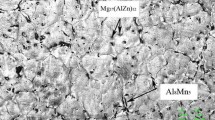
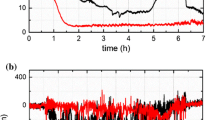
Abstract
Friction maps have been developed to explain the behavior of aluminum alloys under dynamic tribological conditions generated by the simultaneous effects of temperature and strain rate. A specially designed tribometer was used to measure the coefficient of friction (COF) of AA5083 strips subjected to sliding with a simultaneous application of tensile strain in the temperature range of 693 K to 818 K (420 °C to 545 °C) and strain rates between 5 × 10−3 s−1 and 4 × 10−2 s−1. The mechanisms of plastic deformation, namely, diffusional flow, grain boundary sliding (GBS), and solute drag (SD), and their operation ranges were identified. Relationships between the bulk deformation mechanism and COF were represented in a unified map by superimposing the regions of dominant deformation mechanisms on the COF map. The change in COF (from 1.0 at 693 K (420 °C) and 1 × 10−2 s−1 to 2.1 at 818 K (545 °C) and 4 × 10−2 s−1) was found to be largest in the temperature–strain rate region, where GBS was the dominant deformation mechanism, as a result of increased surface roughness. The role of bulk deformation mechanisms on the evolution of the surface oxide layer damage was also examined.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
References
R. Verma, A.K. Ghosh, S. Kim, and C. Kim: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1995, vol. 191A, pp. 143–50.
R. Verma, P.A. Friedman, A.K. Ghosh, S. Kim, and C. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 1889–98.
R.M. Cleveland, A.K. Ghosh, and J.R. Bradley: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 351A, pp. 228–36.
O.D. Sherby and J. Wadsworth: Prog. Mater. Sci., 1989, vol. 33, pp. 169–21.
J.G. Schroth: in Advances in Superplasticity and Superplastic Forming, E.M. Taleff, P.A. Friedman, P.E. Krajewski, R.S. Mishra, and J.G. Schroth, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2004, pp. 9–20.
C. Kim, M.G. Konopnicki, and F.G. Lee: in Advances in Superplasticity and Superplastic Forming, E.M. Taleff, P.A. Friedman, P.E. Krajewski, R.S. Mishra, and J.G. Schroth, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2004, pp. 77–84.
A.T. Morales: in Advances in Superplasticity and Superplastic Forming, E.M. Taleff, P.A. Friedman, P.E. Krajewski, R.S. Mishra, and J.G. Schroth, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2004, pp. 51–64.
M.D. Hanna, P.E. Krajewski, and J.G. Schroth: Proc. STLE/ASME Int. Joint Tribology Conf., San Diego, CA, 2007, IJTC2007-44043, pp. 705–07.
P. Krajewski: U.S. Patent 5,819,572, Oct. 13, 1998.
B. Navinsek and P. Panjan: Surf. Coat. Technol., 1995, vols. 74–75, pp. 919–26.
B. Navinsek, P. Panjan, and I. Milosev: Surf. Coat. Technol., 1997, vol. 97, pp. 182–91.
J. Edwards: Coating and Surface Treatment Systems for Metals, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1996, pp. 72–183.
C. Herring: J. Appl. Phys., 1950, vol. 21, pp. 437–45.
J. Harper and J.E. Dorn: Acta Metall., 1957, vol. 5, pp. 654–65.
T.G. Langdon and P. Yavari: Acta Metall., 1982, vol. 30, pp. 881–87.
J.N. Wang and T.G. Langdon: Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 2487–92.
P. Yavari, D.A. Miller, and T.G. Langdon: Acta Metall., 1982, vol. 30, pp. 871–79.
F.A. Mohamed: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1978, vol. 32A, pp. 37–40.
J. Weertman: J. Appl. Phys., 1957, vol. 28, pp. 362–64.
R.Z. Valiev and O.A. Kaibyshev: Acta Metall., 1983, vol. 31, pp. 2121–28.
T.G. Langdon: Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 2437–43.
T.G. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1991, vol. 137A, pp. 1–11.
M.F. Ashby and R.A. Verrall: Acta Metall., 1973, vol. 21, pp. 149–63.
R.C. Gifkins: Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 1225–32.
E.M. Taleff, G.A. Henshall, T.G. Nieh, D.R. Lesuer, and J. Wadsworth: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 1081–91.
M.A. Kulas, W.P. Green, E.M. Taleff, P.E. Krajewski, and T.R. McNelley: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 1249–61.
W.P. Green, M.A. Kulas, A. Niazi, K. Oishi, E.M. Taleff, P.A. Krajewski, and T.R. McNelley: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 2727–38.
T.R. McNelley, K. Oh-Ishi, A.P. Zhilyaev, S. Swaminathan, P.E. Krajewski, and E.M. Taleff: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 50–64.
D.E. Cipoletti, A.F. Bower, Y. Qi, and P.E. Krajewski: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2009, vol. 504A, pp. 175–82.
M. Fishkis and J.C. Lin: Wear, 1997, vol. 206, pp. 156–70.
G. Buytaert, H. Terryn, S. Van Gils, B. Kernig, B. Grzemba, and M. Mertens: Surf. Interface Anal., 2005, vol. 37, pp. 534–43.
D.J. Field, G.M. Scamans, and E.P. Butler: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 463–72.
C. Lea and J. Ball: Appl. Surf. Sci., 1984, vol. 17, pp. 344–62.
M.H. Zayan, O.M. Jamjoom, and N.A. Razik: Oxid. Met., 1990, vol. 34, pp. 323–33.
M.F. Frolish, J.C. Walker, C. Jiao, W.M. Rainforth, and J.H. Beynon: Tribol. Int., 2005, vol. 38, pp. 1050–58.
P. Hancock and J.R. Nicholls: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1988, vol. 4, pp. 398–06.
M. Schutze: Protective Oxide Scales and Their Breakdown, 1st ed., John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester, 1997, pp. 67–114.
H.E. Evans: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1988, vol. 4, pp. 415–20.
H.R. Le, M.P.F. Sutcliffe, P.Z. Wang, and G.T. Burstein: Acta Mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 911–20.
M.G. Zelin: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 3533–42.
V.P. Pojda, V.V. Bryukhovets’ky, A.V. Pojda, R.I. Kuznetsova, V.F. Klepikov, and D.L. Voronov: Phys. Met. Metall., 2007, vol. 103, pp. 414–23.
Y. Takayama, T. Tozawa, and H. Kato: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 1263–70.
W.D. Cao, X.P. Lu, and H. Conrad: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 697–706.
J.K. Chang, E.M. Taleff, P.E. Krajewski, and J.R. Ciulik: Scripta Mater., 2009, vol. 60, pp. 459–62.
J. Koike, M. Mabuchi, and K. Higashi: Acta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 43, pp. 199–206.
W.J.D. Shaw: J. Mater. Sci., 1989, vol. 24, pp. 4114–19.
S.F. Claeys, J.W. Jones, and J.E. Allison: in Dispersion Strengthened Aluminum Alloys, Y.W. Kim and W.M. Griffith, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1988, pp. 323–36.
R. Benzing, I. Goldblatt, V. Hopkins, W. Jamison, K. Mecklenburg, and M. Peterson: Friction and Wear Devices Catalog, 2nd ed., American Society of Lubrication Engineers, Park Ridge, Ill, 1976, pp. 1–458.
J.A. Schey: Tribology in Metalworking: Friction, Fabrication and Wear, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1983.
S. Kalpakjian: Annals CIRP, 1985, vol. 34 (2), pp. 585–92.
J.A. Schey and M.K. Smith: Proc. Sheet Metal and Stamping Symp., Society of Automotive Engineers, Detroit, MI, 1993, SP-944, pp. 261–67.
P.E. Krajewski and A.T. Morales: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2004, vol. 13, pp. 700–09.
X. Meng-Burany, T.A. Perry, A.K. Sachdev, and A.T. Alpas: Wear, 2011, vol. 270, pp. 152–62.
A.R. Riahi, A. Edrisy, and A.T. Alpas: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, vol. 203, pp. 2030–35.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Messrs. M.P. Balogh’s (GM) and R.A. Waldo’s (GM) assistance with the characterization work and Mr. A. Jenner’s (University of Windsor) contributions to the construction of the high-temperature tribometer. This work is supported by General Motors of Canada and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada through an Industrial Research Chair Grant (ATA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 7, 2010.
Appendix
Appendix
General creep equation:
where A is the material constant, σ is the flow stress, n is the stress exponent, E is the temperature-compensated Young’s modulus, Q is the activation energy for deformation, and R is the universal gas constant.
Diffusional flow creep:
SD creep:
GBS:
For Eqs. [A2] through [A6], D L is the lattice diffusion coefficient, D gb is the GB diffusion coefficient and D s is the solute atom diffusion coefficient, b is the Burgers vector, d is the grain size, E is the temperature compensated Young’s modulus, k is the Boltzmann’s constant, and k 1 through k 5 are material constants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., Morales, A.T., Riahi, A.R. et al. Role of Plastic Deformation on Elevated Temperature Tribological Behavior of an Al-Mg Alloy (AA5083): A Friction Mapping Approach. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 2384–2401 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0649-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0649-4