Abstract
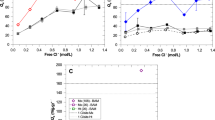
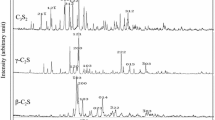
High-basicity sinter is the predominant Fe-bearing material used in blast furnace process in East Asia. The dissolution of SiO2 into molten calcium ferrite influences the assimilation process. In this study, a rotating cylinder method was used to explore the dissolution kinetics of SiO2 into CaO-Fe2O3-SiO2 slag. The influencing factors, including temperature, rotating time and speed, and initial composition of the slag, were considered. Results showed that the dissolution rate increased with increasing rotation speed and temperature, whereas the increase in ω(SiO2) or ω(Fe2O3)/ω(CaO) ratio in the initial slag composition decreased the dissolution rate. The diffusion coefficient and activation energy of SiO2 during the dissolution process ranged from 2.09 × 10−6 to 6.40 × 10−6 cm2 s−1 and 106.62 to 248.20 kJ mol−1, respectively. Concentration difference between the boundary layer and bulk phase was the primary driving force of the dissolution process; however, this process was also influenced by the slag viscosity and ion diffusivity.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
1.P. R. Dawson, J. Ostwald and K. M. Hayes: Trans. Inst. Min. Metall., 1985, vol. 94, pp. C71-C78.
S. J. Zhang and S. T. Wang: IRON AND STEEL, 1992, vol. 27, pp. 7-12.
F. Matsuno and T. Harada: Sumitomo Metals, 1979, vol. 1, pp. 1-12.
X.M. Guo: The generation and mineralogy of calcium ferrite at sinter, 1999, pp. 143, 156.
M. I. Pownceby, T. R. C. Patrick: Eur. J. Mineral., 2000, vol. 12, pp. 455-468.
M. I. Pownceby, J. M. F. Clout: Trans. Instn Min. Metall., 2000, vol. 109, pp. 36-48.
M. I. Pownceby, T. R. C. Patrick: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2002, vol. 33, pp. 79-89.
N. V. Y. Scarlett, I. C. Madsen, I. M. Pownceby, et al.: J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2004, vol. 37, pp. 362-368.
X. Ding, X. M. Guo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 1-9.
X. Ding, X. M. Guo, C. Y. Ma, et al.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 1146-1153.
N. A. S. Webster, M. I. Pownceby, I. C. Madsen, et al.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 2097-2105.
X. Gao and W. Q. Liu: China Steel, 2009, vol. 10, pp. 25-27.
13.K. Inoue, T. Ikeda: J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1982, vol. 68: 2190-2199.
M. F. Jin, G. S. Li, L. W. Dou, C. Shang and F. M. Shen: Iron and Steel, 2009, vol. 44, pp.7-11.
16.N. Taguchi, T. Otomo and K. Tasaka: J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1983, vol. 69: 1409-1416.
B. N. Samaddar, W. D. Kingery, A. R. Cooper and JR.: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1964, vol. 47, pp. 249-254.
T. Maeda, K. Nishioka, K. Nakashima and M. Shimizu: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 2046-2051.
S. L. Xiang, X. W. Lv, B. Yu, C. G. Bai and J. Q. Yin: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 2106-2017.
S. Feichtinger, S. K. Michelic, Y. B. Kang and C. Bernhard: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2014, vol. 97, pp. 316-325.
A. R. Cooper, JR. and W. D. Kingery: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1964, vol. 47, pp. 37-43.
A. H. Bui, H. M. Ha, I. S. Chung and H. G. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp.1856-1863.
K. H. Sandhage and G. J. Yurek: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1990, vol. 73, pp. 3633-3642.
J. H. Liu, F. Verhaeghe, M. X. Guo, B. Blanpain and P. Wollants: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, vol. 90, pp. 3818-3824.
K. Yajima, H. Matsuura and F. Tsukikashi: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 191-194.
X. Yu, R. J. Pomfret and K. S. Coley: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28, pp. 275-279.
27.V. G. Levich: Physicochemical Hydrodynamics, Prentice-Hall, New York, 1962, 60-72
28.X.H. Huang, S. L. Cao (2008) The theory of ironmaking and steelmaking metallurgy, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 211
K. R. Harris: J. Chem. Phys., 2009, vol. 131, pp. 054503.
S. Taira, K. Nakashima and K. Mori: ISIJ Int., 1993, vol. 33, pp. 116-123.
R. D. Shannon: Acta Crystallogr. A, 1976, vol. A32, pp. 751.
Acknowledgment
This study has been financially supported by NSFC (Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51104192 and No. 51522403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 30, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, B., Lv, X., Xiang, S. et al. Dissolution Kinetics of SiO2 into CaO-Fe2O3-SiO2 Slag. Metall Mater Trans B 47, 2063–2071 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0627-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0627-8