Abstract
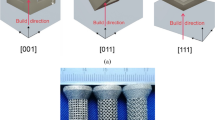
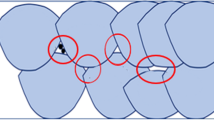
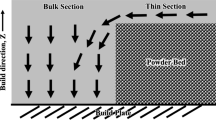
In the electron beam powder bed fusion (EB-PBF) process, a substantial number of high-gamma prime Ni-based superalloys are considered as non-printable due to a high propensity to form cracks. In this research, we focused on computational modeling framework to predict solidification-related cracking phenomena in EB-PBF processes. The cracking analysis was performed on cylindrical overhang structures where the cracks are observed only on one side of the part. Comprehensive microstructural characterization correlated the cracking tendency to low-melting point liquid-film formation along columnar grain boundaries with high misorientation angles due to partitioning of alloying elements. Uncoupled numerical thermal and mechanical models were used to rationalize the relationship between process parameters, build geometry, and cracking. The simulations showed asymmetric temperature distributions and associated asymmetric tensile thermal stresses over a cross section due to differences in section modulus and periodic changes in beam scanning directions. The results provide a potential pathway based on spatially varying beam scanning strategies to reduce the cracking tendency during additive manufacturing of complex geometries on the overhang structure in high-gamma prime nickel-based superalloys.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Identification of the powder producers should not be considered as the endorsement.
References
M. Seifi, A. Salem, J. Beuth, O. Harrysson and J.J. Lewandowski: JOM, 2016, vol. 68, pp. 747-764.
N.J. Harrison, I. Todd and K. Mumtaz: Acta Mater., 2015, vol. 94, pp. 59-68.
M. Ramsperger, R.F. Singer and C. Körner: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 1469-1480.
R. Baldan, P.R.S.A. e Silva, C.A. Nunes and G.C. Coelho: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, vol. 22, pp. 2337-2342.
A. Basak and S. Das: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 705, pp. 806-816.
L.N. Carter, M.M. Attallah and R.C. Reed: in Superalloys 2012, Roger C. Reed Eric S. Huron, Mark C. Hardy, Michael J. Mills, Rick E. Montero, Pedro D. Portella and Jack Telesman, eds., The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2012, pp. 577–86.
E. Chauvet, P. Kontis, E.A. Jägle, B. Gault, D. Raabe, J.-J. Blandin, R. Dendievel, B. Vayre, S. Abed and G. Martin: Acta Mater., 2018, vol. 142, pp. 82-94.
L.N. Carter, C. Martin, P.J. Withers and M.M. Attallah: J. Alloys Compd., 2014, vol. 615, pp. 338-347.
D. Gu, W. Meiners, K. Wissenbach and R. Poprawe: Int. Mater. Rev., 2012, vol. 57, pp. 133-164.
J.C. Lippold, S.D. Kiser and J.N. DuPont: Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of Nickel-Base Alloys. Wiley, Hoboken, 2011.
S. Kou: Welding Metallurgy. Wiley, Hoboken 2003.
J. Zhang: In Superalloys 2004, T.M. Pollock K.A. Green, H. Harada, T.E. Howson, R.C. Reed, J.J. Schirra, and S, Walston, eds., The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2004, pp. 727–33.
J.-W. Park, J. Vitek, S. Babu and S. David: Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 2004, vol. 9, pp. 472-482.
C. Cross: On the Origin of Weld Solidification Cracking, In Hot Cracking Phenomena in Welds. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005, pp. 3-18.
W. Savage and A. Aronson: Weld J, 1966, vol. 45, pp. 85s-89s.
S. Kou: JOM, 2003, vol. 55, pp. 37-42.
N. Wang, S. Mokadem, M. Rappaz and W. Kurz: Acta Mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 3173-3182.
T.P. Mitchell, R. Sanderson and B.G. Dance: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vol. 539, pp. 3985-3990.
L. Ma and H. Bin: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2007, vol. 34, pp. 898-903.
S. Catchpole-Smith, N. Aboulkhair, L. Parry, C. Tuck, I. Ashcroft and A. Clare: Addit. Manuf., 2017, vol. 15, pp. 113-122.
B. Cheng, S. Shrestha and K. Chou: Addit. Manuf., 2016, vol. 12, pp. 240-251.
M.F. Zaeh and M. Kahnert: Prod. Eng., 2009, vol. 3, pp. 217-224.
M.M. Kirka, Y. Lee, D.A. Greeley, A. Okello, M.J. Goin, M.T. Pearce and R.R. Dehoff: JOM, 2017, vol. 69, pp. 523-531.
Y.S. Lee, M.M. Kirka, N. Raghavan and R.R. Dehoff: in Solid Free. Fabr.Symp., University of Texas at Austin, 2017, pp. 1005–17.
A.E. Patterson, S.L. Messimer and P.A. Farrington: Technologies, 2017, vol. 5, p. 15.
M. Thomas, G.J. Baxter and I. Todd: Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 108, pp. 26-35.
P. Delroisse, P.J. Jacques, E. Maire, O. Rigo and A. Simar: Scr. Mater., 2017, vol. 141, pp. 32-35.
N. Sridharan, M. Norfolk and S.S. Babu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 2517-2528.
N. Raghavan, R. Dehoff, S. Pannala, S. Simunovic, M. Kirka, J. Turner, N. Carlson and S.S. Babu: Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 112, pp. 303-314.
Y. Lee and W. Zhang: Addit. Manuf., 2016, vol. 12, pp. 178-188.
W. Yan, W. Ge, Y. Qian, S. Lin, B. Zhou, W.K. Liu, F. Lin and G.J. Wagner: Acta Materialia, 2017, vol. 134, pp. 324-333.
S.A. Khairallah, A.T. Anderson, A. Rubenchik and W.E. King: Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 108, pp. 36-45.
C. Körner, E. Attar and P. Heinl: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2011, vol. 211, pp. 978-987.
A. Klassen, V.E. Forster, V. Juechter and C. Körner: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2017, vol. 247, pp. 280-288.
D. Riedlbauer, T. Scharowsky, R.F. Singer, P. Steinmann, C. Körner and J. Mergheim: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2017, vol. 88, pp. 1309-1317.
J.B. M. S. Alnaes, J. Hake, A. Johansson, A.L. B. Kehlet, C. Richardson, J. Ring, M. E. Rognes, G.N. Wells: The FEniCS Project Version 1.5, Archive of Numerical Software, 2015, vol. 3, pp. 9–23.
A. Logg and G.N. Wells: ACM Trans. Math. Softw., 2010, vol. 37, p. 20.
B.E. Abali: Computational Reality. 1 ed. Springer, Singapore, 2017.
K. Abderrazak, S. Bannour, H. Mhiri, G. Lepalec and M. Autric: Comput. Mater. Sci, 2009, vol. 44, pp. 858-866.
N. Saunders, U. Guo, X. Li, A. Miodownik and J.-P. Schillé: JOM, 2003, vol. 55, pp. 60-65.
ABAQUS Documentation, Dassault Systémes Simulia Corp, Providence, RI, USA, 2011.
O. Muránsky, C.J. Hamelin, M.C. Smith, P.J. Bendeich and L. Edwards: Comput. Mater. Sci, 2012, vol. 54, pp. 125-134.
M. Smith and A. Smith: Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip., 2009, vol. 86, pp. 79-95.
L. Wang, N. Wang and N. Provatas: Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 126, pp. 302-312.
Z. Feng, S. David, T. Zacharia and C. Tsai: Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 1997, vol. 2, pp. 11-19.
Acknowledgments
The research was sponsored by the US Department of Energy, Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, Advanced Manufacturing Office under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725 with UT-Battelle, LLC. The authors thank Dr. Alex Plotkowski of ORNL for constructive criticism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Notice of Copyright. This manuscript has been authored by UT-Battelle, LLC under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725 with the U.S. Department of Energy. The United States Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a non-exclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, world-wide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for United States Government purposes. The Department of Energy will provide public access to these results of federally sponsored research in accordance with the DOE Public Access Plan (http://energy.gov/downloads/doe-public-access-plan).
Manuscript submitted February 7, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.S., Kirka, M.M., Kim, S. et al. Asymmetric Cracking in Mar-M247 Alloy Builds During Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing. Metall Mater Trans A 49, 5065–5079 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4788-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4788-8