Abstract
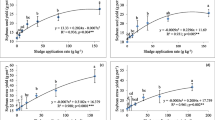
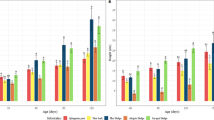
A study was conducted to evaluate the effects of sludge (industrial and residential) on seed germination and growth performance of Acacia auriculiformis seedlings at the nursery of Institute of Forestry and Environmental Sciences, Chittagong University (IFESCU), Bangladesh. Before sowing of the seeds, different combinations of sludge were incorporated with the nutrient-deficient natural forest soils. Seed germination and growth parameters of the seedlings (shoot and root length, collar diameter, fresh and dry weight of shoot, and root and total dry biomass) were recorded after one, two and three months of seed sowing. Physio-chemical parameters (pH, organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) and heavy metals (chromium, nickel, manganese, cadmium and zinc) of each treatment were also analyzed before sowing of seeds and after harvesting of seedlings. Results show that the seed germination percentage and the seedling growth parameters varied significantly in the soil added with sludge in comparison to control. The highest germination percentage (90%) was observed in the treatment of soil with residential sludge of 2:1 compared to control. The highest growth and biomass of the seedlings as well as the maximum percentage of organic carbon and nutrients (N, P and K) were also recorded in the same combination. Soil added with industrial sludge had a higher concentration of heavy metal than that of residential sludge. The highest concentrations of heavy metals were found in soil added with industrial sludge of 1:1. It is recommended that soil added with residential sludge of 2:1 provide good condition for better seed germination and growth of A. auriculiformis seedlings in degraded forest soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Wahab S. 1985. Potassium nitration and nitrogen fixation by nodulation legumes. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 8(1): 9–20.
Ahlberg G, Gustafason O, Wedal P. 2006. Leaching of metals from sewage sludge during one year and their relation to particle size. Environ Pollut, 144: 545–553.
Bates TE, Lane TH, Frank R. 1979. How and where to use sewage sludge in crop production. In: C.P. Mitchell (ed.). Nutrient Relations in Short Rotation Forestry. Forestry Research Paper, pp. 98–128.
Becker MW, Basak AC, Ladha JK, Datta SKD, Ottow JCG. 1991. Effect of NPK on growth and nitrogen fixation of Sesbania rostrata as a green manure for lowland rice (Oxyza sativa L.). Plant and soil, 132: 149–158.
Chandra R, Yadav S, Mohan D. 2008. Effect of distillery sludge on seed germination and growth parameters of green gram (Phaseolus mungo L.). J Hazard Mater, 152: 431–439.
Das DK, Alam MK. 2001. Trees of Bangladesh. Bangladesh Forest Research Institute. pp. 10–11.
Ebbs SD, Lasat MM, Brady DJ, Cornish J, Gordon R, Kochian LV. 1997. Phytoextraction of cadmium and zinc from a contaminated soil. J Environ Qual, 26: 1424–1430.
Fresquez PR, Aguilar R, Francis RE, Aldon EF. 1991. Heavy metal uptake by blue grama growing in a degraded semiarid soil amended with sewage sludge. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 57–58: 903–912.
Fuentes A, Liorens M, Saez J, Aguilar IM, Ortuno FJ, Juan F, Victor MF. 2004. Phytotoxicity and heavy metals speciation of stabilized sewage sludge. J Hazard Mater, 108: 161–169.
Gardiner DT, Miller RW, Badamchian B, Azzari AS, Sisson DR. 1995. Effects of repeated sewage sludge application on plant accumulation of heavt metals. Agri Ecosyst Environ, 55: 1–6.
Guidi G, Hall JE. 1984. Effects of sewage sludge on the physical and chemical properties of soils. In: P. L. Hermite and H. Ott. (eds.), Processing and Use of Sewage Sludge. Dordrecht. Netherlands: D. Reidel Publishing Co.,. pp. 295–306.
Hossain MK, Miller HG. 1994. Sewage sludge fertilization in forest ecosystem. The Malaysian Forester, 57(4): 187–197.
Huang C, Bazzar FA, Vanderhoef LN. 1974. The inhibition of soybesn metsbolism by cadmium and lead. Plant Physiol, 54: 122–124.
Iqbal GMA, Huda SMS, Sujauddin M, Hossain MK. 2007. Effects of sludge on germination and initial growth performance of Leucaena leucocephala seedlings in the nursery. Journal of Forestry Research, 18(3): 226–230.
Jobra M, Andres P. 2000. Effects of sewage sludge on the establishment of the herbaceous ground cover after soil restoration. J Soil Water Conserv, 3: 322–326.
Korentajer L. 1991. A review of agricultural use of sewage sludge: benefits and potential hazards. Water SA, 17(3): 189–196.
Labrecque M, Teodorescu TI, Diagle S. 2006. Effect of wastewater sludge on growth and heavy metal bioaccumulation of two Salix species. Plant and soil, 171(2): 303–306.
Logan TJ, Chaney RL. 1983. Utilization of municipal wastewaters and sludge on land — metals. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Utilization of Municipal Wastewater and Sludge on Land, Denver, Co. pp. 235–323.
McCalla TM, Peterson JR, Lue-Hing C. 1977. Properties of agricultural and municipal wastes. pp. 11–43. In: D. G. Brockway (ed.), Evaluation of Northern Pine Plantations as Disposal Sites for Municipal and Industrial Sludge. Thesis paper, Department of Forestry, Michigan State University, USA. 11P.
Osman KT, Rahman MM, Barua P. 2001. Effects of some forest tree species on soil properties in Chittagong University Campus, Bangladesh. Indian Forester, 127(4): 431–442.
Riekerk H, Zasoski RJ. 1979. Effect of dewatered sludge application to a Doglas fir forest soil, on the soil, leachate and groundwater composition. In: W. E. Sopper and S. N. Kerr (eds.). Utilization of Municipal Sewage Effluent and sludge on Forest and Disturbed Land. Pennsylvania State University Press, University Park. pp. 35–46.
Riha SJ, Naylor L, Senesae GP. 1983. Hybrid poplar production using municipal sewage sludge as a fertilizer resource. New York State Energy Research and Development Activity. 11 pp.
Selivanovskaya SYu, Latypova VZ, Naumova RP, Ravzieva GM. 1997. On the possibility of involvement of microelements of sewage sludge into biogeochemical circulation. Environ Radioecol Appl Ecol, 1: 13–19.
Selivanovskaya SYu, Latypova VZ. 1999. Nekotorye aspecty normirovaniya kachestva i utulizazii osadkov stochnich vod. Ecologicheskaya Chimiya, 8(2): 119–129 (in Russian).
Selivanovskaya SYu, Latypova VZ. 2006. Effect of composted sewage sludge on microbial biomass, activity and pine seedlings in nursery forest. Waste management, 26: 1253–1258.
Singh RP, Agrawal M. 2008. Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Management, 28(2): 347–358.
Tiessen H, Moir JO. 1993. Total and organic carbon. In: Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, M.E. Carter, Ed. Lewis Publishers, Ann Arbor, MI. pp. 187–211.
Van den Berg JJ. 1993. Effects of sewage sludge disposal. Land Degrad Rehabil, 4: 407–413.
Warman PR, Termeer WC. 2005. Evaluation of sewage sludge, septic waste and sludge compost application to corn and forage: yield and N, P, and K content of crops and soils. Bioresour Technol, 96: 955–961.
Wu QT, Hei L, Wong JWC, Schwartz C, Morel JL. 2007. Co-cropping for phyto-separation of zinc and potassium from sewage sludge. Chemos, 68: 1954–1960.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biography: Md. Lokman Hossain (1983–), male, M. Sc. Student (Environmental Science), Institute of Forestry & Environmental Sciences, Chittagong University, Chittagong-4331, Bangladesh.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, M.L., Huda, S.M.S. & Hossain, M.K. Effects of industrial and residential sludge on seed germination and growth parameters of Acacia auriculiformis seedlings. Journal of Forestry Research 20, 331–336 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-009-0056-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-009-0056-5