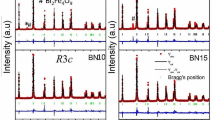
Abstract
Materials with multifunctional properties are currently being studied for countless technological applications. In the present work, an experimental and theoretical study of the iron-chromite spinel FeCr2O4 produced by the solid-state reaction technique is reported. Structural analysis from x-ray diffraction experiments revealed the crystallization of the material into a cubic structure and morphological and compositional studies showed the granular character, with nanometric and micrometric dimensions whose compositions are as expected from its chemical stoichiometry. Optical characterization reveals semiconducting behavior with bandgap 1.52 eV and the magnetic response shows weak ferromagnetic character at room temperature. The density of electronic states in the ground state evidences characteristic semiconducting for one spin polarization and conducting for the other close to the Fermi level, which is compatible with a half-metallic behavior with magnetic moment of 2.0 µB per unit cell.









Similar content being viewed by others

References
M.A. Rafiq, A. Javed, M.N. Rasul, M. Nadeem, F. Iqbal, A. Hussain, Structural, electronic, magnetic and optical properties of AB2O4 (A = Ge, Co and B = Ga, Co) spinel oxides. Mater. Chem. Phys. 257, 123794 (2021).
Q. Zhao, Z. Yan, C. Chen, and J. Chen, Spinels: Controlled Preparation, Oxygen Reduction/Evolution Reaction Application, and Beyond. Chem. Rev. 117, 10121 (2017).
A. Šutka, and K.A. Gross, Spinel Ferrite Oxide Semiconductor Gas Sensors. Sensor Actuat. B-Chem 222, 95 (2016).
H. Suzuki, T. Furubayashi, G. Cao, H. Kitazawa, A. Kamimura, K. Hirata, and T. Matsumoto, Metal-Insulator Transition and Superconductivity in Spinel-Type System Cu1-xZnxIr2S4. J. Phys. Soc. Japan 68, 2495 (1999).
K. Kawano, S.B. Madhu, M. Mizutamari, and R. Nakata, Paramagnetic Properties of the Spinel-Type Al1-xMnx-Sulphate Salts for its Pillared Intercalation into a Clay Mineral. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 64, 477 (2003).
H.M.I. Abdallah, and T. Moyo, Superparamagnetic Behavior of MnxNi1-xFe2O4 spinel Nanoferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 361, 170 (2014).
T. Fukai, Y. Furukawa, S. Wada, and K. Miyatani, NMR Study of Antiferromagnetic Spinel CoCo2O4 in Paramagnetic and Ordered State. J. Phys. Soc. Japan 65, 4067 (1996).
I.P. Muthuselvam, and R.N. Bhowmik, Structural phase stability and magnetism in Co2FeO4 spinel oxide. Solid State Sci. 11, 719 (2009).
A. Hakeem, T. Alshahrani, G. Muhammad, M.H. Alhossainy, A. Laref, A.R. Khan, I. Ali, H.M.T. Farid, T. Ghrib, S.R. Ejaz, and R.Y. Khosa, Magnetic, dielectric and structural properties of spinel ferrites synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 11, 158 (2021).
J.G. Azadani, W. Jiang, J.-P. Wang, T. Low, Ferromagnetic phase of the spinel compound MgV2O4 and its spintronics properties. Phys. Rev. B 102, 155144 (2020).
A. Sundaresan, N.V. Ter-Oganessian, Magnetoelectric and multiferroic properties of spinels. J. Appl. Phys. 129, 060901 (2021).
L.C. Garrido, C.E. Deluque Toro, I. Díaz, D.A. Landínez Téllez, J. Roa-Rojas, First-principles calculations to investigate elastic, electronic and thermophysical properties of the Dy2Bi2Fe4O12 ferromagnetic semiconductor. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 36, 095015 (2021).
S. Wang, H. Tian, C. Ren, J. Yu, and M. Sun, Electronic and optical properties of heterostructures based on transition metal dichalcogenides and graphene-like zinc oxide. Sci. Rep. 8, 12009 (2018).
S. Wang, M.S. Ukhtary, R. Saito, Strain effect on circularly polarized electroluminescence in transition metal dichalcogenides. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 033340 (2020).
K. Hoang, M. Oh, and Y. Choi, Electronic structure, polaron formation, and functional properties in transition-metal tungstates. RSC Adv. 8, 4191 (2018).
K. Hoang, and M.D. Johannes, Defect chemistry in layered transition-metal oxides from screened hybrid density functional calculations. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 5224 (2014).
K. Hoang, and M. Johannes, Defect Physics and Chemistry in Layered Mixed Transition Metal Oxide Cathode Materials: (Ni Co, Mn) vs (Ni Co, Al). Chem. Mater. 28, 1325 (2016).
S.A. Wolf, J. Lu, M.R. Stan, E. Chen, and D.M. Treger, The Promise of Nanomagnetics and Spintronics for Future Logic and Universal Memory. Proc. IEEE 98, 2155–2168 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2010.2064150.
L. Chen, S. Yan, P.F. Xu, J. Lu, W.Z. Wang, J.J. Deng, X. Qian, Y. Ji, J.H. Zhao, Low-temperature magnetotransport behaviors of heavily Mn-doped (Ga,Mn)As films with high ferromagnetic transition temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 182505 (2009).
M.C. Bennett, M.C. Aronson, D.A. Sokolov, C. Henderson, and Z. Fisk, Ferromagnetism, superconductivity and secondary phases in the dilute magnetic semiconductor Pt1−xRExSb2 (RE = La, Ce, Gd, Yb). J. Alloys Compd. 400, 2 (2005).
C. Benhalima, S. Amari, L. Beldi, and B. Bouhafs, First-Principles Study of Ferromagnetism in Iron Chromite Spinels: FeCr2O4 and CrFe2O4. SPIN 9, 1950014 (2019).
W. Kim, C.S. Kim, Spin-ordering Transition and Distortion of Local Sites in Spinel Fe0.9Cd0.1Cr2O4 by Using Mössbauer Spectroscopy. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 58, 276 (2011).
K. Singh, A. Maignan, C. Simon, C. Martin, FeCr2O4 and CoCr2O4 spinels: Multiferroicity in the collinear magnetic state? Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 172903 (2011).
K. Tomiyasu, H. Hiraka, K. Ohoyama, K. Yamada, Resonance-Like Magnetic Excitations in Spinel Ferrimagnets FeCr2O4 and NiCr2O4 Observed by Neutron Scattering. J. Phys. Soc. Japan 77, 124703 (2008).
D.A. Landínez Téllez, D. Martínez Buitrago, E.W. Barrera, J. Roa-Rojas, Crystalline structure, magnetic response and electronic properties of RE2MgTiO6 (RE=Dy, Gd) double perovskites. J. Mol. Struct. 1067, 205 (2014).
C.E. Alarcón-Suesca, C.E. Deluque Toro, A.V. Gil Rebaza, D.A. Landínez Téllez, J. Roa-Rojas, Ab-initio studies of electronic, structural and thermophysical properties of the Sr2TiMoO6 double perovskite. J. Alloys Compd. 771, 1080 (2019).
B.H. Toby, and R.B. Von Dreele, GSAS-II: the genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 46, 544 (2013).
P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, G. K. H. Madsen, D. Kvasnicka, J. Luitz, R. Laskowski, F. Tran and L. D. Marks, WIEN2k, An Augmented Plane Wave + Local Orbitals Program for Calculating Crystal Properties (Karlheinz Schwarz, Techn. Universität Wien, Austria), 2018. ISBN 3-9501031-1-2.
P. Hohenberg, and W. Khon, Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. B 864, 136 (1964).
W. Khon, and L.S. Sham, Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Phys. Rev. A 1133, 140 (1965).
D.A. Andersson, and C.R. Stanek, Mixing and non-stoichiometry in Fe–Ni–Cr–Zn–O spinel compounds: density functional theory calculations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 15550 (2013).
Ş Uğur, S. Akbudak, A. Kushwaha, and G. Bayrak, Study of structural, elastic, electronic, and vibrational properties of MRh2O4 (M = Cd and Zn) spinels: DFT-based calculations. J. Mol. Model. 26, 140 (2020).
J.A. Cuervo Farfán, C.E. Deluque Toro, C.A. Parra Vargas, D.A. Landínez Téllez, J. Roa-Rojas, Experimental and theoretical determination of physical properties of Sm2Bi2Fe4O12 ferromagnetic semiconductors. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 14925 (2020).
C. E. Deluque Toro, A. S. Mosquera Polo, A. V. Gil Rebaza, D. A. Landínez Téllez, J. Roa-Rojas, Ab Initio study of the electronic structure, elastic properties, magnetic feature and thermodynamic properties of the Ba2NiMoO6 material. J. Low Temp. Phys. 192, 265 (2018).
P. Blaha, K.Schwarz, F. Tran, R. Laskowski, G.K.H. Madsen, L.D. Marks, WIEN2k: An APW+lo program for calculating the properties of solids. J. Chem. Phys. 152, 074101 (2020).
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof, Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
E. Parthé, L. Gelato, B. Chabot, M. Penzo, K. Cenzual, and R. Gladyshevskii, TYPIX Standardized and crystal chemical characterization of inorganic structure types. Gmelein Handbook of Inorganic and Organometallic Chemistry, 8th ed., (Berlin: Springer, 1993).
C.A. Schneider, W.S. Rasband, and K.W. Eliceiri, NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9, 671 (2012).
V. Kumar, S.K. Sharma, T. Sharma, and V. Singh, Band gap determination in thick films from reflectance measurements. Optical Mater. 12, 115 (1999).
A.A. Christy, O.M. Kvalheim, and R.A. Velapoldi, Quantitative analysis in diffuse reflectance spectrometry: A modified Kubelka-Munk equation. Vib. Spectrosc. 9, 19 (1995).
T. Ramachandran, and F. Hamed, The effect of fuel to nitrates ratio on the properties of FeCr2O4 nanopowders. Mater. Res. Bull. 95, 104 (2017).
S. Nakamura, and A. Fuwa, Spin Order in FeCr2O4 Observed by Mössbauer Spectroscopy. Phys. Procedia 75, 747 (2015).
V.R. Estrada Contreras, C.E. Alarcón Suesca, C.E. Deluque Toro, D.A. Landínez Téllez, J. Roa-Rojas, Crystalline, ferromagnetic-semiconductor and electronic features of the terbium-based cobalt-ferrite Tb2FeCoO6. Ceram. Int. 47, 14408 (2021).
A.V. Gil Rebaza, C.E. Deluque Toro, H.H. Medina Chanduví, D.A. Landínez Téllez, J. Roa-Rojas,Thermodynamic evidence of the ferroelectric Berry phase in europium-based ferrobismuthite Eu2Bi2Fe4O12. J. Alloys Compd. 884, 161114 (2021).
P. Dowben, Half Metallic Ferromagnets. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19, 310301 (2007).
S. Wang, and J. Yu, Magnetic Behaviors of 3d Transition Metal-Doped Silicane: a First-Principle Study. J Supercond. Nov. Magn. 31, 2789 (2018).
W. Sa-Ke, T. Hong-Yu, Y. Yong-Hong, W. Jun, Spin and valley half metal induced by staggered potential and magnetization in silicene. Chin. Phys. B 23, 017203 (2014).
Acknowledgments
This work was partially financed by Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología— MINCIENCIAS, on the project FP80740-243-2019 and División de Investigación y Extensión DIEB, Universidad Nacional de Colombia Sede Bogotá.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cerón, J.A.G., Téllez, D.A.L. & Roa-Rojas, J. Weak Ferromagnetism in the FeCr2O4 Semiconductor Spinel with Half-Metallic Feature in the Ground State. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 822–830 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09348-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09348-y