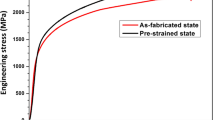
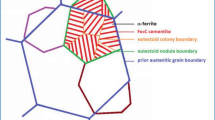
Abstract
The processes governing the deformation and damage of C70 pearlitic steel were investigated in nanometer and micrometer scales using electron backscatter diffraction technique and “in-situ” scanning electron microscope tensile testing. The ferrite behavior was identified by “in-situ” x-ray tensile tests. Investigations were carried out on annealed microstructure with two interlamellar spacings of Sp = 170 and Sp = 230 nm. It is shown that pearlite yielding is controlled by the deformation mechanisms occurring in ferrite. Deformation and damage mechanisms were proposed. At low strain, pearlite deforms homogeneously with low misorientation (<5°) inside the pearlite colonies and elongates the cementite plates. At high strain, pearlite deforms heterogeneously in intense localized shear bands inside the more favorably oriented pearlite colonies. Misorientation reaches values up to 15°. Cementite deforms by an offset of lamella along the shear bands. The nucleation of these shear bands occurs at strain level of E 11 = 7% for coarse pearlite and at a higher value for fine pearlite. Damage occurs by brittle fracture of the elongated cementite lamellae parallel to the tensile axis and which are developed by shear micro-cracks along the slip bands. The plastic-induced damage is thus delayed by the fine pearlite structure.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CLM:
-
Circular line method
- E 11 :
-
Macroscopic strain
- EBSD:
-
Electron backscatter diffraction technique
- HT:
-
Heat treatment
- IPF:
-
Inverse pole figure
- GAM:
-
Grain average misorientation
- KAM:
-
Kernel average images
- PQM:
-
Pattern quality map
- Sp:
-
Interlamellar spacing (nm)
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- σy :
-
Yield stress
- Σ11 :
-
Macroscopic stress
References
A.J. Perez-Unzueta and J.H. Beynon, Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Pearlitic Rail Steels, Wear A, 1993, 162-164, p 173-182
G. Langford, Deformation of Pearlite, Metall. Trans. A, 1977, 8A, p 861-875
O.P. Modi et al., Effect of Interlamellar Spacing on the Mechanical Properties of 0.65% C Steel, Mater. Charact., 2001, 46, p 347-352
O.P. Modia et al., Effect of Interlamellar Spacing on the Mechanical Properties of 0.65% C Steel, Mater. Charact., 2001, 46, p 347-352
A.M. Elwazri, P. Wanjara, and S. Yuea, The Effect of Microstructural Characteristics of Pearlite on the Mechanical Properties of Hypereutectoid Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng A, 2005, 404, p 91-98
T. Shinozaki et al: Influence of Lamellar Spacing on Deformation Behavior of Pearlite Steels Studied by “in-situ” Neutron Diffraction. In: The 3rd International Conference on Advanced Structural Steels Gyeongju; Korea. 2006
C. Lei et al., Effect of Microstructure of Cementite on Interphase Stress State in Carbon Steel, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2007, 14, p 31-38
O.P. Modi et al., Effect of Interlamellar Spacing on the Mechanical Properties of 0.65% C Steel, Mater. Charact., 2001, 46, p 347-352
C. Lei et al., Characterization of Deformability of Spheroidal Cementite by Residual Stress Measurement, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2008, 17, p 445-453
J.M. Hyzak and M. Bernstein, The Role of Microstructure on the Strength and Toughness of Fully Pearlitic Steels, Metall. Trans. A, 1976, 7A, p 1218-1224
H. Yahyaoui et al., Effect of Interlamellar Spacing on the Elastoplastic Behavior of C70 Pearlitic Steel: Experimental Results and Self-consistent Modeling, Mater. Des., 2014, 55, p 888-897
A.R. Marder and B.L. Bramfitt, The Effect of Morphology on the Strength of Pearlite, Metall. Trans. A, 1976, 7A, p 365-372
M. Dollar, I.M. Bernstein, and A.W. Thompson, Influence of Deformation Substructure on Flow and Fracture of Fully Pearlitic Steel, Acta Metall., 1988, 36, p 311-320
D.A. Porter, K.E. Easterling, and G.D.W. Smith, Dynamic Studies of the Tensile Deformation and Fracture of Pearlite, Acta Metall., 1978, 26, p 1405-1414
S. Li et al., In Situ TEM Studies of the Mechanisms of Crack Nucleation and Propagation in Fully Lamellar Microstructures, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2003, 19, p 902-906
X.U. Yongbo, Some Observation of Flow Localization and Shear Cracking in Pearlite During Deformation, Chin. J. Met. Sci. Technol., 1989, 5, p 135-137
X. Hu et al., Modeling Work Hardening of Pearlitic Steels by Phenomenological and Taylor-Type Micromechanical Models, Acta Mater., 2006, 54, p 1029-1040
I.C. Noyan and J.B. Cohen, Residual Stress-Measurement by Diffraction and Interpretation, Springer, Berlin, 1987
L. Le Joncour et al., Damage in Duplex Steels Studied at Mesoscopic and Macroscopic Scales, Mech. Mater., 2010, 42, p 1048-1063
Acknowledgments
G. Gonzalez would like to thank the financial support from CONACYT through Project No. 166896 necessary for EBSD detector acquisition. Part of this research was made during a sabbatical year of GG at PIMM. This visit was made possible by support from PASPA-UNAM, CONACYT and ENSAM-CNAM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sidhom, H., Yahyaoui, H., Braham, C. et al. Analysis of the Deformation and Damage Mechanisms of Pearlitic Steel by EBSD and “in-situ” SEM Tensile Tests. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 24, 2586–2596 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1537-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1537-7