Abstract
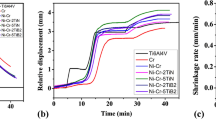
TiB-reinforced titanium matrix composites were synthesized using vacuum arc melting to enhance the hardness and wear resistance of pure (Ti). The microstructure showed a macroscopically uniform distribution of TiB whiskers in the Ti matrix. The hardness of the composite increased from 799 (with TiB content 50 vol.%) to 895 HV (with TiB content 85 vol.%) compared to the 236 HV hardness of pure Ti. Dry sliding reciprocating wear tests under four different loads of 10, 15, 20, and 25 N were carried out against a steel ball as a counterface at a constant frequency of 4 Hz. The coefficient of friction and wear rate decreased with increasing TiB content. The observed behavior has been explained based on the hardness of the composites, the presence of loose wear particles over the worn surface, formation of a transfer layer of wear debris over the surface and its degree of compaction, extent of coverage, and presence of lubricious oxides (TiO2, B2O3 and H3BO3). The operative mechanism of wear is a mix of ploughing, adhesion and oxidation for pure Ti, whereas the same for composites is adhesion, oxidation, delamination, and abrasion. The composite having 80 vol.% TiB has shown the lowest coefficient of friction among all the composites.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.D. Hayat, H. Singh, Z. He and P. Cao, Titanium Metal Matrix Composites: An Overview, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf., 2019, 121, p 418–438.
B.S. Li, J.L. Shang, J.J. Guo and H.Z. Fu, Formation of TiBw Reinforcement in In-Situ Titanium Matrix Composites, J. Mater. Sci., 2004, 39, p 1131–1133.
M. Niu, X. Zhang and J. Yang, Tribological Behaviour of Fe3Al-Ba0.25Sr0.75SO4 Self-Lubricating Composites in Vacuum and Air, Vacuum, 2018, 154, p 315–321.
X. Zhang, Y. Sun, M. Niu, M. Shao and X. Geng, Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of In Situ TiC Reinforced Fe3Al(Fe-23Al-3Cr) Matrix Composites by Mechanical Alloying and Vacuum Hot-Pressing Sintering Technology, Vacuum, 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109544
X. Zhang, M. Niu, C. Wu and J. Chen, The Effect of Titanium Addition on the Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Ni3Si Alloys Prepared by Powder Metallurgy Method, Materwiss. Werksttech., 2019, 50, p 1537–1544.
X. Zhang, M. Zhang, M. Shao, X. Geng, Y. Sun, M. Niu, Y. Miao and X. Wang, Comparative Study on Tribological Behavior of Fe3Al Alloy Against Different Counterparts in Seawater, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30, p 8030–8039.
V. Jindal, A. Sarda, A. Degnah and K.S. Ravi, Chandran, Effect of iron & boron content on the Spark Plasma Sintering of Ti-B-Fe alloys, Adv. Powder Technol., 2019, 30, p 423–427.
K. Morsi and V.V. Patel, Processing and Properties of Titanium-Titanium Boride (TiBw) Matrix Composites: A Review, J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42, p 2037–2047.
D.A. Angel, T. Mikó, F. Kristály, M. Benke and Z. Gácsi, Development of TiB and Nanocrystalline Ti-Reinforced Novel Hybrid Ti Nanocomposite Produced by Powder Metallurgy, J. Mater. Sci., 2022, 57, p 4130–4144.
S. Li, Y. Han, X. Wang, G. Huang, M. Fang, H. Shi, J. Le and W. Lu, Novel Strategy of Planting Nano-TiB Fibers with Ultra-Fine Network Distribution Into Ti-Composite Powder and its Thermal Transition Mechanism, Compos. Commun., 2022, 29, 101002.
X. Yi, G. Shen, X. Meng, H. Wang, Z. Gao, W. Cai and L. Zhao, The Higher Compressive Strength (TiB+La2O3)/Ti–Ni Shape Memory Alloy Composite with the Larger Recoverable Strain, Compos. Commun., 2021, 23, 100583.
D.L. Ouyang, S.W. Hu, C. Tao, X. Cui, Z.S. Zhu and S.Q. Lu, Experiment and Modeling of TiB2/TiB Boride Layer of Ti-6Al-2Zr-1Mo-1V Alloy, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2021, 31, p 3752–3761.
C. Zhang, F. Kong, S. Xiao, H. Niu, L. Xu and Y. Chen, Evolution of Microstructural Characteristic and Tensile Properties During Preparation of TiB/Ti Composite Sheet, Mater. Des., 2012, 36, p 505–510.
M. Ozerov, N. Stepanov and S. Zherebtsov, Wear Resistance of Ti/TiB Composites Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering, AIP Conf. Proc., 2017, 1909, p 020164.
M. Selvakumar, T. Ramkumar, M. Mohanraj and P. Chandramohan, Experimental Investigations of Reciprocating Wear Behavior of Metal Matrix (Ti/TiB) Composites, Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng., 2020, 20, p 1–9.
Q. An, L. Huang, S. Jiang, Y. Bao, M. Ji, R. Zhang and L. Geng, Two-Scale TiB/Ti64 Composite Coating Fabricated by Two-Step Process, J. Alloy. Compd., 2018, 755, p 29–40.
M. Xia, A. Liu, Z. Hou, N. Li, Z. Chen and H. Ding, Microstructure Growth Behavior and its Evolution Mechanism During Laser Additive Manufacture of in-Situ Reinforced (TiB+TiC)/Ti Composite, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 728, p 436–444.
P.K. Farayibi, T.E. Abioye, A. Kennedy and A.T. Clare, Development of Metal Matrix Composites by Direct Energy Deposition of ‘Satellited’ Powders, J. Manuf. Process., 2019, 45, p 429–437.
Y. Hu, W. Cong, X. Wang, Y. Li, F. Ning and H. Wang, Laser Deposition-Additive Manufacturing of TiB-Ti Composites with Novel Three-Dimensional Quasi-Continuous Network Microstructure: Effects on Strengthening and Toughening, Compos. Part B Eng., 2018, 133, p 91–100.
S. Pouzet, P. Peyre, C. Gorny, O. Castelnau, T. Baudin, F. Brisset, C. Colin and P. Gadaud, Additive Layer Manufacturing of Titanium Matrix Composites Using the Direct Metal Deposition Laser Process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2016, 677, p 171–181.
R. Banerjee, A. Genç, P.C. Collins and H.L. Fraser, Comparison of Microstructural Evolution in Laser-Deposited and Arc-Melted In-Situ Ti-TiB, Composites, 2004, 35, p 2143–2152.
H.T. Tsang, C.G. Chao and C.Y. Ma, Effects of Volume Fraction of Reinforcement on Tensile and Creep Properties of In-Situ MMC, Scr. Mater., 1997, 37, p 1359–1365.
W. Lu, D. Zhang, X. Zhang, R. Wu, T. Sakata and H. Mori, Microstructural Characterization of TiB in In Situ Synthesized Titanium Matrix Composites Prepared by Common Casting Technique, J. Alloy. Compd., 2001, 327, p 240–247.
R. Kumar, L. Liu, M. Antonov, R. Ivanov and I. Hussainova, Hot Sliding Wear of 88 wt.% TiB-Ti Composite from SHS Produced Powders, Materials (Basel), 2021, 14, p 1242.
H. Attar, S. Ehtemam-Haghighi, D. Kent, I.V. Okulov, H. Wendrock, M. Bonisch, A.S. Volegov, M. Calin, J. Eckert and M.S. Dargusch, Nanoindentation and Wear Properties of Ti and Ti-TiB Composite Materials Produced by Selective Laser Melting, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2017, 688, p 20–26.
Y. Bao, L. Huang, Q. An, S. Jiang, L. Geng and X. Ma, Wire-Feed Deposition TiB Reinforced Ti Composite Coating: Formation Mechanism and Tribological Properties, Mater. Lett., 2018, 229, p 221–224.
A.S. Patil, V.D. Hiwarkar, P.K. Verma and R.K. Khatirkar, Effect of TiB 2 Addition on the microstructure and Wear Resistance of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated through Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), J. Alloy. Compd., 2019, 777, p 165–173.
R. Kumar, M. Antonov, L. Liu and I. Hussainova, Sliding Wear Performance of In-Situ Spark Plasma Sintered Ti-TiBw Composite at Temperatures up to 900 °C, Wear, 2021, 476, p 203663.
I.Y. Kim, B.J. Choi, Y.J. Kim and Y.Z. Lee, Friction and Wear Behavior of Titanium Matrix (TiB+TiC) Composites, Wear, 2011, 271, p 1962–1965.
J.F. Archard, Contact and Rubbing of Flat Surfaces, J. Appl. Phys., 1953, 24, p 981–988.
B.J. Kooi, Y.T. Pei and J.T.M. De Hosson, The Evolution of Microstructure in a Laser Clad TiB-Ti Composite Coating, Acta Mater., 2003, 51, p 831–845.
D. Gu, Y.C. Hagedorn, W. Meiners, G. Meng, R.J.S. Batista, K. Wissenbach and R. Poprawe, Densification Behavior, Microstructure Evolution, and Wear Performance of selective Laser Melting Processed Commercially Pure Titanium, Acta Mater., 2012, 60, p 3849–3860.
P. Helmer, J. Halim, J. Zhou, R. Mohan, B. Wickman, J. Björk and J. Rosen, Investigation of 2D Boridene from First Principles and Experiments, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, p 2109060.
E. Benko, T.L. Barr, S. Hardcastle, E. Hoppe, A. Bernasik and J. Morgiel, XPS Study of the cBN-TiC System, Ceram. Int., 2001, 27, p 637–643.
N. Hellgren, A. Sredenschek, A. Petruins, J. Palisaitis, F.F. Klimashin, M.A. Sortica, L. Hultman, P.O.Å. Persson and J. Rosen, Synthesis and Characterization of TiBx (1.2 ≤ x ≤ 2.8) Thin Films Grown by DC Magnetron Co-Sputtering from TiB2 and Ti Targets, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2022, 433, p 128110.
C.T. Wang, H.S. Lin and W.P. Wang, Hydrothermal Synthesis of Fe [sbnd] and Nb-Doped Titania Nanobelts and their Tunable Electronic Structure toward Photovoltaic Application, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process., 2019, 99, p 85–91.
R. Huang, R. Liang, H. Fan, S. Ying, L. Wu, X. Wang and G. Yan, Enhanced Photocatalytic Fuel Denitrification over TiO2/α-Fe2O3 Nanocomposites under Visible Light Irradiation, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, p 1–10.
F. Liu, L. Feng, J. Ren, X. Zhang and J. Jia, Tribological Properties of In Situ Fabricated Fe-Al Matrix Composites Containing SrAl2O4, FeAl2O4, and FeO at Elevated Temperatures, Tribol. Trans., 2021, 64, p 593–605.
S.S. Sahay, K.S. Ravichandran, R. Atri, B. Chen and J. Rubin, Evolution of Microstructure and Phases in In Situ Processed Ti-TiB Composites Containing High Volume Fractions of TiB Whiskers, J. Mater. Res., 1999, 14, p 4214–4223.
S.C. Tjong and Y.-W. Mai, Processing-Structure-Property Aspects of Particulate-and Whisker-Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composites, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2008, 68, p 583–601.
K.S. Ravi Chandran, K.B. Panda and S.S. Sahay, TiBw-Reinforced Ti composites: processing, properties, application prospects, and Research Needs, Jom, 2004, 56, p 42–48.
L. Huang, T. Duan, Q. An, Y. Chen, J. Bai, L. Geng and S. Lin, Gas Tungsten Arc Welding of Network Structured Titanium Matrix Composite, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2018, 23, p 357–364.
Z. Xinghong, X. Qiang, H. Jiecai and V.L. Kvanin, Self-Propagating High Temperature Combustion Synthesis of TiB/Ti Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2003, 348, p 41–46.
R. Tyagi, S.K. Nath and S. Ray, Effect of Martensite Content on Friction and Oxidative Wear Behavior of 0.42 Pct Carbon Dual-Phase Steel, Metall Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 2002, 33, p 3479–3488.
Y. Qin, L. Geng and D. Ni, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Extruded Titanium Matrix Composite Reinforced by In Situ TiB Whisker and TiC Particle, J. Mater. Sci., 2011, 46, p 4980–4985.
J. Li, M. Sun, X. Ma and G. Tang, Structure and Tribological Performance of Modified Layer on Ti6Al4V alloy by Plasma-Based ion Implantation with Oxygen, Wear, 2006, 261, p 1247–1252.
H.J. Song and Z.Z. Zhang, Study on the Tribological Behaviors of the Phenolic Composite Coating Filled with Modified Nano-TiO2, Tribol. Int., 2008, 41, p 396–403.
Z. Min, Friction and Wear Properties of TiB 2P/Al Composite, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf., 2006, 37, p 1916–1921.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjan, A., Tyagi, R. & Jindal, V. Reciprocating Wear of Ti-TiB In Situ Composites Synthesized via Vacuum Arc Melting. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 9985–9996 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07002-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07002-0