Abstract
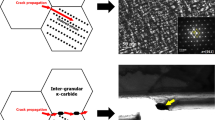
Grain coarsening prevention while accelerating the carburizing process is critical for the manufacturer for case hardening components such as gears to improve efficiency. In this research, a novel method is proposed to prevent austenite grain growth by introducing the ferrite phase that could retard the austenite boundary movement. The addition of aluminum promotes the ferrite phase. Aluminum as strong ferrite former raises the A3 temperature so that the ferrite phase is present at high carburizing temperature. The effect of 1 wt.% aluminum on the microstructure evolution during pseudo-carburizing treatment in 20CrMn steel is investigated in details. It is shown that the formation of ferrite during pseudo-carburizing at 930 °C for 5h prevents austenite grain coarsening. The obtained mechanical properties are similar to non-aluminum added 20CrMn steel pseudo-carburized at 830 °C for 16h. When 20CrMn was pseudo-carburized at 930 °C for 5h, significant austenite grain growth was observed, which result in low impact toughness after the subsequent quenching and tempering treatment. The “ferrite pinning” effect effectively inhibits the grain growth at high temperature, revealed by metallography investigation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Asi, A.C. Can, J. Pineault and M. Belassel, The Effect of High Temperature Gas Carburizing on Bending Fatigue Strength of SAE 8620 Steel, Mater. Des., 2009, 30(5), p 1792–1797.
M. Zajusz, K. Tkacz Smiech and M. Danielewski, Modeling of Vacuum Pulse Carburizing of Steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 258, p 646–651.
S.A. Abdul Azis, I. Jauhari and N.W. Ahamad, Improving Surface Properties and Wear Behaviors of Duplex Stainless Steel Via Pressure Carburizing, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 210, p 142–150.
Q.X. Yang, X.J. Ren, Y.K. Gao, Y.L. Li, Y.H. Zhao and M. Yao, Effect of Carburization on Residual Stress Field of 20CrMnTi Specimen and Its Numerical Simulation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 392(1–2), p 240–247.
H.J. Kim and Y.J. Kweon, The Effects of Retained Austenite on Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Carburized Steels, Wear, 1996, 193(1), p 8–15.
M.F. Yan and Z.R. Liu, Study on Microstructure and Microhardness in Surface Layer of 20CrMnTi Steel Carburized at 880 Degrees C with and Without RE, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2001, 72(1), p 97–100.
Y.H. Yang, M.Q. Wang, J.C. Chen and H. Dong, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Gear Steels After High Temperature Carburization, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2013, 20(12), p 140–145.
J.I. Goldstein and A.E. Moren, Diffusion Modeling of the Carburization Process, Metall. Trans. A, 1978, 9(11), p 1515–1525.
D.K. Matlock, K.A. Alogab, M.D. Richards and J.G. Speer, Surface Processing to Improve the Fatigue Resistance of Advanced Bar Steels for Automotive Applications, Mater. Res., 2005, 8(4), p 453–459.
Y. Han, J. Shi, L. Xu, W.Q. Cao and H. Dong, TiC Precipitation Induced Effect on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Low Carbon Medium Manganese Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 530, p 643–651.
P. Ghosh, R.K. Ray, C. Ghosh and D. Bhattacharjee, Comparative Study of Precipitation Behavior and Texture Formation in Continuously Annealed Ti and Ti Plus Nb Added Interstitial-Free High-Strength Steels, Scr. Mater., 2008, 58(11), p 939–942.
S.G. Hong, H.J. Jun, K.B. Kang and C.G. Park, Evolution of Precipitates in the Nb-Ti-V Microalloyed HSLA Steels During Reheating, Scr. Mater., 2003, 48(8), p 1201–1206.
P. Ghosh, C. Ghosh and R.K. Ray, Thermodynamics of Precipitation and Textural Development in Batch-Annealed Interstitial-Free High-Strength Steels, Acta Mater., 2010, 58(11), p 3842–3850.
Yu. Qingbo and Y. Sun, Abnormal Growth of Austenite Grain of Low-Carbon Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 420(1–2), p 34–38.
Q. Sha and Z. Sun, Grain Growth Behavior of Coarse-Grained Austenite in a Nb-V-Ti Microalloyed Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 523(1–2), p 77–84.
J.M. Cabrera, A. Al Omar and J.M. Prado, Abnormal Grain Growth in a Medium-Carbon Microalloyed Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 1996, 31(5), p 1303–1309.
O. Flores and L. Martinez, Abnormal Grain Growth of Austenite in a V-Nb Microalloyed Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 1997, 32(22), p 5985–5991.
J.S. Park and Y.K. Lee, Determination of Nb(C, N) Dissolution Temperature by Electrical Resistivity Measurement in a Low-Carbon Microalloyed Steel, Scr. Mater., 2007, 56(3), p 225–228.
D.A. Porter and K.E. Easterling, Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, Chapman & Hall, London, 1992.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and R. Honeycombe, Steels: Microstructure and Properties, Elsevier Ltd, Oxford, 2011.
Y.L. Yang, G.G. Cheng, S.J. Li, M. Zhao, G.P. Feng and T. Li, A Coupled Model of TiN Inclusion Growth in GCr15SiMn During Solidification in the Electroslag Remelting Process, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2015, 22(12), p 1266–1272.
W.J. Ma, Y.P. Bao, L.H. Zhao and M. Wang, Control of the Precipitation of TiN Inclusions in Gear Steels, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2014, 21(3), p 234–239.
W. Yan, Y.Y. Shan and K. Yang, Influence of TiN Inclusions on the Cleavage Fracture Behavior of Low-Carbon Microalloyed Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, 38(6), p 1211–1222.
H.L. Yi, K.Y. Lee and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Stabilization of Ferrite in Hot Rolled δ-TRIP Steel, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, 27(2), p 525–529.
H.L. Yi, S.K. Ghosh, W.J. Liu, K.Y. Lee and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Nonequilibrium solidification and ferrite in δ-TRIP steel, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, 26(7), p 817–823.
C. García de Andrés, F.G. Caballero, C. Capdevila and L.F. Alvarez, Application of Dilatometric Analysis to the Study of Solid-Solid Phase Transformations in Steels, Mater. Charact., 2002, 48(1), p 101–111.
J.C. Pang, B.Y. Xu, G.D. Wang, Q. Lu, J.F. Wang and H.L. Yi, Effect of Silicon and Aluminum in Ferrite on Tensile and Impact Properties, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2017, 33(15), p 1806–1810.
J. Han, S.J. Lee, C.Y. Lee, S. Lee, S.Y. Lee and S.Y. Jo, The Size Effect of Initial Martensite Constituents on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Intercritically Annealed Fe-9Mn-0.05C Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 633, p 9–16.
F. HajyAkbary, J. Sietsma, G. Miyamoto, N. Kamikawa, R.H. Petrov, T. Furuhara and M.J. Santofimia, Analysis of the Mechanical Behavior of a 0.3C-1.6Si-3.5Mn (wt%) Quenching and Partitioning Steel, Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 677, p 505–514.
A. Kumar, S.B. Singh and K.K. Ray, Influence of Bainite/Martensite-Content on the Tensile Properties of Low Carbon Dual-Phase Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 474(1–2), p 270–282.
Acknowledgments
The research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51722402), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. N170705001), the 111 Project (Grant No. B16009) and the Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (No. xlyc1907128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L.Q., Xiong, X.C., Wang, G.D. et al. Suppression of Austenite Grain Coarsening by Ferrite Pinning during Pseudo-carburizing Treatment. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 2381–2388 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05615-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05615-5