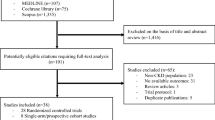
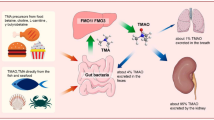
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major disease that threatens human health. With the progression of CKD, the risk of cardiovascular death increases, which is associated with the elevated levels of uremic toxins (UTs). Representative toxins such as indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate are involed in CKD progression and cardiovascular events inseparable from the key role of endothelial dysfunction. The therapeutic strategies of UTs are aimed at signaling pathways that target the levels and damage of toxins in modern medicine. There is a certain relevance between toxins and "turbid toxin" in the theory of Chinese medicine (CM). CM treatments have been demonstrated to reduce the damage of gut-derived toxins to the heart, kidney and blood vessels. Modern medicine still lacks evidence-based therapies, so it is necessary to explore the treatments of CM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fernandez-Prado R, Esteras R, Perez-Gomez MV, Gracia-Iguacel C, Gonzalez-Parra E, Sanz AB, et al. Nutrients turned into toxins: microbiota modulation of nutrient properties in chronic kidney disease. Nutrients 2017;9:489.
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2017;389:1238–1252.
Koizumi M, Tatebe J, Watanabe I, Yamazaki J, Ikeda T, Morita T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates indoxyl sulfate-induced cellular senescence in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Atheroscler Thromb 2014;21:904–916.
Meijers BK, van Kerckhoven S, Verbeke K, Dehaen W, Vanrenterghem Y, Hoylaerts MF, et al. The uremic retention solute p-cresyl sulfate and markers of endothelial damage. Am J Kidney Dis 2009;54:891–901.
Marzocco S, Dal Piaz F, Di Micco L, Torraca S, Sirico ML, Tartaglia D, et al. Very low protein diet reduces indoxyl sulfate levels in chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif 2013;35:196–201.
Shibahara H, Shibahara N. Cardiorenal protective effect of the oral uremic toxin absorbent AST-120 in chronic heart disease patients with moderate CKD. J Nephrol 2010;23:535–540.
Schulman G, Berl T, Beck GJ, Remuzzi G, Ritz E, Arita K, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled EPPIC trials of AST-120 in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 2015;26:1732–1746.
Motojima M, Hosokawa A, Yamato H, Muraki T, Yoshioka T. Uremic toxins of organic anions up-regulate PAI-1 expression by induction of NF-kappaB and free radical in proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int 2003;63:1671–1680.
Zou C, Lu ZY, Wu YC, Yang LH, Su GB, Jie XN, et al. Colon may provide new therapeutic targets for treatment of chronic kidney disease with Chinese medicine. Chin J Integr Med 2013;19:86–91.
Li S, Rao XR, Wang SX, Zhang GH, Li XM, Dai XW, et al. Study on the relationship between blood stasis syndrome and clinical pathology in 227 patients with primary glomerular disease. Chin J Integr Med 2009;15:170–176.
Li S, Rao XR, Song JY, Meng LQ, Qu L, Li XM. Effects of Huanshuai Recipe Oral Liquid on restructuring glomerular microvasculature and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in subtotal nephrectomized rats. Chin J Integr Med 2010;16:239–246.
Wang XJ, Rao XR, Li S, Wang L, Liu C, Zhang GH, et al. Effect of Huanshuai Recipe Oral Liquid on renal dysfunction progression in patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Chin J Integr Med 2015;21:811–816.
Li S, Rao XR, Dai XW, Pei K, Wang L, Huo BM, et al. Beneficial effects of Fu-Zheng-Qu-Zhuo Oral Liquid combined with standard integrated therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease (stage 3–4): a randomized placebocontrolled clinical trial. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e7448.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C., Rao, Xr. Understanding and Therapeutic Strategies of Chinese Medicine on Gut-Derived Uremic Toxins in Chronic Kidney Disease. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 24, 403–405 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2926-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2926-6