Abstract
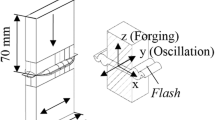
Linear friction welding allows solid-state joining of near-beta (β) titanium alloy Ti-5553 (Ti-5Al-5V-5Mo-3Cr). In the as-welded condition, the weld zone (WZ) exhibits β grain refinement and marked softening as compared with Ti-5553 in the solution heat treated and aged condition. The softening of the weldment is attributed to the depletion of the strengthening alpha (α) phase in the WZ and the adjacent thermo-mechanically affected zone (TMAZ). Specifically, in near-β titanium alloys, the strength of the material mainly depends on the shape, size, distribution, and fraction of the primary α and other decomposition products of the β phase. Hence, a combination of pre- and post-weld heat treatments were applied to determine the conditions that allow mitigating the α phase depletion in the WZ and TMAZ of the welds. The mechanical response of the welded samples to the heat treatments was determined by performing microhardness measurements and tensile testing at room temperature with an automated 3D deformation measurement system. It was found that though the joint efficiency in the as-welded condition was high (96 pct), strain localization and failure occurred in the TMAZ. The application of post-weld solution heat treatment with aging was effective in restoring α, increasing the joint efficiency (97 to 99 pct) and inducing strain localization and failure in the parent material region.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyer RR, Briggs RD: J Mater Eng Perform 2005; 14: pp. 681-5.
Jones NG, Dashwood RJ, Dye D, Jackson M: Mater Sci Eng 2008; A490: pp. 369-77.
Clement N, Lenain A, Jacques PJ. JOM 2007; 59: pp. 50-3.
Veeck S, Lee D, Boyer R, Briggs R. J Adv Mater 2005; 37: p. 40.
S. Nag, R. Banerjee, R. Srinivasan. J.Y. Hwang, M. Harper, and H.L. Fraser: Acta Mater., 2009; vol. 57, pp. 2136–47.
B.A. Welk: M.Sc. Thesis, The Ohio State University, 2010.
Fanning JC: J Mater Eng Perform 2005; 14: pp. 788-92.
Dalgaard E, Wanjara P, Gholipour J, Cao X, Jonas JJ. Acta Mater 2012; 60: pp. 770-80.
R. Panza-Giosa: Ph.D. Thesis, McMaster University, Canada, 2006.
Donachie MJ. Titanium: A Technical Guide, second ed. Materials Park: ASM International; 1998.
W.A. Baeslack III, J.R. Davis, and C.E. Cross: in ASM Handbook on Welding, Brazing and Soldering, vol. 6, 10th ed., S.A. David and J.M. Vitek, eds., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1994.
Shariff T, Cao X, Chromik RR, Baradari JG, Wanjara P, Cuddy J, Birur A. CMQ 2011; 50: pp. 263-72.
Shariff T, Cao X, Chromik RR, Baradari JG, Wanjara P, Cuddy J, Birur A. J Mater Sci 2012; 47: pp. 866-75.
Shariff T, Cao X, Chromik RR, Baradari JG, Wanjara P, Cuddy J, Birur A. Mater Sci Forum 2012; 706–9: pp. 2931-36.
Mitchell R, Short AB, Pasang T, Littlefair G. Adv Mat Res 2011; 275: pp. 81-4.
T. Shariff: M. Eng. Thesis, McGill University, Canada, 2010.
H. Wilhelm, R. Furlan, and K.C. Moloney: in Titanium ‘95: Science and Technology, P.A. Blenkinsop , W.J. Evans, and H.M. Flower, eds., Proceedings of 8th World Conference on Titanium, Institute of Materials, London, 1996. pp. 620–27.
Bhamji I, Preuss M, Threadgill PL, Addison AC. Mater Sci Technol 2011; 27: pp. 2-12.
Frankel P, Preuss M, Steuwer A, Withers PJ, Bray S. Mater Sci Technol 2009; 25: pp. 640-50.
Dalgaard E, Wanjara P, Gholipour J, Jonas JJ. Mater Sci Forum 2012; 706–9: pp. 211-6.
Dalgaard E, Wanjara P, Gholipour J, Jonas JJ. CMQ 2012; 51: pp. 269-76.
Nicholas ED, Thomas, WM. Int J Mater Prod Tec 1998; 13: pp. 45-55.
Vairis A, Frost M. Wear 1998; 217: pp.117-31.
Vairis A, Frost M. Mater Sci Eng 1999; A271: pp. 477-84.
Vairis A, Frost M. Mater Sci Eng 2000; A292: pp. 8-17.
Wanjara P, Jahazi M. Metall Mater Trans 2005; 36A: pp. 2149-64.
Romero J, Attallah MM, Preuss M, Karadge M, Bray SE. Acta Mater 2009; 57: pp. 5582-92.
Karadge M, Preuss M, Lovell C, Withers PJ, Bray S. Mater Sci Eng 2007; A459: pp. 182-91.
Li WY, Ma TJ, Zhang Y, Xu QZ, Li JL, Yang SQ. Adv Eng Mater 2008; 10: pp. 89-92.
Dalgaard E, Coghe F, Rabet L, Jahazi M, Wanjara P, Jonas JJ. Adv Mat Res 2009; 89-91: pp. 124-9.
Li WY, Ma TJ, Li JL. Mater Des 2010; 31: pp. 1497-507.
Ma T, Chen T, Li WY, Wang S, Yang S. Mater Charact 2011; 62: pp. 130-5.
Nyakana S, Fanning JC, Boyer R. J Mater Eng Perform 2007; 14: pp. 799-811.
E. Dalgaard: Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University, Canada, 2011.
Jones NG, Dashwood RJ, Dye D, Jackson M. Metall Mater Trans 2009; 40A: pp. 1944-54.
Furuhara T, Poorganji B, Abe H, Maki T. JOM 2007; 59: pp. 64-7.
Reynolds A.P., Duvall F. Welding Research Supplement 1999; 78: pp. 355s-60s.
Boyer R, Welsch G, Collings EW. Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys, Materials Part: ASM International; 1994: p. 493.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to M. Guerin and M. Banu for their technical assistance during this study. The authors are also grateful to R. Ivanov for his support in acquiring the SEM images of the fracture surfaces.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 5, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wanjara, P., Dalgaard, E., Gholipour, J. et al. Effect of Pre- and Post-weld Heat Treatments on Linear Friction Welded Ti-5553. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 5138–5157 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2475-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2475-y