Abstract
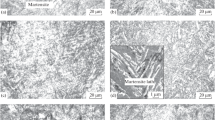
Low-carbon Cu-Ni-Mo-Ti-Nb steel having more than 1700 MPa tensile strength and good low-temperature impact toughness was successfully designed and processed for automobile, defence and structural applications. The steel was thermomechanical controlled processed at a different finish rolling temperatures (750-850 °C) and cooled at two different conditions: air cooling and water quenching. Evolutions of microstructure and precipitates were thoroughly characterised to understand the effect of different factors, such as steel composition, finish rolling temperature and cooling rate on the mechanical properties. The results indicate that the steel processed at 750 °C finish rolling temperature (FRT) followed by water quenching has exhibited superior tensile properties with a yield strength of 1034-1449 MPa, the tensile strength of 1598-1726 MPa and total elongation of 10-13%. Such an ultrahigh-strength level is primarily attributed to the combined effect of lower bainite dominated microstructure along with precipitation hardening. The satisfactory low-temperature toughness is promoted by low finish rolling temperature and higher amount of misorientation offered by the boundaries within the lower bainite.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.V. Philip and T.J. McCaffy, Ultrahigh Strength Steel, Tenth edition, ASM International, USA, Metals Handbook, 1990, p 431–448
J.G. Speer, D.K. Matlock, B.C. De Cooman, and J.G. Schroth, Carbon Partitioning into Austenite After Martensite Transformation, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(9), p 2611–2622
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Bainite in Steels, 2nd ed., IOM Communications, London, 2001
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Large Chunks of Very Strong Steel, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2005, 21, p 1293–1302
G. Caballero, C. Garcia-Mateo, and M.K. Miller, Modern Steels at Atomic and Nanometre Scales, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2015, 31, p 764–772
T. Gladman, The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels, London, UK, Institute of Materials, 1997, p 240
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and R. Honeycombe, Steels: Microstructure and Properties, 3rd ed., Elsevier Ltd., Amsterdam, 2006, p 221
R. Kuziak, R. Kawalla, and S. Waengler, Advanced High Strength Steels for Automotive Industry, Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng., 2008, 8, p 103–117
M. Zhao, K. Yang, and Y. Shan, The Effects of Thermo-Mechanical Control Process on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Commercial Pipeline Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 335, p 14–20
S. Mandal, N.K. Tewary, S.K. Ghosh, D. Chakrabarti, and S. Chatterjee, Thermo-Mechanically Controlled Processed Ultrahigh Strength Steel: Microstructure, Texture and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 663, p 126–140
T. Heller, B. Engl, G. Stich, and G. Thiemann, in Proc. Int. Conf. TMP’ 2000 London, London, (2000), p. 438
F.B. Pickering, Physical Metallurgy and the Design of Steels, Applied Science Publishers, London, 1978, p 101–126
A. Takahashi and M. Iino, Microstructural Refinement by Cu Addition and Its Effect on Strengthening and Toughening of Sour Service Line Pipe Steels, ISIJ Int., 1996, 36, p 241–245
A.J. Craven, K. He, L.A.J. Garvie, and T.N. Baker, Complex Heterogeneous Precipitation in Titanium-Niobium Microalloyed Al-Killed HSLA Steels-I (Ti, Nb) (C, N) Particles, Acta Mater., 2000, 48, p 3857–3868
R.D.K. Misra, G.C. Weatherly, J.E. Hartmann, and A.J. Boucek, Role of structure and microstructure in the enhancement of strength and fracture resistance of ultra-high strength hot rolled steels, in 42nd MWSP Conference Proceedings ISS, vol. 38 (2000) pp. 391–405
H. Kejian and T.N. Baker, The Effects of Small Titanium Additions on the Mechanical Properties and the Microstructures of Controlled Rolled Niobium-Bearing HSLA Plate Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1993, 169(1–2), p 53–65
S. Tirnanic, R. Curcic, D. Tirnanic, and D. Drobnjak, Properties of Thermo-Mechanically Rolled Nb/Ti Micro-alloyed Steel Sheets, Steel Res., 1989, 60, p 561–565
Y. Funakawa, T. Shiozaki, K. Tomita, T. Saito, H. Nakata, K. Sato, M. Suwa, T. Yawamoto, Y. Murao, and E. Maeda, Patent on High Strength Hot Rolled Steel Sheet and Method of Manufacturing the Same, Pub. No.: US 2003/0063996 A1
F.B. Pickering and B. Garbarz, Strengthening in Pearlite Formed from Thermo-Mechanically Processed Austenite in Vanadium Steels and Implications for Toughness, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1989, 5, p 227–237
S. Mukherjee, I.B. Timokhina, C. Zhu, S.P. Ringer, and P.D. Hodgson, Three-Dimensional Atom Probe Microscopy Study of Interphase Precipitation and Nanoclusters in Thermomechanically Treated Titanium-Molybdenum Steels, Acta Mater., 2013, 61, p 2521–2530
S. Zhang, P. Wang, D. Li, and Y. Li, Investigation of the Evolution of Retained Austenite in Fe-13%Cr-4%Ni Martensitic Stainless Steel During Intercritical Tempering, Mater. Des., 2015, 84, p 385–394
Z.B. Jiao, J.H. Luan, M.K. Miller, and C.T. Liu, Precipitation Mechanism and Mechanical Properties of an Ultra-High Strength Steel Hardened by Nanoscale NiAl and Cu Particles, Acta Mater., 2015, 97, p 58–67
Z.W. Zhang, C.T. Liu, Y.R. Wen, A. Hirata, S. Guo, G. Chen, M.W. Chen, and B.A. Chin, Influence of Aging and Thermomechanical Treatments on the Mechanical Properties of a Nanocluster-Strengthened Ferritic Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, 43, p 351–359
R.D.K. Misra, H. Nathani, J.E. Hartmann, and F. Siciliano, Microstructural Evolution in a New 770 MPa Hot Rolled Nb-Ti Micro-alloyed Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 394, p 339–352
H. Xie, L.-X. Du, J. Hu, and R.D.K. Misra, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Novel 1000 MPa Grade TMCP Low Carbon Microalloyed Steel with Combination of High Strength and Excellent Toughness, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 612, p 123–130
X.-L. Li, C.-S. Lei, X.-T. Deng, Z.-D. Wang, Y.-G. Yu, G.-D. Wang, and R.D.K. Misra, Precipitation Strengthening in Titanium Micro-alloyed High-Strength Steel Plates with New Generation-Thermomechanical Controlled Processing (NG-TMCP), J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 689, p 542–553
Z. Peng, L. Li, J. Gao, and X. Huo, Precipitation Strengthening of Titanium Micro-Alloyed High-Strength Steel Plates with Isothermal Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 657, p 413–421
A. Karmakara, S. Biswas, S. Mukherjee, D. Chakrabarti, and V. Kumar, Effect of Composition and Thermo-Mechanical Processing Schedule on the Microstructure, Precipitation and Strengthening of Nb-Microalloyed Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 690, p 158–169
F. Fletcher, Meta-analysis of TNR Measurements: determining new empirical models based on composition and strain, in Austenite Processing Symposium (Internal Company Presentation) (2008), pp. 1–14
C. Ma, L. Hou, J. Zhang, and L. Zhuang, Influence of Thickness Reduction per Pass on Strain, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of 7050 Al Alloy Sheet Processed by Asymmetric Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 650, p 454–468
C. Jun, T. Shuai, L. Zhen-Yu, and W. Guo-Dong, Microstructural Characteristics with Various Cooling Paths and the Mechanism of Embrittlement and Toughening in Low-Carbon High Performance Bridge Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 559, p 241–249
N. Tsuji, R. Ueji, Y. Minamino, and Y. Saito, A New and Simple Process to Obtain Nano-Structured Bulk Low-Carbon Steel with Superior Mechanical Property, Scr. Mater., 2002, 46(4), p 305–310
S. Queyreau, G. Monnet, and B. Devincre, Orowan Strengthening and Forest Hardening Superposition Examined by Dislocation Dynamics Simulations, Acta Mater., 2010, 58, p 5586–5595
R.D.K. Misra, Z. Jia, R. O’Malley, and S.J. Jansto, Precipitation Behavior During Thin Slab Thermomechanical Processing and Isothermal Aging of Copper-Bearing Niobium-Microalloyed High Strength Structural Steels: The Effect on Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 8772–8780
M.P. Phaniraj, Y.-M. Shin, J. Lee, N.H. Goo, D.-I. Kim, J.-Y. Suh, W.-S. Jung, J.-H. Shim, and I.-S. Choi, Development of High Strength Hot Rolled Low Carbon Copper-Bearing Steel Containing Nanometer Sized Carbides, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 633, p 1–8
R.K. Ray and J.J. Jonas, Transformation Textures in Steels, Int. Mater. Rev., 1990, 35, p 1–36
K. Zhu, O. Bouaziz, C. OberbilligHuang, and M. Huang, An Approach to Define the Effective Lath Size Controlling Yield Strength of Bainite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(24–25), p 6614–6619
S. Chen, Y.G. An, and C. Lahaije, Toughness Improvement in Hot Rolled HSLA Steel Plates Through Asymmetric Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 625, p 374–379
B. Hutchinson, J. Hagström, O. Karlsson, D. Lindell, M. Tornberg, F. Lindberg, and M. Thuvander, Microstructures and Hardness of As-Quenched Martensites (0.1–0.5%C), Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 5845–5858
Y. You, C. Shang, N. Wenjin, and S. Subramanian, Investigation on the Microstructure and Toughness of Coarse Grained Heat Affected Zone in X-100 Multi-Phase Pipeline Steel with High Nb Content, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 558, p 692–701
A.J. Kaijalainen, P. Suikkanen, L.P. Karjalainen, and J.J. Jonas, Effect of Austenite Pancaking on the Microstructure, Texture, and Bendability of an Ultrahigh-Strength Strip Steel, Metal. Mater. Trans. A., 2014, 45, p 1273–1283
B.C. De Cooman, Structure-Properties Relationship in TRIP Steels Containing Carbide-Free Bainite, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2004, 8, p 285–303
P. Wang, S.P. Lu, N.M. Xiao, D.Z. Li, and Y.Y. Li, Effect of Delta Ferrite on Impact Properties of Low Carbon 13Cr-4Ni Martensitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 3210–3216
A.A. Gornia and P.R. Mei, Effect of Controlled-Rolling Parameters on the Ageing Response of HSLA-80 Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 197, p 374–378
B. Mishra, K. Kumbhar, K.S. Kumar, K.S. Prasad, and M. Srinivas, Effect of Copper Addition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ultrahigh Strength NiSiCrCoMo Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 651, p 177–183
M.D. Mulholland and D.N. Seidman, Multiple Dispersed Phases in a High-Strength Low-Carbon Steel: an Atom-Probe Tomographic and Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction Study, Scr. Mater., 2009, 60, p 992–995
S. Liu, H. Tana, H. Guo, C. Shang, and R.D.K. Misra, The Determining Role of Aluminum on Copper Precipitation and Mechanical Properties in Cu-Ni-Bearing Low Alloy Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 676, p 510–521
C.N. Hulme-Smith and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Mechanical Properties of Thermally-Stable, Nanocrystalline Bainitic Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 700, p 714–720
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, G., Ghosh, S.K., Chakrabarti, D. et al. Correlation Between Structure and Properties of Low-Carbon Cu-Ni-Mo-Ti-Nb Ultrahigh-Strength Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 6516–6528 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3767-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3767-y