Abstract
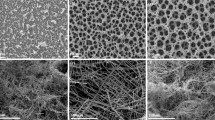
Tin oxide is a commonly used gas-sensing material, which can be applied as an n- or p-type gas sensor. To improve the gas-sensing performance of tin oxide, we successfully synthesized tin oxide foam via an ice-templating or freeze-casting method. The tin oxide foam samples showed different morphological features depending on the major processing parameters, which include sintering temperature, sintering time, and the amount of added powder. Based on scanning electron microscopy images, we could identify dual pore structure of tin oxide foam containing ‘wall’ pores ranging from 5.3 μm to 10.7 μm, as well as smaller secondary pores (a few micrometers in size) on the wall surfaces. Gas-sensing performance tests for the synthesized tin oxide foams reveal a sensitivity of 13.1, a response time of 192 s, and a recovery time of 160 s at an ethanol gas concentration of 60 ppm at 300°C. This is a remarkable result given that it showed p-type semiconductor behavior and was used without the addition of any catalyst.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Schedin, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, E.W. Hill, P. Blake, M.I. Katsnelson, and K.S. Novoselov, Nat. Mater. 6, 652 (2007).
B.F. Bessac and S.-E. Jordt, Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 7, 269 (2010).
C. Hou, J. Li, D. Huo, X. Luo, J. Dong, M. Yang, and X. Shi, Sens. Actuators B. 161, 244 (2012).
A. Hempel-Jorgensen, S.K. Kjaergaard, L. Molhave, and K.H. Hudnell, Arch. Environ. Health 54, 416 (1999).
M.L. Boeglin, D. Wessels, and D. Henshel, Environ. Res. 100, 242 (2006).
G.F. Fine, L.M. Cavanagh, A. Afonja, and R. Binions, Sensors 10, 5469 (2010).
N. Yamazoe, Sens. Actuators B. 5, 7 (1991).
B. Zhang, W. Fu, H. Li, X. Fu, Y. Wang, H. Bala, X. Wang, G. Sung, J. Cao, and Z. Zhang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 363, 560 (2016).
J.F. Boyle and K.A. Jones, J. Electron. Mater. 6, 717 (1977).
J. Xu, Q. Pan, Y. Shun, and Z. Tian, Sens. Actuators B. 66, 277 (2000).
T. Waitz, T. Wagner, T. Sauerwald, C.-D. Kohl, and M. Tiemann, Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 653 (2009).
X.-L. Li, T.-J. Lou, X.-M. Sun, and Y.-D. Li, Inorg. Chem. 43, 5442 (2004).
B. Karunagaran, P. Uthirakumar, S.J. Chung, S. Velumani, and E.-K. Suh, Mater. Charact. 58, 680 (2007).
I. Hotovy, V. Rehacek, P. Siciliano, S. Capone, and L. Spiess, Thin Solid Films 418, 9 (2002).
J. Zhang, J. Liu, Q. Peng, X. Wang, and Y. Li, Chem. Mater. 18, 867 (2006).
H. Nguyen and S.A. El-Safty, J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 8466 (2011).
S. Pokhrel, C.E. Simion, V. Quemener, N. Barsan, and U. Weimar, Sens. Actuators B . 133, 78 (2008).
N. Barsan, C. Simion, T. Heine, S. Pokhrel, and U. Weimar, J. Electroceram. 25, 11 (2010).
H.-J. Kim and J.-H. Lee, Sens. Actuators B. 192, 607 (2014).
K. Pirkanniemi and M. Sillanpää, Chemosphere 48, 1047 (2002).
M.M. Bettahar, G. Costentin, L. Savary, and J.C. Lavalley, Appl. Catal. A. 145, 1 (1996).
Y. Motooka and A. Ozaki, J. Catal. 5, 116 (1966).
S.S. Kaye and J.R. Long, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 6506 (2005).
M. Kodu, T. Avarmaa, A. Floren, and R. Jaaniso, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33, 2335 (2013).
J. Huang, L. Wang, C. Gu, and J.-J. Shim, Mater. Lett. 136, 371 (2014).
N. Yamazoe, G. Sakai, and K. Shimanoe, Catal. Surv. Asia 7, 63 (2003).
W.Y. Yin, B.Q. Wei, and C.W. Hu, Chem. Phys. Lett. 471, 11 (2009).
T. Sahm, L. Mädler, A. Gurlo, N. Barsan, S.E. Pratsinis, and U. Weimar, Sens. Actuators B. 98, 148 (2004).
L.C. Tien, S.J. Pearton, D.P. Norton, and F. Ren, Appl. Phys. A 91, 29 (2008).
G.X. Wang, J.S. Park, M.S. Park, and X.L. Gou, Sens. Actuators B. 131, 313 (2008).
D.J. Wales, J. Grand, V.P. Ting, R.D. Burke, K.J. Edler, C.R. Bown, S. Mintova, and A.D. Burrows, Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 4290 (2015).
N.T.P. Nhung, P.V. Tong, C.M. Hung, N.V. Duy, N.V. Chien, N.V. Vinh, N.T. Tuyen, and N.D. Hoa, RSC Adv. 6, 64215 (2016).
Y.H. Cho, X. Liang, Y.C. Kang, and J.-H. Lee, Sens. Actuators B. 207, 330 (2015).
Y.C. Goswami, V. Kumar, and P. Rajaram, Mater. Lett. 128, 425 (2014).
P. Ivanov, E. Llobet, X. Vilanova, J. Brezmes, J. Hubalek, and X. Correig, Sens. Actuators, B 99, 201 (2004).
R. Zhang, T. Zhou, L. Wang, Z. Lou, J. Deng, and T. Zhang, New J. Chem. 40, 6796 (2016).
C.M. Hung, N.D. Hoa, N.V. Duy, N.V. Toan, D.T.T. Le, and N.V. Hieu, J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 1, 45 (2016).
H. Jo, M.J. Kim, H. Choi, Y.-E. Sung, H. Choe, and D.C. Dunand, Metall. Mater. Trans. E 3, 46 (2016).
E.R. Leite, J.A. Cerri, E. Longo, J.A. Varela, and C.A. Paskocima, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 669 (2001).
T. Kimura, S. Inada, and T. Yamaguchi, J. Mater. Sci. 24, 220 (1989).
C.I. Drowley, 1-Application of Materials Characterization Techniques to Silicon Epitaxial Growth (Woburn: Butterworth Heinemann, 1993).
M.K. Shobana, V. Rajendran, K. Jeyasubramanian, and N.S. Kumar, Mater. Lett. 61, 2616 (2007).
M.K. Shobana, W. Nam, and H. Choe, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13, 3535 (2013).
B. Ravel and M. Newville, J. Synchrotron Radiat. 12, 537 (2005).
X.-T. Chen, K.-X. Wang, Y.-B. Zhai, H.-J. Zhang, X.-Y. Wu, X. Wei, and J.-S. Chen, Dalton Trans. 43, 3137 (2014).
G. Leveque, S. Abanades, J.-C. Jumas, and J. Olivier-Fourcade, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53, 5668 (2014).
H. Park, J.H. Um, H. Choi, W.-S. Yoon, Y.-E. Sung, and H. Choe, Appl. Surf. Sci. 399, 132 (2017)
K. Nagashima and Y. Furukawa, J. Cryst. Growth 171, 577 (1997).
G.W. Young, S.H. Davis, and K. Brattkus, J. Cryst. Growth 83, 560 (1987).
S. Deville, E. Saiz, and A.P. Tomsia, Acta Mater. 55, 1965 (2007).
J.H. Um, M. Choi, H. Park, Y.-H. Cho, D.C. Dunand, H. Choe, and Y.-E. Sung, Sci. Rep. 6, 18626 (2016).
Y.-H. Cho, J. Wolfenstine, E. Rangasamy, H. Kim, H. Choe, and J. Sakamoto, J. Mater. Sci. 47, 5970 (2012).
S.I. Bae and S. Baik, J. Mater. Sci. 28, 4197 (1993).
K. Mirabbaszadeh and M. Mehrabian, Phys. Scr. 85, 0357001 (2012).
V. Kruefua, A. Wisitsoraatb, D. Phokharatkulb, A. Tuantranontb, and S. Phanichphant, Sens. Actuators, B 236, 466 (2016).
W. Guo, L. Fu, Y. Zhang, K. Zhang, L.Y. Liang, Z.M. Liu, H.T. Cao, and X.Q. Pan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 042113 (2010).
I. Jimenez, J. Arbiol, G. Dezanneau, A. Cornet, and J.R. Morante, Sens. Actuators B. 93, 475 (2003).
K.S. Choi, S. Park, and S.P. Chang, Sens. Actuators B. 238, 871 (2017).
Y.J. Chen, L. Nie, X.Y. Xur, Y.G. Wang, and T.H. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 083105 (2006).
N. Lavanya, C. Sekar, S. Ficarra, E. Tellone, A. Bonavita, S.G. Leonrdi, and G. Neri, Mater. Sci. Eng., C 62, 53 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nam, K., Kim, HG., Choi, H. et al. Morphology and Gas-Sensing Properties of Tin Oxide Foams with Dual Pore Structure. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 3748–3756 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5242-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5242-6