Abstract
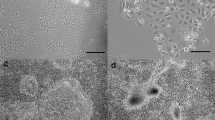
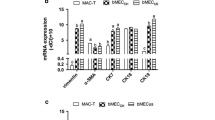
To study milk synthesis in dairy goat mammary gland, we had established an in vitro lactating dairy goat mammary epithelial cell (DGMEC) line. Mammary tissues of Guan Zhong dairy goats at 35 d of lactation were dispersed and cultured in a medium containing epithelial growth factor, insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin transferrin serum, and fetal bovine serum. Epithelial cells were enriched by digesting with 0.25% trypsin repeatedly to remove fibroblast cells and were identified as epithelial origin by staining with antibody against cytokeratine 18. The DGMECs displayed monolayer, cobble-stone, epithelial-like morphology, and formed alveoli-like structures and island monolayer aggregates which were the typical characteristics of mammary epithelial cells. A one-half logarithmically growth curve and cytoplasmic lipid droplets in these cells were observed. In this paper, we also studied the lactating function of DGMECs. Results showed that DGMECs could secrete lactose and β-casein. Lactating function of the cells had no obvious change after 48 h treated by insulin, while prolactin could obviously raise the secretion of milk proteins and lactose.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertucci P. Y.; Quaglino A.; Pozzi A. G.; Kordon E. C.; Pecci A. Glucocorticoid-induced impairment of mammary gland involution is associated with STAT5 and STAT3 signaling modulation. Endocrinology. 151: 5730–5740; 2010.
Buser A. C.; Gass-Handel E. K.; Wyszomierski S. L.; Doppler W.; Leonhardt S. A.; Schaack J.; Rosen J. M.; Watkin H.; Anderson S. M.; Edwards D. P. Progesterone receptor repression of prolactin/signal transducer and activator of transcription 5-mediated transcription of the beta-casein gene in mammary epithelial cells. Mol Endocrinol. 21: 106–125; 2007.
Danielson K. G.; Oborn C. J.; Durban E. M.; Butel J. S.; Medina D. Epithelial mouse mammary cell line exhibiting normal morphogenesis in vivo and functional differentiation in vitro. P Natl Acad Sci U S A 81: 3756–3760; 1984.
Duchler M.; Schmoll F.; Pfneisl F.; Brem G.; Schellander K. OMEC II: a new ovine mammary epithelial cell line. Biol Cell 90: 199–205; 1998.
German T.; Barash I. Characterization of an epithelial cell line from bovine mammary gland. In Vitro Cell Dev An. 38: 282–292; 2002.
Gibson C. A.; Vega J. R.; Baumrucker C. R.; Oakley C. S.; Welsch C. W. Establishment and characterization of bovine mammary epithelial cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev An 27: 585–594; 1991.
Gordon K. E.; Binas B.; Chapman R. S.; Kurian K. M.; Clarkson R. W.; Clark A. J.; Lane E. B.; Watson C. J. A novel cell culture model for studying differentiation and apoptosis in the mouse mammary gland. Breast Cancer Res. 2: 222–235; 2000.
Huynh H. T.; Pollak M. HH2a, an immortalized bovine mammary epithelial cell line expresses the gene encoding mammary derived growth inhibitor (MDGI). In Vitro Cell Dev An. 31: 25–29; 1995.
Ilan N.; Barash I.; Gootwine E.; Shani M. Establishment and initial characterization of the ovine mammary epithelial cell line NISH. In Vitro Cell Dev An 34: 326–332; 1998.
Janne J.; Alhonen L.; Hyttinen J. M.; Peura T.; Tolvanen M.; Korhonen V. P. Transgenic bioreactors. Biotechnol Annu Rev 4: 55–74; 1998.
Kittrell F. S.; Oborn C. J.; Medina D. Development of mammary preneoplasias in vivo from mouse mammary epithelial cell lines in vitro. Cancer Res 52: 1924–1932; 1992.
Link N.; Aubel C.; Kelm J. M.; Marty R. R.; Greber D.; Djonov V.; Bourhis J.; Weber W.; Fussenegger M. Therapeutic protein transduction of mammalian cells and mice by nucleic acid-free lentiviral nanoparticles. Nucleic Acids Res 34: e16; 2006.
Madsen M.; Lykkesfeldt A. E.; Laursen I.; Nielsen K. V.; Briand P. Altered gene expression of c-myc, epidermal growth factor receptor, transforming growth factor-alpha, and c-erb-B2 in an immortalized human breast epithelial cell line, HMT-3522, is associated with decreased growth factor requirements. Cancer Res 52: 1210–1217; 1992.
Niemann H.; Kues W. A. Application of transgenesis in livestock for agriculture and biomedicine. Anim Reprod Sci 79: 291–317; 2003.
Pantschenko A. G.; Woodcock-Mitchell J.; Bushmich S. L.; Yang T. J. Establishment and characterization of a caprine mammary epithelial cell line (CMEC). In Vitro Cell Dev An 36: 26–37; 2000.
Qian L.; Lopez V.; Seo Y. A.; Kelleher S. L. Prolactin regulates ZNT2 expression through the JAK2/STAT5 signaling pathway in mammary cells. Am J Physiol Cell Ph 297: 369–377; 2009.
Rose M. T.; Aso H.; Yonekura S.; Komatsu T.; Hagino A.; Ozutsumi K.; Obara Y. In vitro differentiation of a cloned bovine mammary epithelial cell. J Dairy Res 69: 345–355; 2002.
Rosen J. M.; Wyszomiersk S. L.; Hadsell D. Regulation of milk protein gene expression. Annu Rev Nutr 19: 407–436; 1999.
Sun Y. L.; Lin C. S.; Chou Y. C. Establishment and characterization of a spontaneously immortalized porcine mammary epithelial cell line. Cell Biol Int 30: 970–976; 2006.
Wheeler M. B.; Walters E. M. Transgenic technology and applications in swine. Theriogenology 56: 1345–1369; 2001.
Zavizion B.; Gorewit R. C.; Politis I. Subcloning the MAC-T bovine mammary epithelial cell line: morphology, growth properties, and cytogenetic analysis of clonal cells. J Dairy Sci 78: 515–527; 1995.
Zhao K.; Liu H. Y.; Zhou M. M.; Liu J. X. Establishment and characterization of a lactating bovine mammary epithelial cell model for the study of milk synthesis. Cell Biol Int 34: 717–721; 2010.
Zheng Y. M.; He X. Y. Characteristics and EGFP expression of porcine mammary gland epithelial cells. Res Vet Sci 89: 383–390; 2010.
Acknowledgment
This work was founded by National Key Basic Research Program of China (project no. 2011CB100804).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: T. Okamoto
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(XLS 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, HL., Li, QZ., Gao, XJ. et al. Establishment and characterization of a lactating dairy goat mammary gland epithelial cell line. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 48, 149–155 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-012-9481-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-012-9481-4