Abstract
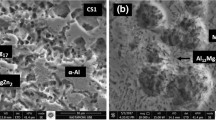
The effect of Zn content on microstructure, existing phases, and mechanical properties of rapidly solidified MgZn x Y1LaMM1Mn0.5 alloys (X = 2, 3, 4 at. pct) has been investigated. To assess the microstructural characterization of nanocrystalline alloys, the study also includes microstructural characterization of the master alloys. The microstructure of the alloys in as-rapidly solidified condition consisted of supersaturated magnesium dendrites and fine (Mg,Zn)17La2 and W phase (Mg3Y2Zn3) segregated at grain and cell boundaries. During continuous heating, the metastable solid solution in Mg dendrites breaks down, increasing the volume fraction of second-phase particles. After annealing for 1 hour at 673 K (400 °C), very small spherical Mn-rich precipitates appeared in the three alloys and a long-period stacking ordered (LPS) phase of rectangular morphology precipitated inside the Mg grains in the alloy with the lowest Zn content. The nanocrystalline nature of the ribbons accounts for the high hardness and yield stress values in as-rapidly solidified state, although both decrease with increasing zinc content. This fact has been related to a coarser microstructure and higher volume fraction of the W phase as the Zn content increases. The highest yield stress value of 350 MPa is attained by the MgZn2Y1LaMM1 ribbon in as-rapidly solidified condition. A decrease in yield stress values (about 50 MPa) is observed for all ribbons when they are heated at 673 K (400 °C) for 1 hour.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Zeng, Y. Zhsang, C. Lu, W. Ding, Y. Wang, and Y. Zhu: J. Alloy. Compd., 2005, vol. 4395, pp. 213–19.
I.J. Kim, D.H. Bae, and D.H. Ki: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2003, vol. 359, pp. 313–18.
M. Yamasaki, K. Hashimoto, K. Hagihara, and Y. Kawamura: Acta Mater., 2011, vol. 59, pp. 3646–58.
D.K. Xu, W.N. Tang, L. Liu, Y.B. Xu, and E.H. Han: J. Alloy. Compd., 2007, vol. 432, pp. 129–34.
D.K. Xu, E. Han, L. Liu, and Y.B. Xu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 1727–37.
J.Y. Lee, D.H. Kim, H.K. Lim, and D.H. Kim: Mater. Lett., 2005, vol. 59, pp. 3801–05.
Y. Kawamura, K. Hayashi, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto: Mater. Trans. JIM., 2001, vol. 42, pp. 1172–76.
Z.P. Luo and S.Q. Zhang: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 2000, vol. 19, pp. 813–15.
T. Itoi, T. Seimiya, Y. Kawamura, and M. Hiroshashi: Scripta Mater., 2004, vol. 54, pp. 107–11.
D.H. Ping, K. Hono, Y. Kawamura, and A. Inoue: Phil. Mag. Lett., 2002, vol. 82, pp. 543–51.
Y. Kawamura, T. Kasahara, S. Izumi, and M. Yamasaki: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 55, pp. 453–56.
G. Garcés, P. Pérez, S. González, and P. Adeva: Int. J. Mater. Res., 2006, vol. 97, pp. 404–08.
P. Pérez, S. González, G. Garcés, G. Caruana, and P. Adeva: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 485, pp. 194–99.
Q. Li, Q. Wang, Y. Wang, X. Zeng, and W. Ding: J. Alloy. Compd. 2007, vol. 427, pp. 115–23.
W. Xiao, J. Wang, J. Yang, S. Jia, and L. Wang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 485, pp. 55–60.
I.J. Kim, D.H. Bae, and D.H. Ki: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 359, pp. 313–18.
A. Müller, G. Garcés, P. Pérez, and P. Adeva: J. Alloy. Compd., 2007, vol. 443, pp. L1–L5.
Q. Li, Q. Wang, H. Zhou, X. Zeng, Y. Zhang, and W. Ding: Mater. Lett., 2005, vol. 59, pp. 2549–54.
G. Nussbaum, P. Sainfort, G. Regazz, and H. Gjestland: Scripta Metall., 1989, vol. 23, pp. 1079–84.
J. Cai, G.C. Mac, Z. Liud, H.F. Zhang, A.M. Wang, and Z.Q. Hua: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, vol. 456, pp. 364–67.
X. Guoa, S. Remennik, C. Xu, and D. Shechtman: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 473, pp. 266–73.
S. González, G. Garcés, P. Adeva, and P. Pérez: Mater. Charact., 2012, vol. 64, pp. 53–61.
X. Zhang, D. Kevorkov, I. Jung, and M. Pekguleryuz: J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, vol. 482, pp. 420–28.
M. Matsuda, S. Li, Y. Kawamura, Y. Ikuhara, and M. Nishida: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 393, pp. 269–74.
Y.M. Zhu, A.J. Morton, and J.F. Nie: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 2936–47.
Z.H. Huang, S.M. Liang, R.S. Chen, and E.H. Han: J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, vol. 468 pp. 170–78.
P. Pérez. G. Garcés, and P. Adeva: J. Alloy. Compd., 2010, vol. 491, pp. 192–99.
J. Zhang, H.D. Du, W. Liang, C. Xu, and B. Lu: J. Alloy. Compd., 2007, vol. 427, pp. 244–50.
D.K. Xu, W.N. Tang, L. Liu, Y.B. Xu, and E.H. Han: J. Alloy. Compd., 2008, vol. 461, pp. 248–52.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by MICIN under project MAT2009-07811.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted September 16, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez, P., Garcés, G., Maeso, M. et al. Effect of Zn Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of MgZnYLaMM Alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 4383–4396 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1239-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1239-9