Abstract
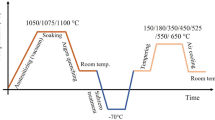
Thermo-mechanical treatments (TMT) at different rolling deformation temperatures were utilized to process a martensitic heat-resistant stainless steel 403Nb containing 12 wt pct Cr and small additions of Nb and V. Microstructures and mechanical properties at room and elevated temperatures were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and hardness, tensile, and creep tests. The results showed that high-temperature mechanical behavior after TMT can be greatly improved and microstructures with refined martensitic lath and finely dispersed nanosized MX carbides could be produced. The particle sizes of M23C6 and MX carbides in 403Nb steel after conventional normalizing and tempering (NT) treatments are about 50 to 160 and 10 to 20 nm, respectively, while those after TMT at 1123 K (850 °C) and subsequent tempering at 923 K (650 °C) for 2 hours reach about 25 to 85 and 5 to 10 nm, respectively. Under the condition of 260 MPa and 873 K (600 °C), the tensile creep rupture life of 403Nb steel after TMT at 1123 K (850 °C) is 455 hours, more than 3 times that after conventional NT processes. The mechanisms for improving mechanical properties at elevated temperature were analyzed in association with the existence of finely dispersed nanosized MX particles within martensitic lath. It is the nanosized MX particles having the higher stability at elevated temperature that assist both dislocation hardening and sub-grain hardening for longer duration by pinning the movement of dislocations and sub-grain boundary migration.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Rojas, J. Garcia, O. Prat, L. Agudo, C. Carrasco, G. Sauthoff, and A.R. Kaysser-Pyzalla: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 1372-81.
J. Hald: Int. J. Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2008, vol. 85, pp. 30-37.
Mats Hättestrand, Martin Schwind, and Hans-Olof Andrén: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 250, pp. 27-36.
F. Masuyama: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 612-25.
H. Ghassemi-Armaki, R.P. Chen, K. Maruyama, M. Yoshizawa, and M. Igarashi: Mater. Lett., 2009, vol.63, pp. 2423-25.
K. Maruyama, K. Sawada, and J. Koike: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 641-53.
H.S. Bao, S.C. Cheng, Z.D. Liu, and S.P. Tan: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2010, vol. 17, pp. 67-73.
J. Pešička, A. Aghajani, Ch. Somsen, A. Hartmaier, and G. Eggeler: Scripta Mater., 2010, vol. 62, pp. 353-56.
A. Aghajani, Ch. Somsen, and G. Eggeler: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 5093-106.
S. Straub, P. Polcik, and W. Blum: in Strength of Materials, H. Oikawa, K. Maruyama, S. Takeuchi, and M. Yamaguchi, eds., The Japan Institute of Metals, Sendai, 1994, pp. 623–26.
M. Taneike, F. Abe, and K. Sawada: Nature, 2003, vol. 424, pp. 294-96.
Åsa Gustafson and Mats Hättestrand: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. 333, pp. 279-86.
F. Abe, M. Taneike, and K. Sawada: Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping, 2007, vol. 84, pp. 3-12.
R.L. Klueh, N. Hashimoto, and P. J. Maziasz: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 275-80.
S.N. Prasad and D.S. Sarma: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 399, pp. 161-72.
M. Moallemi, A. Kermanpur, A. Najafizadeh, A. Rezaee, and H. Samaei Baghbadorani: Mater. Lett., 2012, vol. 89, pp. 22-24.
S.K. Dhua, D. Mukerjee, and D.S. Sarma: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 241-53.
A. Munita, R.E. Ricker, D.J. Pitchure, and G. Kimmel: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 2403-13.
R. L. Klueh, N. Hashimoto, and P. J. Maziasz: J. Nuclear Mater., 2007, vol. 367-370, pp. 48-53.
S. Hollner, B. Fournier, J. Le Pendu, T. Cozzika, I. Tournié, J.-C. Brachet, and A. Pineau: J. Nuclear Mater., 2010, vol. 405, pp. 101-108.
J. Pešička, R. Kužel, A. Dronhofer, and G. Eggeler: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 4847-62.
Z.Y. Zeng, L.Q. Chen, F.X. Zhu, and X.H. Liu: J. Mater. Sci. Tech., 2011, vol. 27, pp. 913-19.
Z.Y. Zeng, L.Q. Chen, F.X. Zhu, and X.H. Liu: Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.), 2011, vol. 24, pp. 381–89.
A. Kostka, K.-G. Tak, R.J. Hellmig, Y. Estrin, and G. Eggeler: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 539-50.
F. Abe, T.U. Kern, and R. Viswanathan: in Creep-resistant Steels, Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, 2008.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51271051, 50634030), the National High Technology Research and Development Program (2012AA03A508), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Grant No. N100507003) is greatly appreciated. The authors wish to thank Prof. Tian Sugui and Dr. Xie Jun, Shenyang University of Technology, for their support in the creep test.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 27, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Zeng, Z., Zhao, Y. et al. Microstructures and High-Temperature Mechanical Properties of a Martensitic Heat-Resistant Stainless Steel 403Nb Processed by Thermo-Mechanical Treatment. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 1498–1507 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2105-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2105-0