Abstract
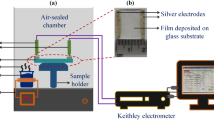
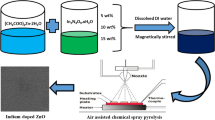
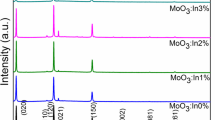
The current work delivers room-temperature ammonia (NH3) gas-detectable pristine, Nb-doped TiO2 air- and vacuum-annealed films obtained through the solution-combustion process. Polycrystalline anatase crystal structured films without any dopant oxide phases were processed at 400°C on glass substrates. The crystallinity was higher in pristine films than in doped films; the morphological features were similar in all the films. The films were > 50% transparent, and the estimated optical energy band gap was greater in doped films than in pristine films. All the films detected NH3 gas (25 ppm to 100 ppm) at room temperature, and the gas response was highly dependent on the crystallinity and relative area fraction of adsorbed oxygen (% of OA). The vacuum-annealed pristine film exhibited a better gas response than the other films at all NH3 gas concentrations due to high crystallinity and % of OA (10.15%). The film demonstrated maximum gas response of ~16 towards 100 ppm of NH3 gas and displayed good selectivity. Even though the doping reduced the crystallite size from ~17 nm to ~9 nm, it also diminished the crystallinity of the films, which significantly impacted the deterioration of their gas response.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.M. Majhi, A. Mirzaei, H.W. Kim, S.S. Kim, and T.W. Kim, Recent advances in energy-saving chemiresistive gas sensors: a review. Nano Energy 79, 1 (2021).
D. Kwak, Y. Lei, and R. Maric, Ammonia gas sensors: a comprehensive review. Talanta 204, 713 (2019).
V.E. Bochenkov and G.B. Sergeev, Sensitivity, selectivity, and stability of gas-sensitive metal-oxide nanostructures. Met. Oxide Nanostruct. Appl. 3, 31 (2010).
G.F. Fine, L.M. Cavanagh, A. Afonja, and R. Binions, Metal oxide semi-conductor gas sensors in environmental monitoring. Sensors. 10, 5469 (2010).
G. Manjunath, P. Nagaraju, and S. Mandal, A comparative study on enhancer and inhibitor of glycine–nitrate combustion ZnO screen-printed sensor: detection of low concentration ammonia at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 10366 (2020).
A. Ramesh, D.S. Gavaskar, P. Nagaraju, S. Duvvuri, S.R.K. Vanjari, and C. Subrahmanyam, Mn-doped ZnO microspheres prepared by solution combustion synthesis for room temperature NH3 sensing. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 12, 100349 (2022).
G. Korotcenkov, Metal oxides for solid-state gas sensors: what determines our choice? Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 139, 1 (2007).
H.G. Moon, Y.S. Shim, D.H. Kim, H.Y. Jeong, M. Jeong, J.Y. Jung, S.M. Han, J.K. Kim, J.S. Kim, H.H. Park, J.H. Lee, H.L. Tuller, S.J. Yoon, and H.W. Jang, Self-activated ultrahigh chemosensitivity of oxide thin film nanostructures for transparent sensors. Sci. Rep. 2, 1 (2012).
G. Eranna, B.C. Joshi, D.P. Runthala, and R.P. Gupta, Oxide materials for development of integrated gas sensors: a comprehensive review. Crit. Re. Solid State Mater. Sci. 29, 111 (2004).
X. Tian, X. Cui, T. Lai, J. Ren, Z. Yang, M. Xiao, B. Wang, X. Xiao, and Y. Wang, Gas sensors based on TiO2 nanostructured materials for the detection of hazardous gases: a review. Nano Mater. Sci. 3, 390 (2021).
S. Singh, H. Kaur, V.N. Singh, K. Jain, and T.D. Senguttuvan, Highly sensitive and pulse-like response toward ethanol of Nb doped TiO2 nanorods based gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 171–172, 899 (2012).
V. Nechita, J. Schoonman, and V. Musat, Ethanol and methanol sensing characteristics of Nb-doped TiO2 porous thin films. Phys. Status solidi. 209, 153 (2012).
V. Galstyan, E. Comini, G. Faglia, A. Vomiero, L. Borgese, E. Bontempi, and G. Sberveglieri, Fabrication and investigation of gas sensing properties of Nb-doped TiO2 nanotubular arrays. Nanotechnology 23, 235706 (2012).
S. Phanichphant, C. Liewhiran, K. Wetchakun, A. Wisitsoraat, and A. Tuantranont, Flame-made Nb-doped TiO2 ethanol and acetone sensors. Sensors. 11, 472 (2011).
N.A. Dahoudi, Low temperature gas sensing coatings made through wet chemical deposition of niobium doped titanium oxide colloid. Mater. Sci. Appl. 02, 265 (2011).
M.C. Carotta, M. Ferroni, D. Gnani, V. Guidi, M. Merli, G. Martinelli, M.C. Casale, and M. Notaro, Nanostructured pure and Nb-doped TiO2 as thick film gas sensors for environmental monitoring. Sens. Actuators. B. Chem. 58, 310 (1999).
L. Gan, C. Wu, Y. Tan, B. Chi, J. Pu, and L. Jian, Oxygen sensing performance of Nb-doped TiO2 thin film with porous structure. J. Alloys. Compd. 585, 729 (2014).
R.K. Sharma, M.C. Bhatnagar, and G.L. Sharma, Mechanism in Nb doped titania oxygen gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 46, 194 (1998).
Y. Yamada, Y. Seno, Y. Masuoka, T. Nakamura, and K. Yamashita, NO2 sensing characteristics of Nb doped TiO2 thin films and their electronic properties. Sens. Actuators. B. Chem. 66, 164 (2000).
W. Wen and J.M. Wu, Nanomaterials via solution combustion synthesis: a step nearer to controllability. RSC Adv. 4, 58090 (2014).
M.G. Kim, M.G. Kanatzidis, A. Facchetti, and T.J. Marks, Low-temperature fabrication of high-performance metal oxide thin-film electronics via combustion processing. Nat. Mater. 10(5), 382 (2011).
E. Carlos, R. Martins, E. Fortunato, and R. Branquinho, Solution combustion synthesis: towards a sustainable approach for metal oxides. Che. Eur. J. 26, 9099 (2020).
G. Manjunath, P. Nagaraju, and S. Mandal, Ultra-sensitive clogging free combustible molecular precursor-based screen-printed ZnO sensors: a detection of ammonia and formaldehyde breath markers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 5713 (2021).
R.V. Vardhan, G. Manjunath, P. Nagaraju, and S. Mandal, Ammonia gas detection by solution combustion-processed pristine & Ti-doped ZnO transparent films: a reverse effect of doping on gas response. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 986 (2023).
C. Wang, J. Meinhardt, and P. Löbmann, Growth mechanism of Nb-doped TiO2 sol-gel multilayer films characterized by SEM and focus/defocus TEM. J. Solgel. Sci. Technol. 53, 148 (2010).
L. Zhao, X. Zhao, J. Liu, A. Zhang, D. Wang, and B. Wei, Fabrications of Nb-doped TiO2 (TNO) transparent conductive oxide polycrystalline films on glass substrates by sol-gel method. J. Solgel. Sci. Technol. 53, 475 (2010).
K.C. Ok, J. Park, J.H. Lee, B. du Ahn, J.H. Lee, K.B. Chung, and J.S. Park, Semiconducting behavior of niobium-doped titanium oxide in the amorphous state. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 2012 (2012).
M. Fallah, M.R. Zamani-Meymian, R. Rahimi, and M. Rabbani, Effect of annealing treatment on electrical and optical properties of Nb doped TiO2 thin films as a TCO prepared by sol-gel spin coating method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 316, 456 (2014).
B.K. Kaleji, R. Sarraf-Mamoory, and A. Fujishima, Influence of Nb dopant on the structural and optical properties of nanocrystalline TiO2 thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132, 210 (2012).
M. Regragui, M. Addou, A. Outzourhit, J.C. Bernéde, E.E. Idrissi, E. Benseddik, and A. Kachouane, Preparation and characterization of pyrolytic spray deposited electrochromic tungsten trioxide films. Thin Solid Films 358, 40 (2000).
W. Wu, L. Zhang, X. Zhai, C. Liang, and K. Yu, Preparation and photocatalytic activity analysis of nanometer TiO2 modified by surfactant. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 8, 1 (2018).
N. Joshi, L.F. da Silva, F.M. Shimizu, V.R. Mastelaro, J.C. M’Peko, L. Lin, and O.N. Oliveira, UV-assisted chemiresistors made with gold-modified ZnO nanorods to detect ozone gas at room temperature. Microchim. Acta. 186, 1 (2019).
M.K. Lee, C.M. Shih, S.C. Fang, H.F. Tu, and C.L. Ho, Preparation of niobium-doped titanium oxide film by liquid phase deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 1653 (2007).
A.V. Manole, M. Dobromir, M. Gîrtan, R. Mallet, G. Rusu, and D. Luca, Optical properties of Nb-doped TiO2 thin films prepared by sol-gel method. Ceram. Int. 39, 4771 (2013).
G. Manjunath, R.V. Vardhan, L.L. Praveen, P. Nagaraju, and S. Mandal, Room-temperature detection of ammonia and formaldehyde gases by LaxBa1−xSnO3−δ (x = 0 and 0.05) screen printed sensors: effect of ceria and ruthenate sensitization. Appl. Phys. A. Mater. Sci. Process. 127, 1 (2021).
V. Shelke, M.P. Bhole, and D.S. Patil, Effect of open air annealing on spin coated aluminum doped ZnO nanostructure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 141, 81 (2013).
I.K. Er, A.O. Çağırtekin, A. Ajjaq, M.A. Yıldırım, A. Ateş, and S. Acar, Complex electrical impedance and modulus characterizations of ZnO: Sn thin films in a wide temperature range. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 13594 (2021).
G. Korotcenkov and B.K. Cho, Thin film SnO2-based gas sensors: film thickness influence. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 142, 321 (2009).
K. Shingange, Z.P. Tshabalala, O.M. Ntwaeaborwa, D.E. Motaung, and G.H. Mhlongo, Highly selective NH3 gas sensor based on Au loaded ZnO nanostructures prepared using microwave-assisted method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 479, 127 (2016).
V.R. Shinde, T.P. Gujar, and C.D. Lokhande, Enhanced response of porous ZnO nanobeads towards LPG: effect of Pd sensitization. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 123, 701 (2007).
R.S. Ganesh, M. Navaneethan, G.K. Mani, S. Ponnusamy, K. Tsuchiya, C. Muthamizhchelvan, S. Kawasaki, and Y. Hayakawa, Influence of Al doping on the structural, morphological, optical, and gas sensing properties of ZnO nanorods. J. Alloys Compd. 698, 555 (2017).
R. Pandeeswari and B.G. Jeyaprakash, High sensing response of β-Ga2O3 thin film towards ammonia vapours: influencing factors at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 195, 206 (2014).
M. Poloju, N. Jayababu, and M.V.R. Reddy, Improved gas sensing performance of Al doped ZnO/CuO nanocomposite based ammonia gas sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 227, 61 (2018).
L. Zhu and W. Zeng, Room-temperature gas sensing of ZnO-based gas sensor: a review. Sens. Actuators A. Phys. 267, 242 (2017).
S.W. Choi, J.Y. Park, and S.S. Kim, Dependence of gas sensing properties in ZnO nanofibers on size and crystallinity of nanograins. J. Mater. Res. 26, 1662 (2011).
Z.M. Seeley, A. Bandyopadhyay, and S. Bose, Influence of crystallinity on CO gas sensing for TiO2 films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 164, 38 (2009).
A. Katoch, G.J. Sun, S.W. Choi, J.H. Byun, and S.S. Kim, Competitive influence of grain size and crystallinity on gas sensing performances of ZnO nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 185, 411 (2013).
V.G. Krishnan, P. Elango, and V. Ganesan, Surface characterization and gas sensing performance of yttrium doped TiO2 nanofilms prepared by automated nebulizer spray pyrolysis (ANSP). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 392 (2018).
S.G. Pawar, S.L. Patil, M.A. Chougule, B.T. Raut, P.R. Godase, R.N. Mulik, S. Sen, and V.B. Patil, New method for fabrication of CSA doped PANi-TiO2 thin-film ammonia sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 11, 2980 (2011).
V.G. Krishnan, N. Ravikumar, R. Dilip, and P. Elango, Gas sensing nature and characterization of Zr doped TiO2 films prepared by automated nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Optik 206, 1 (2020).
N. Mintcheva, P. Srinivasan, J.B.B. Rayappan, A.A. Kuchmizhak, S. Gurbatov, and S.A. Kulinich, Room-temperature gas sensing of laser-modified anatase TiO2 decorated with Au nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 507, 1 (2020).
X. Yang, H. Fu, L. Zhang, X. An, S. Xiong, X. Jiang, and A. Yu, Enhanced gas sensing performance based on the fabrication of polycrystalline Ag@TiO2 core-shell nanowires. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 286, 483 (2019).
H. Liu, W. Shen, and X. Chen, A room temperature operated ammonia gas sensor based on Ag-decorated TiO2 quantum dot clusters. RSC Adv. 9, 24519 (2019).
Y. Zhou, Q. Ding, J. Li, Q. Yang, T. Wu, W. Zhu, X. OuYang, L. Liu, and Y. Wang, TiO2/InVO4 n–n heterojunctions for efficient ammonia gas detection and their sensing mechanisms. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 13660 (2019).
A. Kumar, A. Sanger, A. Kumar, and R. Chandra, Fast response ammonia sensors based on TiO2 and NiO nanostructured bilayer thin films. RSC Adv. 6, 77636 (2016).
C. Zhu, X. Cheng, X. Dong, and Y.M. Xu, Enhanced sub-ppm NH3 gas sensing performance of PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites at room temperature. Front. Chem 6, 1 (2018).
H. Liu, W. Shen, X. Chen, and J. Corriou, A high-performance NH3 gas sensor based on TiO2 quantum dot clusters with ppb level detection limit at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 18380 (2018).
H. Tai, Y. Jiang, G. Xie, J. Yu, X. Chen, and Z. Ying, Influence of polymerization temperature on NH3 response of PANI/TiO2 thin film gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B. 129, 319 (2008).
Z. Ye, H. Tai, T. Xie, Y. Su, Z. Yuan, C. Liu, and Y. Jiang, A facile method to develop novel TiO2/rGO layered film sensor for detecting ammonia at room temperature. Mater. Lett. 165, 127 (2016).
F. Pan, H. Lin, H. Zhai, Z. Miao, Y. Zhang, K. Xu, B. Guan, H. Huang, and H. Zhang, Pd-doped TiO2 film sensors prepared by premixed stagnation flames for CO and NH3 gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 261, 451 (2018).
V.G. Krishnan, P. Elango, K. Ravikumar, R. Marnadu, O.M. Aldossary, and M. Ubaidullah, Noticeable improvement in the toxic gas-sensing activity of the Zn-doped TiO2 films for sensing devices. New J. Chem. 45, 10488 (2021).
P. Chaudhari and S. Mishra, Effect of CuO as a dopant in TiO2 on ammonia and hydrogen sulphide sensing at room temperature. Measurement 90, 468 (2016).
H. Fu, X. Yang, X. An, W. Fan, X. Jiang, and A. Yu, Experimental and theoretical studies of V2O5@TiO2 core-shell hybrid composites with high gas sensing performance towards ammonia. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 252, 103 (2017).
S.S. Rane, D.A. Kajale, S.S. Arbuj, S.B. Rane, and S.W. Gosavi, Hydrogen, ethanol and ammonia gas sensing properties of nano-structured titanium dioxide thick films. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 9011 (2017).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, NITK Surathkal, India. The authors also thank the Department of Physics, CMR Technical Campus, Hyderabad, for providing gas sensing measurements.
Funding
This work is supported by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology (CRG/2021/001084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RVV designed, performed the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. PN provided the gas sensing experimental facilities. SM gave essential guidance throughout the experimentation and preparation of the manuscript. MG, PN, and SM reviewed and corrected the manuscript. All the authors read and agreed the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vardhan, R.V., Manjunath, G., Nagaraju, P. et al. Tracing of Ammonia Gas by Solution-Combustion-Derived Pristine and Nb-Doped TiO2 Films: Beneficial Impact of Crystallinity and Adsorbed Oxygen on the Gas Response. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 6360–6377 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10577-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10577-6