Abstract
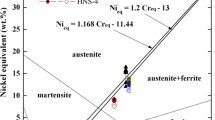
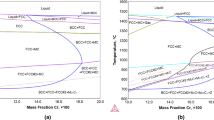
Due to the widespread use and familiarity of austenitic stainless steels (SS) in many industries these alloys are often the first materials used when adapting new processing techniques. The rapid cooling and solidification rates that occur during fusion based additive manufacturing processes like powder bed fusion cause a fundamental shift in the solidification behavior of the material. While the effects that Cr and Ni have on the microstructure have been fairly well documented across a range of solidification conditions, the impact of alloying elements like Mo are not as well understood at rapid solidification rates. For this study, four custom SS alloy feedstocks were made with targeted modification of the Cr and Mo concentrations to maintain a constant Cr/Nieq ratio of ~ 1.7. Two-piston splat quenching was used to produce rapidly solidified samples and the solidification mode, phase, and cell size were investigated. Solidification rates were estimated to be between 0.4 and 1.5 m/s. A comparison of the microsegregation and partitioning behavior of Cr, Ni and Mo in ferrite solidified material was also performed for the different alloy compositions. Variations of the Mo concentration between each feedstock showed no measurable influence on the solidification/cooling rates, solidification morphology, or the partitioning of Mo. However, higher concentrations of Mo were found to significantly increase the amount of ferrite phase in the microstructure by suppressing the ferrite to austenite massive transformation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM: in ASTM A240 / A240M-20a Standard Specification for Chromium and Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure Vessels and for General Applications, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2020, p. 13.
AISI: Design Guidelines for the Selection and Use of Stainless Steel, Specialty Steel Industry of the United States, Pennsylvania, 1993.
A. Pardo, M.C. Merino, A.E. Coy, F. Viejo, R. Arrabal, and E. Matykina: Corros. Sci., 2008, vol. 50, pp. 780–94.
T.D. Anderson, M.J. Perricone, J.N. DuPont, and A.R. Marder: Weld. J., 2007, vol. 86, pp. 281–92.
D. Kong, C. Dong, X. Ni, and X. Li: npj Mater Degradation, 2019, vol. 3, pp. 1–4.
J.N. DuPont: in ASM Handbook Welding Fundamentals and Processes, T. Lienert, T. Siewert, S. Babu, and V. Acoff, eds., ASM International, Almere, Netherlands, 2011, pp. 96–114.
D.M. Wilson: Master of Science, Colorado School of Mines, 2019.
W.M. Tucho, V.H. Lysne, H. Austbø, A. Sjolyst-Kverneland, and V. Hansen: J. Alloys Compd., 2018, vol. 740, pp. 910–25.
S. Cheruvathur, E.A. Lass, and C.E. Campbell: JOM, 2015, vol. 68, pp. 930–42.
O. Andreau, I. Koutiri, P. Peyre, J.-D. Penot, N. Saintier, E. Pessard, T. De Terris, C. Dupuy, and T. Baudin: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2019, vol. 264, pp. 21–31.
B.D.M.S. Pham and P.A. Hooper: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, vol. 704, pp. 102–11.
P. Lu, Z. Cheng-Lin, W. Liang, L. Tong, and L. Xiao-Cheng: Mater. Res. Express, 2020, vol. 6, pp. 1–8.
S. Hossein Nedjad, M. Yildiz, and A. Saboori: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2022, vol. 28, pp. 1–7.
T. Patterson, J. Lippold, and B. Panton: Weld. World, 2022, vol. 66, pp. 1521–34.
A.J. Godfrey: Master of Science, University of Tennessee, 2021.
B. Lane, J. Heigel, R. Ricker, I. Zhirnov, V. Khromschenko, J. Weaver, T. Phan, M. Stoudt, S. Mekhontsev, and L. Levine: Integr. Mater. Manuf. Innov., 2020, vol. 9, pp. 16–30.
W. Kurz and R. Trivedi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1994, vol. 179(180), pp. 46–51.
T. Pinomaa, M. Lindroos, M. Walbrühl, N. Provatas, and A. Laukkanen: Acta Mater., 2020, vol. 184, pp. 1–6.
S. Gao, Z. Hu, M. Duchamp, P.S.S.R. Krishnan, S. Tekumalla, X. Song, and M. Seita: Acta Mater., 2020, vol. 200, pp. 366–77.
P. Deng, H. Yin, M. Song, D. Li, Y. Zheng, B.C. Prorok, and X. Lou: JOM, 2020, vol. 72, pp. 4232–43.
T. Voisin, J. McKeown, J. Ye, N. Calta, Z. Li, T. Roehling, P. Depond, M. Santala, W. Chen, M. Matthews, and Y.M. Wang, SEM 2018 (Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 2018).
S. Dépinoy: Materialia, 2022, vol. 24, pp. 1–4.
J.C. Lippold: Weld. Res. Suppl., 1994, vol. 73, pp. 129–40.
J.W. Elmer and T.W. Eagar: Weld. Res. Suppl., 1990, vol. 04, pp. 141–50.
D. Stefanescu: Science and Engineering of Casting Solidification, Springer, New York, 2002, p. 354.
J.W. Elmer: Doctor of Science in Metallurgy, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1988.
N.L. Chabot, E.A. Wollack, W.F. McDonough, R.D. Ash, and S.A. Saslow: Meteorit. Planet. Sci., 2017, vol. 52, pp. 1133–45.
T. DebRoy, H.L. Wei, J.S. Zuback, T. Mukherjee, J.W. Elmer, J.O. Milewski, A.M. Beese, A. Wilson-Heid, A. De, and W. Zhang: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2018, vol. 92, pp. 112–24.
S. Katayama and A. Matsunawa: in International Congress on Applications of Lasers & Electro-Optics, 1984, pp. 60–67.
Z.A. Hasenbusch, J. M. Roze, S. Morales, G. Harvill, M. Canulette, A. Deal, B. Brown, D. Wilson, L. Nastac, and L.N. Brewer, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2023.
J.A. Brooks and A.W. Thompson: Int. Mater. Rev., 1991, vol. 36, pp. 16–44.
J.M. Vitek, A. Dasgupta, and S.A. David: Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14, pp. 1833–42.
M.J. Perricone, J.N. Dupont, T.D. Anderson, C.V. Robino, and J.R. Michael: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2010, vol. 42A, pp. 700–16.
S. Kou: Welding Metallurgy, 2nd ed., Wiley, 2002, pp. 145–67, 243–49.
P. Bajaj, A. Hariharan, A. Kini, P. Kürnsteiner, D. Raabe, and E.A. Jägle: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, vol. 772, pp. 1–25.
F. Yan, W. Xiong, E. Faierson, and G.B. Olson: Scripta Mater., 2018, vol. 155, pp. 104–08.
T.Z. Kattamis, W.F. Brower, and R. Mehrabian: J. Cryst. Growth, 1973, vol. 19, pp. 229–36.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Honeywell Federal Manufacturing & Technologies under Contract No. DE-NA0002839 with the U.S. Department of Energy. The United States Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a nonexclusive, paid up, irrevocable, world-wide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for the United States Government purposes. No resources from Woodward Inc. or Chevron were used to perform the work reported or for the creation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hasenbusch, Z.A., Harvill, G., Ziska, K. et al. Influence of Molybdenum on Rapid Solidification Microstructure and Microsegregation in Primary Ferrite Solidified Stainless Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 54, 4834–4849 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07206-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07206-6