Abstract
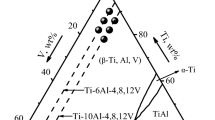
Controlling the microstructure evolution of Ti-(47, 50, 54) at. pct Al alloys by combining the effects of high undercooling and large cooling rate has been investigated. The calculated undercooling and cooling rates of the three component alloy droplets increase as power functions with the decreasing alloy droplet diameter D. With decreasing D, the microstructure of Ti-47 at. pct Al alloy evolves from dendritic dendrites to equiaxed dendrites, and the main microstructure of Ti-50 at. pct Al alloy transforms from a lamellar microstructure to a non-lamellar microstructure, while that of Ti-54 at. pct Al alloy appears as an interweaving microstructure. The α2 phase with a superlattice structure and the α2n phase with a nonsuperlattice structure are confirmed by transmission electron microscopy, and the large difference of Al contents leads to formation of the α2 phase and the α2n phase. Atomic images show that the interface of the α2n phase and γ phase is coherent. The α2n phase precipitates from the γ phase during cooling. The combined effects of high undercooling and large cooling rate suppress the transformation of the α phase to (α2 + γ) phases. The Young’s modulus first increases and then decreases with decreasing D, while the nanohardness is controlled by the combined factors of the microstructure morphology, phase composition, phase ratio, and grain refinement. As for the microhardness, grain refinement dominates the hardening of the Ti-54 at. pct Al alloys, while the combined factors dominate the hardening of Ti-(47, 50) at. pct Al alloys.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. J. A. Lemberg and R. O. Ritchie: Adv. Mater. 24 (2012) 3445-3460.
2. G. Yang, H.C. Kou, J.R. Yang, J.S. Li, H.Z. Fu: Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 112, pp. 121-131.
3. Y. Garip, O. Ozdemir: Meter. Mater. Trans. A., 2018, vol. 49A, pp: 2455-62.
4. M. Thomas, T. Malot, P. Aubry: Meter. Mater. Trans. A., 2017, vol. 48A, pp: 3143-58.
5. H. Clemens and S. Mayer: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2013, vol. 15, pp. 191-215.
6. G. Chen, Y. Peng, G. Zheng, Z. Qi, M. Wang: Nature Materials., 2016, vol. 15, pp. 876-881.
7. H. Zhu, K. Maruyama and J. Matsuda: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, vol 88, pp. 131908-910.
8. E. Schwaighofer, H. Clemens, J. Lindemann, S. Andreas and M. Svea: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2014, vol. 614, pp. 297-310.
Munoz-Moreno R, Ruiz-Navas EM, Srinivasarao B, Torralba JM (2014) J Mater Sci Technol 30:1145-1154
10. T. Zofia, B. Guillaume, F. Gilbert and M. Jean-Philippe: Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 135, pp. 1-13.
11. J. Guyon, A. Hazotte and E. Bouzy: J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, vol. 656, pp. 667–675.
12. M. Seifi, A.A. Salem, D.P. Stako, U. Ackelid, S.L. Semiatin and J.J. Lewandowski: J. Alloy. Compond., 2017, vol. 729, pp. 1118-35.
13. X.F. Ding, J.P. Lin, L.Q. Zhang, Y.Q. Su and G.L. Chen: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 498-506.
14. K. Maruyama, M. Yamaguchi, G. Suzuki, H.L. Zhu, H.Y. Kim and M.H. Yoo: Acta Mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 5185-94.
15. F.T. Kong, N. Cui and Y.Y. Chen: Meter. Mater. Trans. A., 2018, vol. 49A, pp. 5574-84.
16. K.K. Ma, H.M. Wen, T. Hu, T.D. Topping, D. Isheim, D.N. Seidman, E.J. Lavernia and J.M. Schoenung: Acta Mater., 2014, vol. 62, pp. 141-155.
17. Q. Wang, R.R. Chen and X. Gong: Meter. Mater. Trans. A., 2018, vol. 49A, pp. 4555-64.
18. P. Erdely, P. Staron, A. Stark: Acta. Mater., 2019, vol. 164, pp: 110-121.
19. X. Shi, S.C. Duan, W.S. Yang, S. Wen: Meter. Mater. Trans. B., 2018, vol, 49B, pp: 1883-97.
20. H. Jiang, K. Zhang, X.J. Hao, H. Saage, N.Wain, D. Hu, M.H. Loretto and X. Wu, Intermetallics., 2010, vol. 18, pp. 938-944.
21. J.R. Yang, X.Y. Wang, B. Cao, Y.L. Wu, K.R. Zhang and R. Hu: Meter. Mater. Trans. A., 2017, vol. 48A, pp. 5095-5105.
22. P. Lü and H.P. Wang: Scripta. Mater., 2017, vol. 137, pp. 31-35.
23. D. Hu and R.R. Botten: Intermetallics., 2002, vol. 10, pp. 701-715.
H.P. Wang, P. Lü, X. Cai, B. Zhai, J.F. Zhao, and B. Wei: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.128660. Accessed 12 November 2019.
25. R. Bohn, T. Klassen and R. Bormann: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 299-311.
26. W.P. Liu and J.N. Dupont: Meter. Mater. Trans. A., 2004, vol. 35, pp. 1133-40.
27. R. Lengsdorf, D. Holland-Moritz and D.M. Herlach: Scripta. Mater., 2010, vol. 62, pp. 365-367.
28. B.J. Park, H.J. Chang, D.H. Kim and W.T. Kim: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, vol. 85, pp. 6353-55.
29. N. Yan, Z.Y. Hong, D.L. Geng and B. Wei: Appl. Phys. A., 2015, vol. 120, pp. 207-213.
30. Y.H. Wu, J. Chang, W.L. Wang, L. Hu, S.J. Yang and B. Wei: Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 129, pp. 366-377.
31. J.C. Schuster and M.Palm: Journal of phase equilibria & diffusion., 2006, vol. 27, pp. 255-277.
32. E.S. Lee and S. Ahn: Acta metall. Mater. 42 (1994) 3231-3243.
33. M.X. Li, H.P. Wang, N. Yan, B. Wei: Sci. China. Technol. Sc., 2018, vol. 61, pp. 1021-1030.
34. P.S. Grant, B. Cantor, L. Katgerman: Acta metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, pp. 3097-3107.
Acknowledgments
The authors are especially grateful to Professor B. Wei for the experimental support. They also thank Dr. P. Lü, Mr. Q. Wang, Mr. J.F. Zhao, and Mr. D.D. Zuo for their help with the experiments or discussion. This work is financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51734008, 51522102, and 51474175) and supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFB2001800) and the Shaanxi Key Industry Chain Program (Grant No. 2019ZDLGY05-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted October 14, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Z.C., Wang, H.P. Combined Effects of High Undercooling and Large Cooling Rate on the Microstructure Evolution and Hardening Mechanism of Rapidly Solidified Ti-Al Alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 51, 1242–1253 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05616-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05616-z