Abstract
The stem-nodulating tropical legume Sesbania rostrata is a promising green manure species for low input rice-farming systems in lowland areas. However, its success as biofertilizer depends on its biomass production and N2 fixation. Nutrient imbalances and soils low in available nutrients can considerably affect biofertilizer production. Use of mineral N, P, and K fertilizers in growing S. rostrata as biofertilizer for lowland rice was therefore evaluated in pot experiments, and in the fields in Central Luzon, Philippines. Two soils low in Olsen P (3–7.3 mg kg−1) and exchangeable K (0.05–0.08 meq 100g-1) were used. Increasing amounts of N (0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 mg kg-1), P (0, 50, and 100 mg kg-1), and K (0, 100, 200, and 300 mg kg-1) were applied to S. rostrata grown in the greenhouse, whereas small amounts of N, P, and K fertilizers (30, 15, and 33 kg ha-1, respectively) were applied in the field.
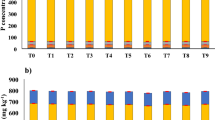
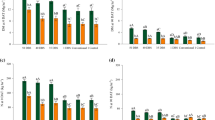
Mineral N application depressed nodulation and N2 fixation in roots. It however, stimulated nodulation and N2 fixation in stems. Applying 30 kg N ha-1 as urea increased total N accumulation by S. rostrata and yield of the subsequent rice crop (IR64). Applied P and K both stimulated growth, nodulation, and N2 fixation of S. rostrata. Nitrogen accumulation in P- and K-fertilized S. rostrata was about 40% higher than that in nonfertilized green manure. Thus integration of mineral N, P, and K fertilizers in a green manure-based rice-farming system can considerably improve biofertilizer production and increase rice grain yield.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker M, Alazard D and Ottow J C G 1986 Mineral nitrogen effect on nodulation and nitrogen fixation of the stem nodulating legume Aeschynomene afraspera. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 149, 485–491.
Beringer H 1978 Functions of potassium in plant metabolism with particular reference to yield. In Potassium in Soils and Crops. Ed. G SSekhon pp 185–202. Potash Research Institute of India, New Delhi.
DeMooy J C, Pesek J and Spaldon E 1973 Mineral nutrition In Soybean Improvement, Production and Use. Ed. B ECaldwell. pp 267–352. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI.
Donald R G K and Ludwig R A 1984 Rhizobium sp. strain ORS 571: Ammonium assimilation and nitrogen fixation. J. Bacteriol. 158, 1144–1151.
Douglas L A and Bremmer J M 1970 Extraction and colorimetric determination of urea in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 34, 859–862.
Dreyfus B L and Dommergues Y R 1980 Non inhibition de la fixation d'azote par l'azote combiné chez une légumineuse à nodules caulinaires, Sesbania rostrata, C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 291, 767–770.
Dreyfus B L, Garcia J L and Gillis M 1988 Characterization of Azorhizobium caulinodans gen. nov., sp. nov., a stem nodulating nitrogen fixing bacterium isolated from Sesbania rostrata. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 38, 89–98.
Eaglesham A R J and Szalay A A 1983 Areal stem nodules on Aeschynomene spp. Plant Sci Lett. 29, 265–272.
Edwards D G 1977 Nutritional factors limiting nitrogen fixed by Rhizobia. In Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Farming Systems of the Tropics. Eds. AAyanaba and P JDart. pp 189–204. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester.
Graham P H and Rosas J C 1979 Phosphorus fertilization and symbiotic nitrogen fixation in common bean. Agron. J. 71, 925–926.
Halepyati A S, Sheelavantar M N and Dixit L A 1987 Breaking dormancy in Sesbania rostrata. Int. Rice Res. Newsl. 12, 36.
Henzell E F 1988 The role of biological nitrogen fixation research in solving problems in tropical agriculture. Plant and Soil 108, 15–21.
Jakobsen I 1985 The role of phosphorus in nitrogen fixation by young pea plants. Physiol. Plant.. 64, 190–196.
Keerthisinghe G, DeDatta S K and Mengel K 1985 Importance of exchangeable and nonexchangeable soil NH4 +-N in nitrogen nutrition of lowland rice. Soil Sci. 140, 194–201.
Ladha J K, Miyan S and Garcia M 1989 Sesbania rostrata as green manure for lowland rice: Growth, N2 fixation, Azorhizobium sp. inoculation and effects on succeeding crop yields and nitrogen balance. Biol. Fertil. Soils 7, 191–197.
Ladha J K, Watanabe I and Saono S 1988 Nitrogen fixation by leguminous green manure and practices for its enhancement in tropical lowland rice. In Sustainable Agriculture. Green Manure in Rice Farming. pp 165–183. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines.
Luse R L, Kang T B, Fox R L and Nangju D 1975 Protein quality in grain legumes grown in the lowland humid tropics, with special reference to West Africa. In Fertilizer Use and Protein Production. pp 64–69. XIth Colloquium of the International Potash Institute, Bornholm, Denmark.
Lynd L Q, Hanlonjr E A and Odelljr G V 1984 Nodulation and nitrogen fixation by arrowleaf clover: The effect of phosphorus and potassium. Soil Biol. Biochem. 16, 589–594.
Mahon J D 1983 Energy relationships. In Nitrogen Fixation. Ed. W JBroughton. Vol. 3, pp 299–335. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Meelu O and Morris R 1988 Green manure management in rice based cropping systems. In Sustainable Agriculture. Green Manure in Rice Farming pp 209–222. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines.
Mengel K, Hagparast M R and Koch K 1974 The effect of potassium on the fixation of molecular nitrogen by root nodules of Vicia faba. Plant Physiol. 54, 535–538.
O'Hara G W, Boonkerd N and Dilworth M J 1988 Mineral constraints to nitrogen fixation. Plant and Soil 108, 93–110.
Pareek R P, Ladha J K and Watanabe I 1990 Estimating N2 fixation by Sesbania rostrata and S. cannabina (Syn. S. aculeata) in lowland rice soil by 15N dilution method. Biol. Fert. Soils. (In press).
Patnaik S and Rao M V 1979 Sources of nitrogen for rice production. In Nitrogen and Rice. pp. 25–43. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines.
Pawlowski K, Ratet P, Schell J and DeBrujn F J 1987 Cloning and characterization of nif A and ntr C genes of the stem nodulating bacterium ORS 571, the nitrogen fixing symbiont of Sesbania rostrata. Mol. Gen. Genet. 206, 207–219.
Rigaud J 1981 Comparison of the efficiency of nitrate and nitrogen fixation in crop yield. In Nitrogen and Carbon Metabolism. Ed. J DBewly. pp 18–46. Nijhoff/Junk Publishers, The Hague, The Netherlands.
Rinaudo G, Alazard D and Moudiongui A 1988 Stem nodulating legumes as green manures for rice in West Africa. In Sustainable Agriculture. Green Manure in Rice Farming. pp 97–109. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines.
Varley J A 1966 Methods for determination of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in plant materials. Analystst 91, 119–126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, M., Diekmann, K.H., Ladha, J.K. et al. Effect of NPK on growth and nitrogen fixation of Sesbania rostrata as a green manure for lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 132, 149–158 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011021
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011021