Abstract
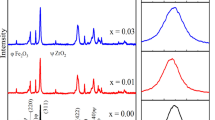
In this report, we describe how copper-doped barium hexaferrite (CBM) influences the structure, elasticity, morphology, composition, and optical behavior in cobalt zinc ferrite (CZF) [(x)%CBM + (100-x)%CZF with x = 90, 80, 70 and 60] nanocomposites prepared by physical mixing. Analysis of the composites is performed using XRD, SEM, EDAX, FTIR, UV, and, PL. XRD confirms the formation of hexagonal and spinel structures along with their other structural parameters. Elastic parameters and Debye temperature are measured using FTIR. Young’s modulus of 90%CBM + 10%CZF shows that the material can be used for shielding applications as well as in high-density optical storage devices. The morphology, particle size distribution, and comparison between crystalline and particle size of the composite are studied by SEM. The purity of the composite produced is analyzed using EDAX studies. From the UV analysis, the optical measurements of the manufactured composite such as transmission, absorption, refractive index, and Urbach energy were analyzed. Both the direct and indirect band gap energies increase with decreasing CBM in the composite. Among all the observed composites, 60%CBM + 40%CZF is found to be a suitable candidate for a visible-light active photocatalyst. The overall structural and optical properties also prove that the material can be used in tunable photonic applications. The refractive index of the composite is between 3.2 and 3.4, which can be used for photo-electrochemical cells, optical detectors, or reflectors. The optical band gap determined by UV–Vis spectroscopy was verified using PL spectra, which shows semiconducting properties that can be exploited in optoelectronic devices, photocatalysts, and sensor applications.















Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
04 May 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10477-9
References
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: A review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Progress Mater. Sci. 57, 1191–1334 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2012.04.001.
D.A. Vinnik, V.E. Zhivulin, A.Y. Starikov, S.A. Gudkova, E.A. Trofimov, A.V. Trukhanov, and A.L. Kozlovsky, Influence of titanium substitution on structure, magnetic and electric properties of barium hexaferrites BaFe12-xTixO19. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 498, 166117 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166544.
M. Hähsler, M. Zimmermann, S. Heißler, and S. Behrens, Sc-doped barium hexaferrite nanodiscs: Tuning morphology and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 500, 166349 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166349.
D. Roy, C. Shivakumara, and P. Kumar, A observation of the exchange spring behavior in hard–soft-ferrite nanocomposite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, L11–L14 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.09.017.
N.A. Algarou, Y. Slimani, M.A. Almessiere, A. Sadaqat, A.V. Trukhanov, M.A. Gondal, A.S. Hakeem, S.V. Trukhanov, M.G. Vakhitov, D.S. Klygach, A. Manikandan, and A. Baykal, Functional Sr0.5Ba0.5Sm0.02Fe11.98O4/x(Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4) Hard-Soft Ferrite Nanocomposites: Structure. Magnetic and Microwave Properties. Nanomaterials 10, 2134 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112134.
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A.V. Trukhanov, A. Sadaqat, A. Demir Korkmaz, N.A. Algarou, H. Aydın, and A. Baykal, MS Toprak Review on functional bi-component nanocomposites based on hard/soft ferrites: Structural, magnetic, electrical and microwave absorption properties. Nano-Struct. Nano-Obj. 26, 100728 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2021.100728.
G. Florio, Structural features of magnetic materials, in A.-G. Olabi (ed.), Encyclopedia of Smart Materials, Elsevier, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815732-9.00095-4
N. Kumari, S. Kour, G. Singh, R. K. Sharma, A brief review on synthesis, properties and applications of ferrites. In AIP Conference Proceedings 2220, (2020): 020164 https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0001323
E. Casbeer, V.K. Sharma, and X.Z. Li, Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of ferrites under visible light: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 87, 1–14 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.11.034.
N. Sukhleen and P. Kunal, Nickel spinel ferrites: a review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 519, 167163 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167163.
H. Qin, Y. He, P. Xu, D. Huang, Z. Wang, H. Wang, and C. Wang, Spinel ferrites (MFe2O4): Synthesis, improvement and catalytic application in environment and energy field. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 294, 102486 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102486.
A. Hajalilou and S.A. Mazlan, A review on preparation techniques for synthesis of nanocrystalline soft magnetic ferrites and investigation on the effects of microstructure features on magnetic properties. Appl. Phys. A 122, 1–15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0217-2.
A. Houbi, Z.A. Aldashevich, Y. Atassi, Z.B. Telmanovna, M. Saule, and K. Kubanych, Microwave absorbing properties of ferrites and their composites: A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 529, 167839 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.167839.
P. Thakur, S. Taneja, D. Sindhu, U. Lüders, A. Sharma, B. Ravelo, and A. Thakur, Manganese zinc ferrites: a short review on synthesis and characterization. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 1569–1584 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05489-z.
P. Thakur, D. Chahar, S. Taneja, N. Bhalla, and A. Thakur, A review on MnZn ferrites: synthesis, characterization and applications. Ceram. Int. 46, 15740–15763 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.287.
P.A. Vinosha, A. Manikandan, A.S.J. Ceicilia, A. Dinesh, G.F. Nirmala, A.C. Preetha, and B. Xavier, Review on recent advances of zinc substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Synthesis characterization and diverse applications. Ceramics Int. 47, 10512–10535 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.289.
P.A. Vinosha, A. Manikandan, A.C. Preetha, A. Dinesh, Y. Slimani, M.A. Almessiere, and G. Nirmala, Review on recent advances of synthesis, magnetic properties, and water treatment applications of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites. J. Superconduct. Novel Magn. 34, 995–1018 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05854-6.
P.P. Bardapurkar, S.S. Shewale, S.A. Arote, S.S. Pansambal, and N.P. Barde, Effect of precursor pH on structural, magnetic and catalytic properties of CoFe2O4@SiO2 green nanocatalyst. Res. Chem. Intermed 47, 1919–1939 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04366-7.
S. Kumar, S. Guha, S. Supriya, L.K. Pradhan, and M. Kar, Correlation between crystal structure parameters with magnetic and dielectric parameters of Cu-Doped barium hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 499, 166213 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166213.
J. Feng, R. Xiong, Y. Liu, Su. Fangyi, and X. Zhang, Preparation of cobalt substituted zinc ferrite nanopowders via auto-combustion route: an investigation to their structural and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 18358–18371 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9950-y.
T. Munawar, F. Iqbal, S. Yasmeen, K. Mahmood, and A. Hussain, Multi metal oxide NiO-CdO-ZnO nanocomposite–synthesis, structural, optical, electrical properties and enhanced sunlight driven photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 46, 2421–2437 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.236.
D. Guruvammal, S. Selvaraj, and S. MeenakshiSundar, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Co doped ZnO DMS nanoparticles by microwave irradiation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 452, 335 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.12.097.
S.K. Paswan, S. Kumari, M. Kar, A. Singh, H. Pathak, J.P. Borah, and L. Kumar, Optimization of structure-property relationships in nickel ferrite nanoparticles annealed at different temperature. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 151, 109928 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109928.
M.A. Eid, A.A. El-Helaly, M.Y. El-Sheikh, H.A. El-Daly, and A.H. Gemeay, Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activities of CuxFe3-xO4/PANI nanocomposites. Egypt. J. Microbiol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.21608/ejm.2022.116185.1206.
K.K. Khichar, S.B. Dangi, V. Dhayal, U. Kumar, S.Z. Hashmi, V. Sadhu, and P.A. Alvi, Structural, optical, and surface morphological studies of ethyl cellulose/graphene oxide nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 41, 2792–2802 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25576.
V.R. Akshay, B. Arun, G. Mandal, and M. Vasundhara, Visible range optical absorption, Urbach energy estimation and paramagnetic response in Cr-doped TiO2 nanocrystals derived by a sol–gel method. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 12991–13004 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP01351B.
Lu. Zhang, S. Han, Y. Li, S. Yang, X. Zhao, and J. Liu, Effect of magnesium on the crystal transformation and electrochemical properties of A2B7-type metal hydride alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161, A1844 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0641412jes.
E. Nurfani, A. Lailani, W. Kesuma, M. Anrokhi, G. Kadja, and M. Rozana, UV sensitivity enhancement in Fe-doped ZnO films grown by ultrafast spray pyrolysis. Opt. Mater. 112, 110768 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110768.
N.P. Barde, S.S. Shewale, P.S. Solanki, N.A. Shah, and P.P. Bardapurkar, Effect of silica matrix on structural, optical and electrical properties of Li0.5Fe2.5O4 nanoparticles. Scripta Mater. 194, 113712 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113712.
M. Kalyan Raju, FT-IR studies of Cu substituted Ni-Zn ferrites for structural and vibrational investigations. Chem. Sci. Trans. 4, 137–142 (2015). https://doi.org/10.7598/cst2015.957.
Q. Zhang, Z. Xia, Y.-B. Cheng, and Gu. Min, High-capacity optical long data memory based on enhanced Young’s modulus in nanoplasmonic hybrid glass composites. Nat. Commun. 9, 1183 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03589-y.
M.K. Manglam, S.N. Rout, S. Kumari, S. Kumar, and M. Kar, Structural, magnetic and optical properties of (0.45) Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4+(055) BaFe12O19 composite. Mater. Today Proc. 57, 418–421 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.12.431.
P.P. Bardapurkar, S.N. Dalvi, V.D. Joshi, P.S. Solanki, V.R. Rathod, N.A. Shah, and N.P. Barde, Effect of silica matrix on structural and optical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Results Surf. Interfaces 8, 100081 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsurfi.2022.100081.
N.M. Ravindra, P. Ganapathy, and J. Choi, Energy gap–refractive index relations in semiconductors–an overview. Infrared Phys. Technol. 50, 21–29 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2006.04.001.
M.N. Mehathaj, N. Padmanathan, and E. Sivasenthil, Doping catalysed unintentional hydrogenation effect on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci Mater. Electron. 33, 11523–11541 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08126-8.
T.M. Hammad, J.K. Salem, A.A. Amsha, and N.K. Hejazy, Optical and magnetic characterizations of zinc substituted copper ferrite synthesized by a co-precipitation chemical method. J. Alloys Compound. 741, 123–130 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.123.
J. Liqiang, Q. Yichun, W. Baiqi, L. Shudan, J. Baojiang, Y. Libin, and S. Jiazhong, Review of photoluminescence performance of nano-sized semiconductor materials and its relationships with photocatalytic activity. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 90, 1773–1787 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2005.11.007.
J.G. Yu, H.G. Yu, B. Cheng, X.J. Zhao, J.C. Yu, and W.K. Ho, The effect of calcination temperature on the surface microstructure and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 thin films prepared by liquid phase deposition. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 13871–13879 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp036158y.
H.Q. Jiang, P. Wang, X.L. Guo, and H.Z. Xian, Preparation and characterization of low-amount Yb3+-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. Russ. Chem. Bull. 55, 1743–1747 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11172-006-0482-x.
S. Allwin, S. Ashwin, and E. Sivasenthil, Multifunctionality of AlBaFe12O19/CoZnFe2O4 hybrid nanocomposite: Promising structural, elastic, morphological, compositional, optical, and magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 174, 111134 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2022.111134
A. N. Kadam, J. Lee, S. V. Nipane, S. W. Lee, Nanocomposites for visible light photocatalysis. In Nanostructured Materials for Visible Light Photocatalysis (pp. 295-317) 20222. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-823018-3.00017-8
M. Hadi, K.M. Batoo, A. Chauhan, O.M. Aldossary, R. Verma, and Y. Yang, Tuning of structural, dielectric, and electronic properties of Cu doped Co–Zn ferrite nanoparticles for multilayer inductor chip applications. Magnetochemistry 7, 53 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7040053.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to our President, Chancellor, Chief Executive Officer, Vice-Chancellor, and Registrar of Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, Coimbatore, India, for providing facilities and encouragement.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS: Conceptualization, methodology, materials preparation, characterization, writing—original draft. AS: formal analysis, writing—review, and editing. SE: supervision, investigation, resources. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10477-9
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sudhakaran, A., Sudhakaran, A. & Sivasenthil, E. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Investigating the Influence of Cu-Doped BaFe12O19 on Physical and Optical Behavior of Its Nanocomposites with CoZnFe2O4. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 2312–2328 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10114-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10114-x