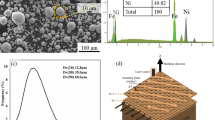
Abstract
To study the effect of the laser energy density (LED) on surface morphology, microstructural evolution, and magnetic properties of Fe-3wt.% Si alloy, the alloy was manufactured via selective laser melting (SLM) technology. The SLM Fe-3wt.% Si parts were characterized by a series of advanced material methods including a 3D profilometer, optical microscope, scanning electron microscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometer, etc. The results show that no obvious microcracks exist in the SLM Fe-3wt.% Si parts. With the LED increases, the porosity rate and the surface roughness of the SLM Fe-3wt.% Si parts decrease. Furthermore, the cross-sectional microstructure of the SLM Fe-3wt.% Si parts is a typical columnar structure with an orientation growth building direction. The microhardness of each SLM Fe-3wt.% Si sample is higher than 200 HV0.1. Besides, the coercivity of SLM Fe-3wt.% Si parts decreases first and then increases with the increase in the LED. The specimen with a LED at 300 J/m exhibits better comprehensive magnetic properties than others. It could be concluded that the magnetic properties of SLM Fe-3wt.% Si alloys are affected by the synergistic effects of manufacturing defects and internal stress.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
24 March 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06818-0
References
G.E. Fish, Soft Magnetic Materials, Proc. IEEE, 1990, 78, p 947–972.
C.-W. Chen, Magnetism and Metallurgy of Soft Magnetic Materials, Courier Corporation, 2013
H. Shokrollahi and K. Janghorban, Soft Magnetic Composite Materials (SMCs), J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 189, p 1–12.
K.I. Arai and K. Ishiyama, Rolled Texture and Magnetic Properties of 3% Silicon Steel, J. Appl. Phys., 1988, 64, p 5352–5354.
J.S. Robles, A.S. Zamarripa, M.G. Mata and J. Cabrera, Texture Evolution of Experimental Silicon Steel Grades Part I: Hot rolling, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2017, 429, p 367–371.
P. Jang, B. Lee and G. Choi, Effects of Annealing on the Magnetic Properties of Fe–6.5% Si Alloy Powder Cores, J. Appl. Phys., 2008, 103, p 07E743.
S. Hong-Yu, H.-T. Liu, H.-H. Lu, H.-Z. Li, W.-Q. Liu, X.-M. Zhang and G.-D. Wang, Effect of Hot Rolling Reduction on Microstructure, Texture and Ductility of Strip-Cast Grain-Oriented Silicon Steel with Different Solidification Structures, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 605, p 260–269.
X. He, X. Li and Y. Sun, Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of High Silicon Electrical Steel Produced by Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2008, 320, p 217–221.
X. Yan, C. Huang, C. Chen, R. Bolot, L. Dembinski, R. Huang, W. Ma, H. Liao and M. Liu, Additive Manufacturing of WC Reinforced Maraging Steel 300 Composites by Cold Spraying and Selective Laser Melting, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2019, 371, p 161–171.
I. Gibson, D.W. Rosen and B. Stucker, Additive Manufacturing Technologies, Springer, New York, 2014.
X. Yan, S. Yin, C. Chen, C. Huang, R. Bolot, R. Lupoi, M. Kuang, W. Ma, C. Coddet and H. Liao, Effect of Heat Treatment on the Phase Transformation and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting, J. Alloys Compd., 2018, 764, p 1056–1071.
A. Uriondo, M. Esperon-Miguez and S. Perinpanayagam, The Present and Future of Additive Manufacturing in the Aerospace Sector: A Review of Important Aspects. Proc, Inst. Mech Eng. G. J. Aerosp Eng., 2015, 229, p 2132–2147.
M. Garibaldi, C. Gerada, I. Ashcroft, R. Hague, H. Morvan, The impact of additive manufacturing on the development of electrical machines for MEA Applications: A feasibility study, in MEA2015 More Electric Aircraft, 2015
B. Zhang, N.-E. Fenineche, H. Liao and C. Coddet, Magnetic Properties of In-Situ Synthesized FeNi3 by Selective Laser Melting Fe-80% Ni Powders, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2013, 336, p 49–54.
B. Zhang, N.-E. Fenineche, H. Liao and C. Coddet, Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe–Ni Alloy Fabricated By Selective Laser Melting Fe/Ni Mixed Powders, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, 29, p 757–760.
C. Mikler, V. Chaudhary, V. Soni, B. Gwalani, R. Ramanujan and R. Banerjee, Tuning the Phase Stability and Magnetic Properties of Laser Additively Processed Fe-30at% Ni Soft Magnetic Alloys, Mater. Lett., 2017, 199, p 88–92.
M. Garibaldi, I. Ashcroft, N. Hillier, S. Harmon and R. Hague, Relationship Between Laser Energy Input, Microstructures and Magnetic Properties of Selective Laser Melted Fe-6.9% wt Si Soft Magnets, Materials Characterization., 2018, 143, p 144–151.
M. Garibaldi, I. Ashcroft, M. Simonelli and R. Hague, Metallurgy of High-Silicon Steel Parts Produced using Selective Laser Melting, Acta Mater., 2016, 110, p 207–216.
S. Alleg, R. Drablia and N. Fenineche, Effect of the Laser Scan Rate on the Microstructure, Magnetic Properties, and Microhardness of Selective Laser-Melted FeSiB, J. Supercond. Novel Magn., 2018, 31, p 3565–3577.
A. Plotkowski, J. Pries, F. List, P. Nandwana, B. Stump, K. Carver and R. Dehoff, Influence of Scan Pattern and Geometry on the microsTructure and Soft-Magnetic Performance of Additively Manufactured Fe-Si, Addit. Manuf., 2019, 29, p 100781.
S. Liu, J. Liu, J. Chen and X. Liu, Influence of Surface Tension on the Molten Pool Morphology in Laser Melting, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2019, 146, p 106075.
C. Ma and D. Bothe, Direct Numerical Simulation of Thermocapillary Flow Based on the Volume of Fluid Method, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 2011, 37, p 1045–1058.
M. Guo, D. Gu, L. Xi, H. Zhang, J. Zhang, J. Yang and R. Wang, Selective Laser Melting Additive Manufacturing of Pure Tungsten: Role of Volumetric Energy Density on Densification, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater, 2019, 84, p 105025.
J. Yi, J. Kang, T. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Hu, T. Feng, Y. Feng and P. Wu, Effect of Laser Energy Density on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Deformation of Inconel 718 Samples Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 786, p 481–488.
M.H. Nasab, D. Gastaldi, N.F. Lecis and M. Vedani, On Morphological Surface Features of the Parts Printed by Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Addit. Manuf., 2018, 24, p 373–377.
D. Gu and Y. Shen, Balling Phenomena in Direct Laser Sintering of Stainless Steel Powder: Metallurgical Mechanisms and Control Methods, Mater. Des., 2009, 30, p 2903–2910.
G. Dursun, S. Ibekwe, G. Li, P. Mensah, G. Joshi and D. Jerro, Influence of Laser Processing Parameters on the Surface Characteristics of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting, Mater. Today: Proc., 2020, 26, p 387–393.
G. Ng, A. Jarfors, G. Bi and H. Zheng, Porosity Formation and Gas Bubble Retention in Laser Metal Deposition, Appl. Phys. A, 2009, 97, p 641–649.
R. Xiao and X. Zhang, Problems and Issues in Laser Beam Welding of Aluminum–Lithium Alloys, J. Manuf. Processes, 2014, 16, p 166–175.
N.T. Aboulkhair, N.M. Everitt, I. Ashcroft and C. Tuck, Reducing Porosity in AlSi10Mg Parts Processed by Selective Laser Melting, Addit. Manuf., 2014, 1, p 77–86.
M. Xia, D. Gu, G. Yu, D. Dai, H. Chen and Q. Shi, Porosity Evolution and its Thermodynamic Mechanism of Randomly Packed Powder-Bed During Selective Laser Melting of Inconel 718 Alloy, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 2017, 116, p 96–106.
C. Qiu, C. Panwisawas, M. Ward, H.C. Basoalto, J.W. Brooks and M.M. Attallah, On the Role of Melt Flow into the Surface Structure and Porosity Development During Selective Laser Melting, Acta Mater., 2015, 96, p 72–79.
M. Boivineau, C. Cagran, D. Doytier, V. Eyraud, M.-H. Nadal, B. Wilthan and G. Pottlacher, Thermophysical Properties of Solid and Liquid Ti-6Al-4V (TA6V) Alloy, Int. J. Thermophys., 2006, 27, p 507–529.
B. Zhang, Y. Li and Q. Bai, Defect Formation Mechanisms in Selective Laser Melting: A Review, Chin J Mech Eng, 2017, 30, p 515–527.
W. Yuan, H. Chen, T. Cheng and Q. Wei, Effects of Laser Scanning Speeds on Different States of the Molten Pool During Selective Laser Melting: Simulation and Experiment, Mater. Des., 2020, 189, p 108542.
E.O. Olakanmi, R. Cochrane and K. Dalgarno, A Review on Selective Laser Sintering/Melting (SLS/SLM) of Aluminium Alloy Powders: Processing, Microstructure, and Properties, Prog. Mater Sci., 2015, 74, p 401–477.
L. Tonelli, A. Fortunato and L. Ceschini, CoCr Alloy Processed by Selective Laser Melting (SLM): Effect of Laser Energy Density on Microstructure, Surface Morphology, and Hardness, J. Manuf. Processes, 2020, 52, p 106–119.
T. Niendorf, S. Leuders, A. Riemer, H.A. Richard, T. Tröster and D. Schwarze, Highly Anisotropic Steel Processed by Selective Laser Melting, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, 44, p 794–796.
D. Stefanescu, R. Ruxanda, Fundamentals of Solidification ed: ASM International 2004, p 71-92
S. Liu, Y. Li, F. Liu, H. Zhang and H. Ding, Effects of relative Positioning of Energy Sources on Weld Integrity for Hybrid Laser arc Welding, Opt. Lasers Eng., 2016, 81, p 87–96.
S.L. Sing, F.E. Wiria and W.Y. Yeong, Selective Laser Melting of Titanium Alloy with 50 wt.% Tantalum: Effect of Laser Process Parameters on Part Quality, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater, 2018, 77, p 120–127.
R. Hilzinger, W. Rodewald, Magnetic materials: fundamentals, products, properties, applications, Vacuumschmelze, 2013
F. Pfeifer and C. Radeloff, Soft Magnetic Ni-Fe and Co-Fe Alloys-Some Physical and Metallurgical Aspects, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1980, 19, p 190–207.
G. Ouyang, X. Chen, Y. Liang, C. Macziewski and J. Cui, Review of Fe-6.5 wt.%Si High Silicon Steel—A Promising Soft Magnetic Material for sub-kHz Application, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2019, 481, p 234–250.
N. Kang, M. El Mansori, F. Guittonneau, H. Liao, Y. Fu and E. Aubry, Controllable Mesostructure, Magnetic Properties of Soft Magnetic Fe-Ni-Si by Using Selective Laser Melting from Nickel Coated High Silicon Steel Powder, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 455, p 736–741.
Acknowledgments
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work. This work is supported by the Sciences Platform Environment and Capacity Building Projects of GDAS (2021GDASYL-20210102005). As one of the authors, Shuohong Gao would like to thank the support from the program of CSC (201801810066). The author, Cheng Chang, would like to thank the support from the program of CSC (201801810106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This invited article is part of a special topical focus in the Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance on Additive Manufacturing. The issue was organized by Dr. William Frazier, Pilgrim Consulting, LLC; Mr. Rick Russell, NASA; Dr. Yan Lu, NIST; Dr. Brandon D. Ribic, America Makes; and Caroline Vail, NSWC Carderock.
The original version of this article was revised: In the second sentence of Conclusion 1, “increase” was inadvertently used in place of “decrease.” The sentence should read “And the decrease in the porosity rate of corresponding specimens is related to the increase in LED.”
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, S., Yan, X., Chang, C. et al. Effect of Laser Energy Density on Surface Morphology, Microstructure, and Magnetic Properties of Selective Laser Melted Fe-3wt.% Si Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 5020–5030 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05591-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05591-w