Abstract
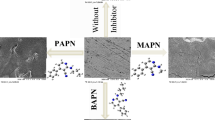
Corrosion inhibition using bolaamphiphile surfactants is related to the ability of these compounds to adsorb on liquid–solid interface. In this work, we have synthesized the 1,10-bis(4-amino-3-methyl-1,2,4-triazole-5-thioyl)decane (DTC10) using a new method developed in our laboratory. The synthesized compounds have been purified and characterized by NMR1H and NMR13C spectroscopy. The inhibiting action of DTC10 toward the corrosion of carbon steel in HCl1M solution was investigated using potentiodynamic and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. We have shown that this compound acts as very good inhibitor for carbon steel in 1M HCl. The values of the transfer resistance, obtained from impedance plots of carbon steel, increase by increasing inhibitor concentration and reach 92% for 10−3M of DTC10. The effects of temperature and immersion time on the inhibition efficiency have also been studied. The effect of temperature was studied between 298 and 328 K; the activation energy Ea and other thermodynamic parameters were calculated. Donating and anti-donating properties of the studied inhibitor 1,10-bis(4-amino-3-methyl-1,2,4-triazole-5-thioyl)decane (DTC10) were illustrated using nucleophilic P− and electrophilic P+ Parr functions based on the density functional theory (DFT). The computational Monte Carlo (MC) method was performed to study the adsorption behavior of DTC10 onto Fe(111) surface in the solution (presence of H3O+, Cl− and H2O particles) and in the vacuum (absence of H3O+, Cl− and H2O particles). Accordingly, the adsorption of DTC10 on the iron surface (111) is more preferred in the solution than in the vacuum.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. El Achouri, M.R. Infante, F. Izquierdo, S. Kertit, H.M. Gouttoya, B. Nciri, Synthesis of some cationic gemini surfactants and their inhibitive effect on iron corrosion in hydrochloric acid medium. Corros. Sci. 43, 19–35 (2001)
D. Chebabe, Z. Ait Chikh, N. Hajjaji, A. Srhiri, F. Zucchi, Corrosion inhibition of Armco iron in 1M HCl solution by alkyltriazoles. Corros. Sci. 45, 309–320 (2003)
N. Hajjaji, I. Rico, A. Srhiri, A. Lattes, M. Soufiaoui, A. Ben Bachir, Effect of N-alkylbetaines on the corrosion of iron in 1M HCl solution. Corros. Sci. 49(4), 326–334 (1993)
J.M. Bastidas, J.L. Polo, E. Cano, Substitutional inhibition mechanism of mild steel hydrochloric acid corrosion by hexylamine and dodecylamine. J. Appl. Electrochem. 30, 1173–1177 (2000)
N.E. Hamner, C.C. Nathan (eds.), Corrosion Inhibitors (Nace Houston, Houston, 1973), p. 1
M.L. Free, Understanding the effect of surfactant aggregation on corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic medium. Corros. Sci. 44, 2865–2870 (2002)
H. Ma, S. Chen, S. Zhao, X. Liu, D. Li, A study of corrosion behavior of copper in acidic solutions containing cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 148, B482–B488 (2001)
M. Damej, H. Benassaoui, D. Chebabe, M. Benmessaoud, H. Erramli, A. Dermaj, N. Hajjaji, A. Srhiri, Inhibition effect of 1,2,4-triazole-5-thione derivative on the Corrosion of Brass in 3% NaCl solution. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 7(3), 738–745 (2016)
B.A. Boukamp, Equivalent Circuit (Princeton Applied Research Corporation, Princeton, 1990)
M.A. Amin, Weight loss, polarization, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, SEM and EDX studies of the corrosion inhibition of copper in aerated NaCl solutions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 36, 215–226 (2006)
D. Chebabe, Z. AitChikh, A. Dermaj, K. Rhattas, T. Jazouli, N. Hajjaji, F. El Mdari, A. Srhiri, Synthesis of bolaamphiphile surfactants and their inhibitive effect on carbon steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid medium. Corros. Sci. 46(11), 2701–2713 (2004)
H. Liu, D. Xu, A.Q. Dao, G. Zhang, Y. Lv, H. Liu, Study of corrosion behavior and mechanism of carbon steel in the presence of Chlorella vulgaris. Corros. Sci. 101, 84–93 (2015)
F.T. Beck, U.A. Kruger, EIS of cathodically deposited wet paint films prior to the stoving process. Electrochim. Acta 41, 1083–1092 (1996)
A. Bousskri, A. Anejjar, R. Salghi, S. Jodeh, R. Touzani, L. Bazzi, H. Lgaz, Corrosion control of carbon steel in hydrochloric acid by new eco-friendly picolinium-based ionic liquids derivative: electrochemical and synergistic studies. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 7(11), 4269–4289 (2016)
A. Yurt, A. Balaban, S.U. Kandemir, G. Bereket, B. Erk, Investigation on some Schiff bases as HCl corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 85, 420–426 (2004)
R.R. Parr, R.G. Yang, Density functional theory of atoms and molecules (Oxford University Press, New York, 1989)
C. Lee, W. Yang, R.G. Parr, Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 37, 785 (1988)
A.D. Becke, A new mixing of Hartree-Fock and local density-functional theories. J. Phys. Chem. 98, 1372 (1993)
M.J. Frisch, G.W. Trucks, H.B. Schlegel et al., Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01 (Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, 2009)
C. Gonzales, H.B. Schlegel, An improved algorithm for reaction path following. J. Chem. Phys. 90, 2154 (1989)
E. Chamorro, P. Pérez, L.R. Domingo, On the nature of Parr functions to predict the most reactive sites along organic polar reactions. Chem. Phys. Lett. 582, 141–143 (2013)
Materials Studio version v8.0, Accelrys Software Inc., San Diego (2016)
L. Afia, O. Hamed, M. Larouj, H. Lgaz, S. Jodeh, R. Salghi, Novel natural based diazepines as effective corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in HCl solution: experimental, theoretical and Monte Carlo simulations. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 70, 2319–2333 (2017)
H. Sun, COMPASS: an ab initio force-field optimized for condensed-phase applications overview with details on alkane and benzene compounds. J. Phys. Chem B 102, 7338–7364 (1998)
H. Sun, P. Ren, J.R. Fried, The COMPASS forcefield: parameterization and validation for phosphazenes. Comput. Theor. Polym. Sci. 8, 229–246 (1998)
D. Frenkel, B. Smit, Understanding Molecular Simulation: From Algorithms to Applications (Academic Press, Cambridge, 2002), pp. 63–163
Z. Zhang, N.C. Tian, X.D. Huang, W. Shang, L. Wu, Synergistic inhibition of carbon steel corrosion in 0.5 M HCl solution by indigo carmine and some cationic organic compounds: experimental and theoretical studies. RSC Adv. 6, 22250–22268 (2016)
S.W. Xie, Z. Liu, G.C. Han, W. Li, J. Liu, Z. Chen, Molecular dynamics simulation of inhibition mechanism of 3, 5-dibromo salicylaldehyde Schiff’s base. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1063, 50–62 (2015)
N. Metropolis, A.W. Rosenbluth, M.N. Rosenbluth, A.H. Teller, E. Teller, Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. J. Chem. Phys. 21, 1087–1092 (1953)
K.F. Khaled, Monte Carlo simulations of corrosion inhibition of mild steel in 0.5 M sulphuric acid by some green corrosion inhibitors. J. Solid State Elctrochem. 13, 1743–1756 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Moroccan Association of theoretical chemists (AMCT) for access to the computational facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chebabe, D., Abbout, S., Damej, M. et al. Electrochemical and Theoretical Study of Corrosion Inhibition on Carbon Steel in 1M HCl Medium by 1,10-Bis(4-Amino-3-Methyl-1,2,4-Triazole-5-Thioyl)Decane. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 20, 1673–1683 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-020-00974-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-020-00974-y