Abstract
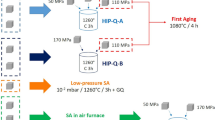
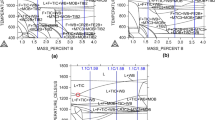
A series of high-nitrogen stainless steels (HNS) containing δ-ferrite, which often retained in HNS, were studied to establish the relationship between composition and microstructure. Both ferrite and nitrogen depletions were found in the center regions of cast ingots, and the depletion of nitrogen in that area was found to be the main reason for the existence of δ-ferrite. Because of the existence of heterogeneity, the variation of microstructure with nitrogen content was detected. Hence, the critical contents of nitrogen (CCN) for the fully austenitic HNS were obtained. Then the effects of elements such as N, Cr, Mn, and Mo on austenite stability were investigated via thermodynamic calculations. The CCN of HNS alloys were also obtained by calculations. Comparing the CCN obtained from experiment and calculation, it was found that the forged microstructure of the HNS was close to the thermodynamic equilibrium. To elucidate the above relationship, by regression analysis using calculated thermodynamic data, nitrogen equivalent and a new constitution diagram were proposed. The constitution diagram accurately distinguishes the austenitic single-phase region and the austenite + ferrite dual-phase region. The nitrogen equivalent and the new constitution diagram can be used for alloying design and microstructural prediction in HNS. According to the nitrogen equivalent, the ferrite stabilizing ability of Mo is weaker than Cr, and with Mn content increases, Mn behaves as a weak austenite stabilizer first and then as a ferrite stabilizer.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.O. Speidel: High Nitrogen Steel 88, J. Foct, A. Hendry, ed., The Institute of Metals, London, 1989, pp 92-96.
M.O. Speidel and H.J. Speidel: High Nitrogen Steel 09, A.G. Svyazhin, V.G. Prokoshkina, K.L. Kossyrev, ed., Misis, Moscow, 2009, pp 121-128.
U.K. Mudali and B. Raj: High nitrogen steels and stainless steels,1st ed., p. 182, Alpha Science International, Pangbourne, UK, 2004.
V.G. Gavriljuk and H. Berns: High Nitrogen Steels, 1st ed., Springer, Berlin, 1999, p. 133.
K.H. Lo, C.H. Shek, and J.K.L. Lai: Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2009, vol. 65, pp. 39-104.
J.W. Simmons: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, vol. 207, pp. 159-169.
P.J. Uggowitzer, R. Magdowski and M.O. Speidel: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp 901-908.
K. Yang and Y.B. Ren: Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2010, vol. 11, pp. 1-13.
J. Menzel, W. Kirschner and G. Stein: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp 893-900.
M. Sumita, T. Hanawa and S.H. Teoh: Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2004, vol. 24, pp. 753-760.
M. Niinomi, M. Nakai and J. Hieda: Acta Biomater., 2012, vol. 8, pp. 3888-3903.
M. Fini, N. Nicoli Aldini, P. Torricelli, G. Giavaresi, V. Borsari, H. Lenger, J. Bernauer, R. Giardino, R. Chiesa and A. Cigada: Biomaterials, 2003, vol. 24, pp. 4929-4939.
M. Talha, C.K. Behera and O.P. Sinha: Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2013, vol. 33(7), pp. 3563-3575.
Y. Ustinovshikov, A. Ruts, O. Bannykh and V. Blinov: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 1119-1125.
T.H. Lee, S.J. Kim and S. Takaki: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37, pp. 3445-3454.
T.H. Lee, H.Y. Ha, B. Hwang and S.J. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, vol. 43, pp. 822-832.
Di Schino, M.G. Mecozzi, M. Barteri and J. M. Kenny: J. Mater. Sci., 2000, vol. 35, pp. 375-380.
D. Baldissin and L. Battezzati: Scr. Mater., 2006, vol. 55, pp. 839-842.
A.L Schaeffler: Met. Prog., 1949, vol. 56, pp. 680-680B.
R.L. Klueh, P.J. Maziasz and E.H. Lee: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1988, vol. 102, pp. 115-124.
C.J. Long and W.T. DeLong: Weld. J., 1973, vol. 52, p. 281.
F.C. Hull: Weld. J., 1973, vol. 52, pp. 193-203.
M. Onozuka, T. Saida, S. Hirai, M. Kusuhashi, I. Sato and T. Hatakeyama: J. Nucl. Mater., 1998, vol. 255, pp. 128-138.
J. Glownia, B. Kalandyk and K. Hübner: Mater. Charact., 2001, vol. 47, pp. 149-155.
M.O. Speidel and P.J. Uggowitzer: Proc. Materials Week 92, R.A Lula, ed., ASM Int., Chicago, 1992, pp 135-142.
M.O. Speidel and H.J. Speidel: High Nitrogen Steel 06, H. Dong, J. Su, and M.O. Speidel, eds., Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2006, pp. 21–29.
J.O. Andersson, T. Helander, L. Höglund, P. Shi and B. Sundman: Calphad, 2002, vol. 26, pp. 273-312.
T.H Lee, C.S. Oh, C.G. Lee, S.J. Kim and S. Takaki: Scr. Mater., 2004, vol. 50, pp. 1325-1328.
C.M. Hong, J. Shi, L.Y. Sheng, W.Q. Cao, W.J. Hui and H. Dong: J. Mater. Sci., 2011, vol. 46, pp. 5097-5103.
D. Heger and T.V. Duong: Defect Diffus. Forum, 1997, vol. 143, pp. 443-448
Arcos Welding Products, Arcos Corporation, Philadelphia, 1975, p. 29.
G. Stein and I. Hucklenbroich: Mater. Manuf. Processes, 2004, vol. 19, pp. 7-17.
H. Berns, V.G. Gavriljuk, and S. Riedner: High Interstitial Stainless Austenitic Steels, 1st ed., Springer, Berlin, 2013, p. 2.
H.O. Andrén, U. Rolander and G. Wahlberg: Le J. Phys. (Paris), 1988, vol. 49, pp. 305-310.
Y.P. Ren, C.F. Li, G.W. Qin, W.L. Pei, H.X. Li and S.M. Hao: J. Mater. Metall., 2011, vol. 10, pp. 129-131.
K.L. Chao, H.Y. Liao, J.J. Shyue and S.S. Lian: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45B, pp. 381-391.
A. Sato, E. Chishima, K. Soma, T. Mori: Acta Mater., 1982, vol. 30(6), pp. 1177-1183.
S.R. Chen, H.A. Davies and W.M. Rainforth: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47(18), pp. 4555-4569.
V. Raghavan: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 237-242.
N. Suutala: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 2121-2130.
L. Weber and P.J. Uggowitzer: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 242, pp. 222-229.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program (2012CB619101) and the National Science & Technology Supporting Program (2012BAI18B01). R.D.K. Misra gratefully acknowledges support from the Center for Structural and Functional Materials, University of Louisiana at Lafayette, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Manuscript submitted September 17, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Ren, Y., Yao, C. et al. Residual Ferrite and Relationship Between Composition and Microstructure in High-Nitrogen Austenitic Stainless Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 5537–5545 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3160-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3160-5