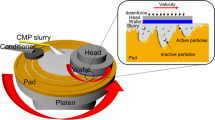
Abstract
Flatness is an important criteria for evaluating wafer quality. Chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) is an effective method to process wafers and to improve the wafer flatness. Therefore, a flatness model is necessary for optimizing CMP process variables through investigating the wafer surface formation mechanism as well as the influences of CMP parameters on the wafer flatness. However, most studies pay attention to the roughness change of a wafer surface. Besides, there is little literature about the flatness of CMP modeling wafers. In this study, a wafer flatness model based on the material removal during CMP was established. The surface pressure distribution of the wafer surface was obtained by finite element simulation. The relative velocity distribution of the abrasive particles and the wafer surface during polishing were acquired by the numerical simulation, introduced to develop the flatness model. Finally, the influences of different process parameters on flatness were investigated. The flatness model established agreement between the calculated and the experimental results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Lee, D.I. Kim, H. Jeong, and K.H. Kwang, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 57, 845 (2010).
H. Hocheng, H.Y. Tsai, and M.S. Tsai, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 40, 1651 (2000).
Y.S. Xie and B. Bhushan, Wear 200, 281 (1996).
Y.B. Tian, Y.J. Ang, Z.W. Zhong, H. Xu, and R. Tan, Mater. Manuf. Process. 28, 488 (2013).
K. Hirose and T. Enomoto, in ASME International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Proceedings (2009), pp. 671–676.
Z.W. Zhong, Y.B. Tian, Y.J. Ang, and H. Wu, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 60, 1197 (2011).
G.S. Lee, H.H. Hwang, C.H. Son, J.W. Choi, W.J. Lee, B.C. Shin, J.D. Seo, K.R. Ku, and H.D. Jeong, Mater. Sci. Forum (Trans tech, Durnten-zurich, 2009), pp. 615–617.
Y. Zhou, G.S. Pan, X.L. Shi, H. Gong, G.H. Luo, and Z.H. Gu, Surf. Coat. Technol. 251, 48 (2014).
D.X. Peng, Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 66, 685 (2014).
C.F. Fang, Z.X. Zhao, L.Y. Lu, and Y.F. Lin, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 88, 575 (2017).
S. Sadakuni, J. Murata, K. Yagi, Y. Sano, K. Arima, T. Okamoto, K. Tachibana, and K. Yamauchi, Phys. Status Solidi C 8, 2223 (2011).
X.K. Hu, Z.T. Song, Z.C. Pan, W.L. Liu, and L.C. Wu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 8230 (2009).
U. Satake, T. Enomoto, and K. Matsuda, in Procedia CIRP Proceedings(2012), pp. 675–676.
Y. Park, H. Lee, Y. Lee, S. Park, and H. Jeong, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 14, 1513 (2013).
A. Une, K. Yoshitomi, M. Mochida, and N. Ogasawara, Microelectron. Eng. 87, 1646 (2010).
P.L. Wang, Z.G. Dong, G. Ya, and Z.B. Duan, Sci. Technol. Eng. 18, 232 (2018) (in Chinese).
C.D. Alberto, L.P. Rafael, G.G. Jorge, and C.C. Jorge, Optik 124, 3909 (2013).
Q.L. Yuan, H. Fu, S.J. Li, T.R. Jiang, and M.S. Yang, Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerospace. Eng. 37, 1969 (2018) (in Chinese).
Z.Z. Zhou, F.Y. Lou, B.H. Lu, and J.L. Yuan, China Mech. Eng. 20, 1207 (2009) (in Chinese).
J.X. Su, D.M. Guo, R.K. Kang, Z.J. Jin, and X.J. Li, China Mech. Eng. 09, 815 (2005) (in Chinese).
W.J. Wang and A.X. Wang, J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 50, 29 (2018) (in Chinese).
L. Shan, J. Levert, L. Meade, J. Tichy, and S. Danyluk, J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 122, 539 (2000).
J.A. Levert, S. Danyluk, and J. Tichy, J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 122, 450 (2000).
H.S. Oh and H.L. Lee, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 Regul. Pap. Short Notes Rev. Pap. 40, 5300 (2001).
G.H. Zhong, Y.D. Ning, Q.G. Zhou, Y.Z. Bian, X. Wang, X. Qu, L. Wang, and E.J. Zhao, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 68, 15 (2017).
S.T. Hu, W.F. Huang, X. Shi, Z.K. Peng, X.F. Liu, and Y.M. Wang, Tribol. Lett. 66, 3 (2018).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2019JBM049). The authors are grateful for the help of Dr. Wenxi WANG on English text improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Li, J., Yi, D. et al. Wafer Flatness Modeling in Chemical Mechanical Polishing. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 353–363 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07799-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07799-y