 291 healthy children. Hum Brain Mapp. doi:10.1002/hbm.22033. (Epub ahead of print)
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15:273–289
Van Dijk KRA, Sabuncu MR, Buckner RL (2012) The influence of head motion on intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage 59:431–438
Wetheril GB, Chen H, Vasudeva RB (1966) Sequential estimation of quantal response curves: a new method of estimation. Biometrika 53:439–454
Yan L, Zhuo Y, Wang B, Wang DJ (2011) Loss of coherence of low frequency fluctuations of BOLD FMRI in visual cortex of healthy aged subjects. Open Neuroimag J 5:105–111
Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, Cao QJ, Sui MQ, Liang M, Tian LX, Jiang TZ, Wang YF (2007) Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev 29:83–91
Zhang S, Li CS (2010) A neural measure of behavioral engagement: task-residual low-frequency blood oxygenation level-dependent activity in the precuneus. Neuroimage 49:1911–1918
Zhang S, Li CS (2012a) Task-related, low-frequency task-residual, and resting state activity in the default mode network brain regions. Front Psychol 3:172
Zhang S, Li CS (2012b) Functional networks for cognitive control in a stop signal task: independent component analysis. Hum Brain Mapp 33:89–104
Zou QH, Zhu CZ, Yang YH, Zuo XN, Long XY, Cao QJ, Wang YF, Zang YF (2008) An improved approach to detection of amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) for resting-state fMRI: fractional ALFF. J Neurosci Methods 172:137–141
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH grant K02DA026990 (Li), a Yale Cancer Center grant for translational pilot study (Chao), and the William O. Seery Foundation (Chao). We thank Dr. Dianne Lee, Olivia Farr, Sarah Bednarski, and Emily Erdman for their many helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, S., Chao, H.HA., Zhang, S. et al. Changes in cerebral morphometry and amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations of BOLD signals during healthy aging: correlation with inhibitory control. Brain Struct Funct 219, 983–994 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0548-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0548-0