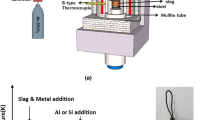
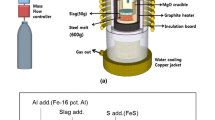
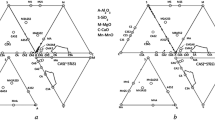
Abstract
Fundamental thermodynamics of the relationship between high-alloyed stainless steel melts (Fe-20 mass pct Cr-13 mass pct Ni-3 mass pct Si) and the inclusions were investigated. The formation mechanism of the inclusions containing the spinel crystals was developed based on the experimental results and from the compositions of the inclusions in the steel samples taken during plant operations. The molar content of alumina in the inclusions was found to be linearly proportional to the increase of aluminum content, indicating that the inclusions could contain alumina even with less than about 200 ppm aluminum in the steel melt, e.g., steel melts that were mainly deoxidized by silicon. Furthermore, the composition of the inclusions is shown to be a function of the activity of the deoxidizers such as aluminum and silicon in the steel melt. From the analysis of the plant samples, it was found that the contents of MgO and Al2O3 in the calcium silicate type inclusions increased continuously as the steel melt transfers from the argon oxygen decarburization (AOD) converter to the tundish. This composition change in the inclusions originated from the reduction of MgO and Al2O3 in the slags or refractories by silicon in the steel melt. Increases of MgO and Al2O3 contents were prominent in tundish samples, and thus, the spinel phase could be crystallized in the calcium silicate inclusion matrix in the tundish; and finally the spinel crystals grew during cooling of the steel melt through the continuous casting (CC) mold and in the slabs. On the other hand, manganese silicate type inclusions containing chromium oxide were observed after tapping of the molten steel to the ladle. The MnO and Cr2O3 in these inclusions was initially reduced by silicon in the steel melt in the ladle treatment (LT) process, followed by further reduction by aluminum through the LT to the CC mold. The fractions of inclusions containing spinel crystals in cast slabs were negligible at the alumina content of less than about 20 mass pct, while they critically increased at alumina contents greater than about 20 mass pct.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
References
A.S. Osio, S. Liu, D.L. Olson: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, vol. 221, pp. 122–33
K.C. Hsieh, S.S. Babu, J.M. Vitek, S.A. David: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, vol. 215, pp. 84–91
C.K. Mukhopadhyay, T. Jayakumar, B. Raj: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, vol. 293, pp. 137–45
E.J. Giordani, V.A. Guimaraes, T.B. Pinto, I. Ferreira: Int. J. Fatigue, 2004, vol. 26, pp. 1129–36
B. Harkness and D. Dyson: Proc. METEC Congr. 94 and 2nd Eur. Continuous Casting Conf., Düsseldorf, June 20–22, 1994, VDEh, Düsseldorf, 1994, pp. 70–77
G.J.W. Kor: Proc. 1st Int. Calcium Treatment Symp., Glasgow, June 30, 1988, IoM, London, 1988, pp. 39–44
J.W. Kim, S.K. Kim, D.S. Kim, Y.D. Lee: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp. S140–S143
M. Hojo, R. Nakao, T. Umezaki, H. Kawai, S. Tanaka, S. Fukumoto: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp. S128–S131
Y. Ehara, S. Nakamura, and Y. Habara: Proc. 4th Eur. Stainless Steel Science and Market Congr., Paris, June 10–13, 2002, ATS, Paris, 2002, vol. 2, pp. 176–81
J.H. Park: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2006, vol. 89, pp. 608–15
J.H. Park: Calphad, 2007, available online 19 June 2007
J.H. Park, Y.B. Kang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, vol. 37B, pp. 791–97
J.H. Park, D.J. Min: Mater. Trans., 2006, vol. 47, pp. 2038–43
H. Itoh, M. Hino, S. Ban-ya: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1997, vol. 83, pp. 773–78
Steelmaking Data Sourcebook, The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, The 19th Committee of Steelmaking, Gordon and Breach Science Publications, New York, NY, 1988, pp. 273–325
K. Suzuki, S. Ban-ya, M. Hino: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 813–17
K. Suzuki, S. Ban-ya, M. Hino: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 2002, vol. 42, pp. 146–49
H. Ohta, H. Suito: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 1301–08
Z. Hong, X. Wu, C. Kun: Steel Res., 1995, vol. 66, pp. 72–76
M. Kowalski, P.J. Spencer, D. Neuschutz: Slag Atlas, 2nd ed., Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Düsseldorf, 1995, pp. 99–154
H. Itoh, M. Hino, S. Ban-ya: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1997, vol. 83, pp. 623–28
O. Kubaschewski: High Temp. High Press., 1972, vol. 4, pp. 1–12
H. Todoroki, K. Mizuno, M. Noda, and T. Tohge: Proc. 84th ISS Steelmaking Conf., Baltimore, MD, Mar. 25–28, 2001, ISS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 2001, pp. 331–41
K. Takahashi, M. Hino: High Temp. Mater. Proc., 2000, vol. 19, pp. 1–10
T. Itoh, T. Nagasaka, M. Hino: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 1051–58
J.H. Park: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, available online 12 March 2007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 3, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J. Formation Mechanism of Spinel-Type Inclusions in High-Alloyed Stainless Steel Melts. Metall Mater Trans B 38, 657–663 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-007-9066-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-007-9066-x