Abstract
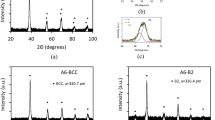
To find a new phase with the potential to improve the high-temperature strength of Ir-based superalloys, the novel idea of introducing silicides into the Ir-Nb binary was implemented. Hypoeutectic Ir-10Nb, eutectic Ir-16Nb, and hypereutectic Ir-25Nb alloys were used as bases, and 5 mol pct Si was added through the removal of Ir. XRD (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and electron-probe microanalysis (EPMA) revealed the formation of a three-phase fcc/L12/silicide microstructure in the Ir-Nb-Si ternary after Si addition. The type of silicide formed was dependent on heat-treated temperatures and Nb content. After heat treatment at 1750 °C and 1600 °C, a tie-triangle composed of fcc/L12/silicide (Ir2Si) appeared in the Ir-10Nb-5Si and Ir-16Nb-5Si alloys; in the Ir-25Nb-5Si alloy, an L12 and silicide (Ir,Nb)2Si tie-line was observed. In the as-cast and 1300 °C heat-treated samples, the Ir-10Nb-5Si microstructure changed to a two-phase fcc/silicide structure, while the Ir-16Nb-5Si alloy maintained a three-phase fcc/L12/silicide structure. The Ir-25Nb-5Si alloy, however, had the same phases as that at 1600 °C. Silicides typically continuously or discontinuously distribute along the interdendritic regions or grain boundaries of the fcc or the L12 phase. With the addition of Si, it was found that both the eutectic point and solid solubility of Nb in Ir would shift toward Ir.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Yamabe, Y. Koizumi, H. Murakami, Y. Ro, T. Maruko, and H. Harada: Scripta Mater., 1996, vol. 35 (2), pp. 211–15.
Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Ro, T. Maruko, and H. Harada: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 537–49.
Y. Gu, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Ro, T. Yokokawa, and H. Harada: Scripta Mater., 1998, vol. 39 (6), pp. 723–28.
Y. Gu, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Ro, T. Yokokawa, and H. Harada: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 30A, pp. 2629–39.
Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Ro, T. Maruko, and H. Harada: Intermetallics, 1999, vol. 7, pp. 49–58.
Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Ro, T. Maruko, and H. Harada: Scripta Mater., 1999, vol. 40 (1), pp. 109–15.
Y. Gu, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Ro, and H. Harada: Scripta Mater., 1999, vol. 40 (11), pp. 1313–19.
X. Yu, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Ro, and H. Harada: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 173–78.
X.H. Yu, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, S. Nakazawa, Y. Ro, and H. Harada: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 1347–53.
P. Hill, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, and I.W. Wolff: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 44, pp. 43–48.
Y. Gu, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, and H. Harada: Scripta Mater., 2002, vol. 46, pp. 137–42.
Y. Gu, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, and H. Harada: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 1281–83.
Y. Yamabe-Mitarai and H. Harada: J. Alloys Compounds, 2003, vol. 361, pp. 169–79.
Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Gu, and H. Harada: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 2207–15.
Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, T.B. Massalski, ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1992, pp. 2082, 2330, 2335, 2336, and 2366.
N.S. Stoloff: in Superalloys II, C.T. Sims, N.S. Stoloff, and W.C. Hagel, eds., John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1987, p. 66.
H. Okamoto: J. Phase Equilibria, 1995, vol. 16 (5), pp. 473–74.
Y. Kimura, T. Shimizu, S. Shiina, and Y. Mishima: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 591–99.
J.B. Sha and Y. Yamabe-Mitarai: National Institute for Materials Science, Ibaraki, Japan, unpublished research, 2004.
F. Chu, D.J. Thoma, K.J. McClellan, P. Peralta, F.X. Li, and E. Fodra: High-Temperature Ordered Intermetallic Alloys VIII, Materials Research Society Symposia Proceedings, Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 1998, vol. 522, pp. KK6.7.1-KK6.7.11.
M.R. Jackson, B.P. Bewlay, and R.G. Rowe: JOM, 1996, vol. 48, pp. 39–44.
B.P. Bewlay, J.J. Lewandowksi, and M.R. Jackson: JOM, 1997, vol. 49, pp. 44–46 and 67.
J.B. Sha, H. Hirai, T. Tabaru, H. Ueno, A. Kitahara, and S. Hanada: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 85–94.
J.B. Sha, H. Hirai, T. Tabaru, H. Ueno, A. Kitahara, and S. Hanada: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 2861–71.
J.B. Sha, H. Hirai, T. Tabaru, H. Ueno, A. Kitahara, and S. Hanada: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2004, vol. A364, pp. 151–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sha, J.B., Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. & Harada, H. Ir-Nb-Si ternary refractory superalloys with a three-phase Fcc/L12/silicide structure for high-temperature applications: Phase and microstructural evolution. Metall Mater Trans A 37, 1831–1839 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0126-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0126-7