Abstract
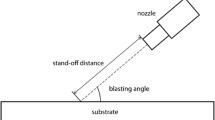
Thermally sprayed coatings improve component lifespan and protect the underlying substrate in high temperature and corrosive environments. The coating adhesion is one of the most important properties with respect to coating performance. Before coating, surfaces are typically cleaned and roughened via manual grit blasting to promote mechanical interlocking of the coating with substrate. With recent interest in implementing ceramics and ceramic composites in the hot section of advanced gas turbine engines, there is a need to better understand how to prepare these nonmetal and composite materials before being coated. In this study, an automated grit blasting system was utilized to observe the effects of parameters such as blast pressure, angle, and nozzle traverse speed on multiple surface roughness parameters of reaction-bonded silicon carbide (rb SiC). The effect of these parameters on the substrate thickness loss during grit blasting was also analyzed. Blast pressure had the largest effect on surface roughness, as well as the highest linear correlation with roughness parameters. The automated robotic system allowed for the controlled study of traverse speeds higher than that typically used for grit blasting (≤ 350 mm/s). Increasing nozzle traverse speed was found to greatly reduce material loss with minimal effect on surface roughness.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A. DiCarlo, H.M. Yun, G.N. Morscher and R.T. Bhatt, SiC/SiC composites for 1200 C and above, Handbook of Ceramic Composites. N.P. Bansal Ed., Springer, Boston, 2005
D. Zhu, Aerospace Ceramic Materials: Thermal, Environmental Barrier Coatings and SiC/SiC Ceramic Matrix Composites for Turbine Engine Applications, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, 2018
P. Fauchais, J.V.R. Heberlein and M. Boulos, Thermal Spray Fundamentals: From Powder to Part, Springer, New York, 2014.
B.J. Griffiths, D.T. Gawne and G. Dong, A Definition of the Topography of Grit-Blasted Surfaces for Plasma Sprayed Alumina Coatings, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 1999, 121, p 49-53.
M. Mellali, P. Fauchais and A. Grimaud, Influence of Substrate Roughness and Temperature on the Adhesion/Cohesion of Alumina Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 1996, 81, p 275-286.
B.J. Griffiths, D.T. Gawne and G. Dong, The Erosion of Steel Surfaces by Grit-Blasting as a Preparation for Plasma Spraying, Wear, 1996, 194, p 95-102.
M.F. Bahbou, P. Nylén and J. Wigren, Effect of Grit Blasting and Spraying Angle on the Adhesion Strength of a Plasma-Sprayed Coating, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2004, 13(4), p 508-514.
H. Begg, M. Riley and H.V. Lovelock, Mechanization of the Grit Blasting Process for Thermal Spray Coating Applications: A Parameter Study, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2016, 25(1–2), p 12-20.
K. Bobzin, M. Ote, T.F. Linke, J. Sommer and X. Liao, Influence of Process Parameter on Grit Blasting as a Pretreatment Process for Thermal Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2016, 25(1–2), p 3-11.
M.F. Bahbou and P. Nylen, Relationship Between Surface Topography Parameters and Adhesion Strength for Plasma Spraying, Thermal Spray Connects: Exploring Its Surface Potential, ASM International, Materials Park, 2005, p 1027-1031
D. Sen, N.M. Chavan, D.S. Rao and G. Sundararajan, Influence of Grit Blasting on the Roughness and the Bond Strength of Detonation Sprayed Coating, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2010, 19(4), p 805-815.
S.K. Asl and M.H. Sohi, Effect of Grit-Blasting Parameters on the Surface Roughness and Adhesion Strength of Sprayed Coating, Surf. Interface Anal., 2010, 42, p 551-554.
K. Bobzin, M. Ote and M.A. Knoch, Surface Pre-Treatment for Thermally Sprayed ZnAl15 Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2017, 26, p 464-472.
B.J. Griffiths, D.T. Gawne and G. Dong, The Role of Grit Blasting in the Production of High-Adhesion Plasma Sprayed Alumina Coatings, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., 1997, 211(1), p 1-9.
J. Day, X. Huang and N.L. Richards, Examination of a Grit-Blasting Process for Thermal Spraying Using Statistical Methods, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2005, 14(4), p 471-479.
M. Mellali, A. Grimaud, A.C. Leger, P. Fauchais and J. Lu, Alumina Grit Blasting Parameters for Surface Preparation in the Plasma Spraying Operation, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 1997, 6(2), p 217-227.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scherbarth, A.D., Blair, T.K. & Pickrell, G. Effects of Automated Grit Blasting on Roughness and Thickness Loss of Reaction-Bonded Silicon Carbide. J Therm Spray Tech 30, 787–795 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-021-01169-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-021-01169-z