Abstract
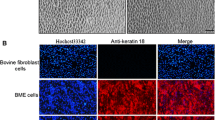
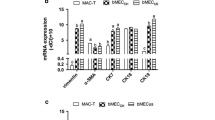
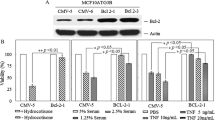
Primary bovine mammary epithelial cells are not ideal models for long-term studies, because primary cells undergo a limited number of proliferations in vitro and enter into a growth-arrest stage called cell replicative senescence; we therefore must establish the immortalized bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMECs) in vitro. More importantly, the mechanisms of the relationship between immortalized and apoptotic cell remain unknown in BMECs. We therefore sought to elucidate the mechanisms of which immortalized cells escape the pathway of apoptotic signal. These cells were successfully immortalized without any signs of senescence. The maximum number of BMEC and E6E7 immortalized cells were reached after 6 d of culture. At this point, there were significantly more E6E7 immortalized cells than primary BMECs (P < 0.01). The population-doubling times of the E6E7 and SV40T immortalized cells were lowest at 48 and 72 h. We failed to detect the expression of the epithelial cell marker E-cadherin in BMECs; however, immortalized cells had low expression of E-cadherin. The expression of β-catenin was markedly expressed in immortalized cells than in BMECs (P < 0.01). Caspase-3, caspase-9, and poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) were detected; however, the cleavage of caspase-3 and PARP was not observed. Our data demonstrate that the expressions of caspase-9, caspase-3, and PARP are not sufficient for the apoptosis of immortalized cells and suggest that E-cadherin and β-catenin might be an important indicator of the development of cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balducci L, Blasi A, Saldarelli M, Soleti A, Pessina A, Bonomi A, Coccè V, Dossena M, Tosetti V, Ceserani V, Navone SE, Falchetti ML, Parati EA, Alessandri G (2014) Immortalization of human adipose-derived stromal cells: production of cell lines with high growth rate, mesenchymal marker expression and capability to secrete high levels of angiogenic factors. Stem Cell Res Ther 5:63
Demers GW, Foster SA, Halbert CL, Galloway DA (1994) Growth arrest by induction of p53 in DNA damaged keratinocytes is bypassed by human papillomavirus 16 E7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:4382–4386
Desmarets LM, Theuns S, Olyslaegers DA, Dedeurwaerder A, Vermeulen BL, Roukaerts ID, Nauwynck HJ (2013) Establishment of feline intestinal epithelial cell cultures for the propagation and study of feline enteric coronaviruses. Vet Res 44:71
Hazan RB, Qiao R, Keren R, Badano I, Suyama K (2004) Cadherin switch in tumor progression. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1014:155–163
Jedrzejczak M, Szatkowska I (2014) Bovine mammary epithelial cell cultures for the study of mammary gland functions. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 50:389–398
Khleif SN, DeGregori J, Yee CL, Otterson GA, Kaye FJ, Nevins JR, Howley PM (1996) Inhibition of cyclin D-CDK4/CDK6 activity is associated with an E2F mediated induction of cyclin kinase inhibitor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:4350–4354
Khudhair N, Luo C, Khalid A, Zhang L, Zhang S, Ao J, Li Q, Gao X (2015) 14-3-3γ affects mTOR pathway and regulates lactogenesis in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 51:697–704
Kiyono T, Foster SA, Koop JI, McDougall JK, Galloway DA, Klingelhutz AJ (1998) Both Rb/p16INK4a inactivation and telomerase activity are required to immortalize human epithelial cells. Nature 396:84–88
Kozlowski M, Gajewska M, Majewska A, Jank M, Motyl T (2009) Differences in growth and transcriptomic profile of bovine mammary epithelial monolayer and three-dimensional cell cultures. J Physiol Pharmacol 60:5–14
Lee GY, Kenny PA, Lee EH, Bissell MJ (2007) 3D culture models of normal and malignant breast epithelial cells. Nat Methods 4:359–365
Levine AJ (1997) p53 the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88:323–331
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N, Clevers H, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (1997) Activation of beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in beta-catenin or APC. Science 275:1787–1790
Rose MT, Aso H, Yonekura S, Komatsu T, Hagino A, Ozutsumi K, Obara Y (2002) In vitro differentiation of a cloned bovine mammary epithelial cell. J Dairy Res 69:345–355
Sorg D, Potzel A, Beck M, Meyer HH, Viturro E, Kliem H (2012) Effects of cell culture techniques on gene expression and cholesterol efflux in primary bovine mammary epithelial cells derived from milk and tissue. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 48:550–553
Svedlund J, Aurén M, Sundström M, Dralle H, Akerström G, Björklund P, Westin G (2010) Aberrant WNT/β-catenin signaling in parathyroid carcinoma. Mol Cancer 9:294
Tong HL, Li QZ, Gao XJ, Yin DY (2012) Establishment and characterization of a lactating dairy goat mammary gland epithelial cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 48:149–155
Wang MZ, Xu BL, Wang HR, Bu DP, Wang JQ, Loor JJ (2014) Effects of arginine concentration on the in vitro expression of casein and mTOR pathway related genes in mammary epithelial cells from dairy cattle. PLoS One 9:e95985
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31301997 and 31572430).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Kang Zhan and Miao Lin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, K., Lin, M., Zhao, QM. et al. Biological characterization of bovine mammary epithelial cell lines immortalized by HPV16 E6/E7 and SV40T. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 52, 906–910 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-016-0063-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-016-0063-8