Abstract
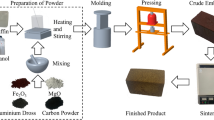
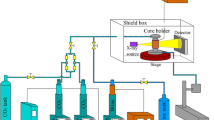
Porous permeable bricks have been widely used in the process of argon bubbling in tundishes due to their gas permeability, stable bubble formation ability and their refractory performance. In this article, the particle packing method was used to prepare porous permeable bricks with different critical sizes of the aggregate particles. Through characterization of the porous permeable brick microstructure, the bubble formation behaviors and bubble size distributions from the porous permeable bricks were analyzed by water model experiments. Correlations of the number of activated pores and the bubble size with the pore structure parameters and pressure gradient were then studied based on a gray system theory approach. The results showed that when the gas flow rate was low, the sizes of the bubbles in a bubble group presented a bimodal or multimodal distribution. As the gas flow rate increased, the pressure gradient inside the porous permeable bricks and the number of activated pores increased. Simultaneously, the size range of the bubbles increased and changed to a normal distribution. Porous permeable bricks with small critical aggregate sizes can produce many small bubbles. Among the parameters considered, the gas permeability directly affected the pressure gradient inside the porous permeable bricks and had the maximum correlation coefficient with the number of activated pores. The pore size distribution was the key factor affecting the size distribution and Sauter mean diameter (SMD) of a bubble group.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.F. Qin, C.G. Cheng, Y. Li, C.M. Zhang, and Y. Jin: Iron Steel., 2016, vol. 54(8), pp. 107–15.
M.J. Zhang, H.Z. Wang, H.Z. Gu, A. Huang, and R.J. Zhu: Steelmaking., 2005, vol. 21(06), pp. 53–6.
Q. Gao, L. Dong, L.Z. Cheng, H.W. Gao, and K.R. Guo: Acta. Metall. Sin., 1987, vol. 01, pp. 144–6.
X.F. Qin, C.G. Chang, Y. Li, C.M. Zhang, J.L. Zhang, and Y. Jin: Metals., 2019, vol. 9(2), pp. 116–31.
A. Cwudzinski: J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall., 2018, vol. 118(5), pp. 545–54.
S. Chatterjee, D.H. Li, and K. Chattopadhyay: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 756–66.
C.E. Aguilar-Rodriguez, J.A. Ramos-Banderas, E. Torres-Alonso, G. Solorio-Diaz, and C.A. Hernandez-Bocanegra: Metallurgist., 2018, vol. 61(11), pp. 1055–66.
A. Cwudzinski: Metall. Res. Technol., 2018, vol. 115(1), pp. 101–8.
S.G. Zheng and M.Y. Zhu: Iron Steel., 2008, vol. 43(6), pp. 25–9.
L.H. Wang, H.G. Lee, and P.C. Hayes: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36(1), pp. 7–16.
H.L. Yang, P. He, and Y.C. Zhai: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54(3), pp. 578–81.
S. Chang, X.K. Cao, C.H. Hsin, Z.S. Zou, M. Isac, and R.I.L. Guthrie: ISIJ Int., 2016, vol. 56(7), pp. 1188–97.
S.C. Koria and S.C. Srivastava: Steel Res. Int., 1999, vol. 70(6), pp. 221–6.
A. Cwudzinski: Steel Res. Int., 2017, vol. 88(9), p. 1600484.
D.F. Chen, X. Xie, M.J. Long, M. Zhang, L.L. Zhang, and Q. Liao: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2014, vol. 45B, pp. 392–8.
T. Maria, P. Arnis, and P. Herbert: Steel Res. Int., 2019, vol. 90, p. 1800639.
H. Gerhard and T. Maria: Steel Res. Int., 2019, vol. 90, p. 1800642.
S. Chang, S. Ge, Z.S. Zong, M.M. Isac, and R.I.L. Guthrie: Steel Res. Int., 2017, vol. 88, p. 1600328.
L.M. Li, Z.Q. Liu, B.K. Li, H. Matsuura, and F. Tsukihashi: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55(7), pp. 1337–46.
R.D. Morales, F.A. Calderon-Hurtado, K. Chattopadhyay, and S.J.G. Guarneros: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2020, vol. 51B, pp. 628–48.
W.J. Liu, J.T.N. Lee, X.P. Guo, A.K. Silaen, and C.Q. Zhou: Steel Res. Int., 2019, vol. 90, p. 1800396.
P. Snabre and F. Magnifotcham: Phys. Condens. Matter., 1998, vol. 4(3), pp. 369–77.
N.Z. Wang, X. Chen, J.Y. Yuan, G.Q. Quan, Y.X. Li, H.W. Zhang, and Y. Liu: Metall Mater. Trans. B., 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 3362–74.
H. Bai and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 1143–59.
J.A. Simmons, J.E. Sprittles, and Y. Shikhmurzaev: J. Mech. Theoret. Appl., 2015, vol. 53, pp. 24–36.
Q.H. Wang, Y.B. Li, S.J. Li, R.F. Xiang, N.N. Xu, and S. OuYang: Mater. Lett., 2017, vol. 197, pp. 48–51.
X. Xiong, Z.F. Wang, X.T. Wang, H. Liu, and Y. Ma: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, vol. 103(3), pp. 2137–45.
K. Koide, S. Kato, Y. Tanaka, and H. Kubota: J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 1968, vol. 1(1), pp. 51–6.
T. Miyahara and A. Tanaka: J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 1997, vol. 30(2), pp. 353–5.
A.A. Mouza, G.K. Dalakoglou, and V.P. Spiros: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2005, vol. 60(5), pp. 1465–75.
N.A. Kazakis, A.A. Mouza, and S.V. Paras: Chem. Eng. J., 2008, vol. 137(2), pp. 265–81.
T. Loimer, G. Machu, and U. Schaflinger: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2004, vol. 59(4), pp. 809–18.
L.F. Zhang, J. Aoki, and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2006, vol. 37B, pp. 361–79.
W. Chen, Y. Ren, L.F. Zhang, and P.R. Scheller: JOM., 2019, vol. 71(3), pp. 1158–68.
J.W.K. Chan and T.K.L. Tong: Mater. Des., 2007, vol. 28(5), pp. 1539–46.
J.W.K. Chan: Int. J. Prod. Res., 2008, vol. 46(11), pp. 2889–912.
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51874215 and 51974213).
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted May 19, 2021; accepted November 22, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, X., Cheng, C., Li, Y. et al. Study on the Initial Formation Behavior of Argon Bubbles in Porous Permeable Brick in Tundishes. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 1224–1235 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02404-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02404-2