Abstract
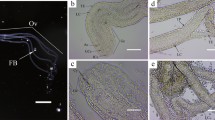
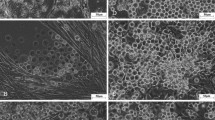
A new continuous cell line from ovarian tissue of commercial variety “Kolar Gold” of silkworm, Bombyx mori, was established and designated as DZNU-Bm-12. The tissue was grown in MGM-448 insect cell culture medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 3% heat-inactivated B. mori hemolymph at 25 ± 1°C. The migration of partially attached small round refractive cells from the fragments of ovarioles began from the beginning of explantation. The cells multiplied partially attached in the primary culture initially, and some of them become freely suspended after 20 passages. The cells were adapted to MGM-448 and TNM-FH media each with 10% FBS and the population doubling time of cell line was about 36 and 24 hr, respectively. The chromosome number was near diploid at initial passages and slightly increased at 176th passage, but a few tetraploids and hexaploids were also observed. DNA profiles using simple sequence repeat loci established the differences between DZNU-Bm-12 and DZNU-Bm-1 and most widely used Bm-5 and BmN cell lines. The cell line was found susceptible to B. mori nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) with 85–90% of the cells harboring BmNPV and having an average of 3–17 OBs/infected cell. We suggest the usefulness of this cell line in BmNPV-based baculoviral expression system and also for studying in vitro virus replication.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlson J. G. Protoplasmic viscosity changes in different regions of the grasshopper neuroblast during mitoses. Biol. Bull. 90: 109–121; 1946. doi:10.2307/1538215.
Chen Q.; Li L.; Yu Z.; Peng J. Establishment of cell lines from embryos of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. In: Kuroda Y.; Kurstak E.; Maramorosch K. (eds) Invertebrate and fish tissue culture. Springer, New York, pp 259–261; 1988.
Farrell P. J.; Behie L. A.; Iatrou K. Transformed insect cells: new sources of human tissue plasminogen activator. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 64: 426–433; 1999. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19990820)64:4<426::AID-BIT5>3.0.CO;2-#.
Farrell P. J.; Lu M.; Prevost J.; Brown C.; Behie L. A.; Iatrou K. High level expression of recombinant glycoproteins from transformed lepidopteran insect cells using a novel expression vector. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 60: 656–663; 1998. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19981220)60:6<656::AID-BIT2>3.0.CO;2–9.
Grace T. D. C. Establishment of a cell line from the silkworm, Bombyx mori.. Nature (London) 216: 613; 1967. doi:10.1038/216613a0.
Hayflick, L. Subculturing human diploid fibroblast cultures. In: Kurse P. F.; Patterson M. K. Jr. (eds) Methods and applications. Academic, New York, pp. 220–223; 1973.
Imanishi S.; Ohtsuki Y. Characteristics of cell lines established from embryonic tissues of several races of the silkworm, Bombyx mori cultured in vitro. J. Seric. Sci. Jpn. 573: 184–188; 1988.
Inoue H.; Mitsuhashi J. A Bombyx mori cell line susceptible to a nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J. Seric. Sci. Jpn. 53: 108–113; 1984.
Khurad A. M.; Kanginakudru S.; Qureshi S. O.; Rathod M. K.; Rai M. M.; Nagaraju J. A new Bombyx mori larval ovarian cell line highly susceptible to nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 92: 59–65; 2006. doi:10.1016/j.jip.2006.03.005.
Lu Y.; Lannan C. N.; Rohovec J. S. Fish cell lines: establishment and characterization of three new cell lines from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodonidella). In vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 263: 275–279; 1990. doi:10.1007/BF02624457.
McIntosh A.; Grasela J. J.; Matteri R. L. Identification of insect cell lines by DNA amplification fingerprinting (DAF). Insect Mol. Biol. 53: 187–195; 1996. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2583.1996.tb00053.x.
Maeda S. Expression of human interferon α in silkworms with a baculovirus Vector. In: Maramorosch K. (ed) Biotechnology in invertebrate pathology and cell culture. Academic, New York, pp 221–233; 1987.
Maeda S. Increased insecticidal effect by a recombinant baculovirus carrying a synthetic diuretic hormone gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 165: 1177–1183; 1989. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(89)92726-5.
Maeda S.; Volrath S. L.; Hanzlink T. N.; Harper S. A.; Majima K.; Maddox D. W.; Hammock B. D.; Fowler E. Insecticidal effects of an insect specific neurotoxin expressed by a recombinant baculovirus. Virology 184: 777–780; 1991. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(91)90451-G.
Miao, X. X.; Xu, S. J.; Li, M. H.; Li, M. W.; Huang, J. H.; Dai, F. Y.; Marino, S. W.; Mills, D. R.; Zeng, P.; Mita, K.; Jia, S. H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. B.; Xiang, H.; Guo, Q. H.; Xu, A. Y.; Kong, X. Y.; Lin, H. X.; Shi, Y. Z.; Lu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wei Huang, W.; Yuji Yasukochi, Y.; Sugasaki, T.; Shimada, T.; Nagaraju, J.; Zhong-Huai Xiang, Z. H.; Wang, S. Y.; Goldsmith, M. R.; Lue, C.; Zhao, G. P.; Huang, Y. P. Simple sequence repeat-based consensus linkage map of Bombyx mori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102(45): 16303–16308; 2005. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507794102
Mitsuhashi J. Isolation of a continuous cell line from larval fat bodies of an Arctiid moth, Spilarctia seriatopunctata (Insecta, Lepidoptera, Arctiidae). Zool. Sci. 1: 415–419; 1984.
Mitsuhashi J. Development of highly nutritive culture media. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 37: 330–337; 2001.
Ninaki O.; Nagayasu K.; Kameoka K.; Fujiwara H.; Miyajima N.; Takada N.; Maekawa H. Establishment of cell lines from Bombyx mori and B. mandarina and attempt of cell fusion. In: Kuroda Y.; Kurstak E.; Maramorosch K. (eds) Invertebrate and fish tissue culture. Springer, New York, pp 243–246; 1988.
Pan M. H.; Xiao S. Q.; Chen M.; Hong X. J.; Lu C. Establishment and characterization of two embryonic cell lines of Bombyx mori.. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 43: 101–104; 2007. doi:10.1007/s11626-006-9009-x.
Pandharipande T. N. Two new continuously growing cell lines from Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera:Bombycidae). App. Entomol. Zool. 29: 604–607; 1994.
Pu X. Y.; Hong X. J.; Chen M. Studies on Mitosis and Chromosomes of BmN Cells. Acta Sericologica Sinica 292: 136–141; 2003.
Quiot J. M. Establishment of cell line (S.P.C. Bm 36) from the ovaries of Bombyx mori L. (Lepidoptera). Sericologia 22: 25–31; 1982.
Raghow R.; Grace T. D. C. Studies on a nuclear polyhedrosis virus in Bombyx mori cell in vitro. I. Multiplication kinetics and ultrastructural studies.. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 47: 384–399; 1974. doi:10.1016/S0022–5320(74)90016–1.
Reddy K. D.; Abraham E. G.; Nagaraju J. Microsatellites in the silkworm, Bombyx mori: Abundance, polymorphism, and strain characterization. Genome 42: 1057–1065; 1999. doi:10.1139/gen-42–6–1057.
Sudeep A. B.; Mishra A. C.; Shouche Y. S.; Pant U.; Mourya D. T. Establishment of two new cell lines from Bombyx mori (L.) (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) and their susceptibility to baculoviruses. Indian J. Med. Res. 115: 189–193; 2002.
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to M. M. Rai and M. K. Rathod for providing healthy larvae for establishing the cultures and BmNPV-infected larvae to obtain inoculum during the study. The authors also thank the reviewers and Associate Editor for their critical and constructive comments to strengthen the paper. The research reported in this paper is partially supported by UGC, New Delhi to AMK [Project No. F. 31-222/2005(SR)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: J. Denry Sato
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khurad, A.M., Zhang, MJ., Deshmukh, C.G. et al. A new continuous cell line from larval ovaries of silkworm, Bombyx mori . In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 45, 414–419 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-009-9197-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-009-9197-2