Abstract
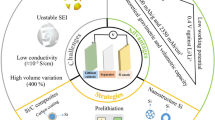
The spinel lithium-ion battery anode material Li4Ti5O12 (LTO) exhibits stable cycling and is less prone to lithium dendrite and solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) films. However, its theoretical capacity and conductivity are low within the electrochemical window of 1.0–3.0 V. In this study, we utilized active carbon (AC) coated and micron Silicon (Si) doped Li4Ti5O12, applying an extended electrochemical window of 0.01–3.0 V during cycling to enhance the material's electrochemical performance. Our investigation revealed that bare LTO sample as well as those with single Silicon doping or active carbon coating experienced rapid decay during high-rate long cycling tests. Conversely, the Silicon-carbon composite LSiAC sample (87 wt% Li4Ti5O12 + 3 wt% AC + 10 wt% Si) demonstrated a capacity of 349.19 mAh g−1 (98.28%) at a 1C rate after 200 cycles, and achieved a capacity of 196.56 mAh g−1 (89.37%) after 1000 cycles at a 5C rate,; in comparison, bare LTO exhibited capacities of only 230 .98 mAh g−1 (1C-89.71%)and 145.63 mAh g−1 (5C-82.48%). This improvement can be attributed to three factors: first, the active carbon enhances material conductivity while the active carbon coating and SEI films simultaneously as a barrier isolating Li4Ti5O12 from the electrolyte LiPF6, thereby preventing structural degradation; second, micron Si doping into Li4Ti5O12 crystals introduces additional capacity and leads to an appropriate amount of expansion during cycling, effectively increasing crystal plane spacing and facilitating Li+ migration. Final, the multi-layer core–shell structure consisting of Li4Ti5O12, active carbon coating, and SEI films acts as the buffer successfully limits the Si-Li15Si4 phase transition volume expansion. The proposed modification process is straightforward and environmentally friendly, making it suitable for industrial-scale production. This approach holds promise in bolstering the competitiveness of spinel Li4Ti5O12 as an anode material in the Lithium-ion battery market.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article [and/or its supplementary materials].
References
Osseo-Asare K, Arriagada FJ (1990) Preparation of SiO2 Nanoparticles in a Non-Ionic Reverse Micellar System. Colloids Surf 50:321–339
Arriagada FJ, Osseo-Asare K (1992) Phase and dispersion stability effects in the synthesis of silica nanoparticles in a non-ionic reverse microemulsion. Colloids Surf 69:105–115
Cheng J, Che R, Liang C, Liu J, Wang M, Xu J (2014) Hierarchical hollow Li4Ti5O12 urchin-like microspheres with ultra-high specific surface area for high rate lithium ion batteries. Nano Res 7:1043–1053
Wen R, Yue J, Ma Z, Chen W, Jiang X, Yu A (2014) Synthesis of Li4Ti5O12 nanostructural anode materials with high charge–discharge capability. Chin Sci Bull 59:2162–2174
Zhang H, Yang Y, Xu H, Wang L, Lu X, He X (2022) Li4Ti5O12 spinel anode: Fundamentals and advances in rechargeable batteries. InfoMat 4:e12228
Schmidt W, Bottke P, Sternad M, Gollob P, Hennige V, Wilkening M (2015) Small Change Great Effect: Steep Increase of Li Ion Dynamics in Li4Ti5O12 at the Early Stages of Chemical Li Insertion. Chem Mater 27:1740–1750
Pang WK, Peterson VK, Sharma N, Shiu J-J, Wu S-H (2014) Lithium migration in Li4Ti5O12 studied using in situ neutron powder diffraction. Chem Mater 26:2318–2326
Tsai P-C, Hsu W-D, Lin S-K (2014) Atomistic structure and ab initio electrochemical properties of Li4Ti5O12 defect spinel for Li ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 161:A439
Ahn D, Xiao X (2011) Extended lithium titanate cycling potential window with near zero capacity loss. Electrochem Commun 13:796–799
Scharner S, Weppner W, Schmid-Beurmann P (1999) Evidence of two-phase formation upon lithium insertion into the Li1.33Ti1.67O4 spinel. J Electrochem Soc 146:857
Li R, Lin C, Wang N, Luo L, Chen Y, Li J, Guo Z (2018) Advanced composites of complex Ti-based oxides as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Composites Hybrid Mat 1:440–459
Tanaka Y, Ikeda M, Sumita M, Ohno T, Takada K (2016) First-principles analysis on role of spinel (111) phase boundaries in Li4+3xTi5O12 Li-ion battery anodes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:23383–23388
Vijayakumar M, Kerisit S, Rosso KM, Burton SD, Sears JA, Yang Z, Graff GL, Liu J, Hu J (2011) Lithium diffusion in Li4Ti5O12 at high temperatures. J Power Sources 196:2211–2220
Ferg E, Gummow RD, De Kock A, Thackeray MM (1994) Spinel anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 141:147
Ge H, Li N, Li D, Dai C, Wang D (2009) Study on the theoretical capacity of spinel lithium titanate induced by low-potential intercalation. The J Physical Chem C 113:6324–6326
He Y-B, Liu M, Huang Z-D, Zhang B, Yu Y, Li B, Kang F, Kim J-K (2013) Effect of solid electrolyte interface (SEI) film on cyclic performance of Li4Ti5O12 anodes for Li ion batteries. J Power Sources 239:269–276
Zhang SS (2021) Design aspects of electrolytes for fast charge of Li-ion batteries. InfoMat 3:125–130
Yan H, Zhang D, Duo X, Sheng X (2021) A review of spinel lithium titanate (Li4Ti5O12) as electrode material for advanced energy storage devices. Ceram Int 47:5870–5895
Sun SY, Yao N, Jin CB, Xie J, Li XY, Zhou MY, Chen X, Li BQ, Zhang XQ, Zhang Q (2022) The crucial role of electrode potential of a working anode in dictating the structural evolution of solid electrolyte interphase. Angew Chem Int Ed 61:e202208743
He Y-B, Ning F, Li B, Song Q-S, Lv W, Du H, Zhai D, Su F, Yang Q-H, Kang F (2012) Carbon coating to suppress the reduction decomposition of electrolyte on the Li4Ti5O12 electrode. J Power Sources 202:253–261
Cheng Q, Tang S, Liu C, Zhao J, Cao Y (2017) Recent advances of Li4Ti5O12 as anode material for high power lithium-ion batteries. Gongneng Cailiao/J Funct Mat 48:12017–12022
Qing-feng S, Xian-ming W, Xian-wen W, Zhi-ru W, Jing-li L (2020) High performance of β-cyclodextrin-derived Li4Ti5O12/C anode composites for lithium-ion battery. Ionics 26:2217–2223
He Y-B, Li B, Liu M, Zhang C, Lv W, Yang C, Li J, Du H, Zhang B, Yang Q-H (2012) Gassing in Li4Ti5O12-based batteries and its remedy. Sci Rep 2:913
Demirel S, Altin S (2019) Structural properties and electrochemical performance V-doping Li2Ti3O7 and Li4Ti5O12 anode materials. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30:11665–11675
Wang Z, Yang W, Yang J, Zheng L, Sun K, Chen D, Sun L, Liu X (2020) Tuning the crystal and electronic structure of Li4Ti5O12 via Mg/La Co-doping for fast and stable lithium storage. Ceram Int 46:12965–12974
Salvatore KL, Lutz DM, Guo H, Yue S, Gan J, Tong X, Liu P, Takeuchi ES, Takeuchi KJ, Marschilok AC (2020) Solution-Based, Anion-Doping of Li4Ti5O12 Nanoflowers for Lithium-Ion Battery Applications. Chem Europ J 26:9389–9402
Ji X, Li D, Lu Q, Guo E, Yao L, Liu H (2018) Electrospinning preparation of one-dimensional Co2+-doped Li4Ti5O12 nanofibers for high-performance lithium ion battery. Ionics 24:1887–1894
Wu H, Chan G, Choi JW, Ryu I, Yao Y, McDowell MT, Lee SW, Jackson A, Yang Y, Hu L (2012) Stable cycling of double-walled silicon nanotube battery anodes through solid–electrolyte interphase control. Nat Nanotechnol 7:310–315
Gao H, Xiao L, Plümel I, Xu G-L, Ren Y, Zuo X, Liu Y, Schulz C, Wiggers H, Amine K (2017) Parasitic reactions in nanosized silicon anodes for lithium-ion batteries, Nano Letters. 1512–1519
Chan C, Peng H.L, Liu G, Mcilwrath GK, Zhang XF, Huggins RA, Cui Y (2008) Nat. Nanotechnol. 3:31–35.
Tang H, Zhang Y, Xiong Q, Cheng J, Zhang Q-C, Wang X, Gu C, Tu J (2015) Self-assembly silicon/porous reduced graphene oxide composite film as a binder-free and flexible anode for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 156:86–93
Epur R, Ramanathan M, Datta MK, Hong DH, Jampani PH, Gattu B, Kumta PN (2015) Scribable multi-walled carbon nanotube-silicon nanocomposites: a viable lithium-ion battery system. Nanoscale 7:3504–3510
Parekh MH, Sediako AD, Naseri A, Thomson MJ, Pol VG (2020) In Situ Mechanistic Elucidation of Superior Si-C-Graphite Li-Ion Battery Anode Formation with Thermal Safety Aspects. Adv Energy Mater 10:1902799
Ding X, Liu X, Huang Y, Zhang X, Zhao Q, Xiang X, Li G, He P, Wen Z, Li J (2016) Enhanced electrochemical performance promoted by monolayer graphene and void space in silicon composite anode materials. Nano Energy 27:647–657
Zhang W, Zuo P, Chen C, Ma Y, Cheng X, Du C, Gao Y, Yin G (2016) Facile synthesis of binder-free reduced graphene oxide/silicon anode for high-performance lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 312:216–222
Firnadya SA, Syahrial AZ, Subhan A (2018) Enhancing battery performance by nano Si addition to Li4Ti5O12 as anode material on lithium-ion battery. Ionics 24:1029–1037
Liu M, Gao H, Hu G, Zhu K, Huang H (2020) Facile preparation of core-shell Si@ Li4Ti5O12 nanocomposite as large-capacity lithium-ion battery anode, Journal of Energy. Chemistry 40:89–98
Takezawa H, Iwamoto K, Ito S, Yoshizawa H (2013) Electrochemical behaviors of nonstoichiometric silicon suboxides (SiOx) film prepared by reactive evaporation for lithium rechargeable batteries. J Power Sources 244:149–157
Zhang N, Li L, Shao Q, Zhu T, Huang X, Xiao X (2019) Fe-doped BiOCl nanosheets with light-switchable oxygen vacancies for photocatalytic nitrogen fixation. ACS Applied Energy Materials 2:8394–8398
Chen C, Huang Y, Zhang H, Wang X, Li G, Wang Y, Jiao L, Yuan H (2015) Small amount of reduce graphene oxide modified Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticles for ultrafast high-power lithium ion battery. J Power Sources 278:693–702
Lv S-X, Chen Q-L, Song F-X, Li Y-N (2021) One-step synthesis of a double conductive layer C-SiOx-TiO2 co-coated Li4Ti5O12 anode material toward a high-rate and large-capacity lithium-ion battery. Appl Surf Sci 555:149637
Zhang Q, Lu H, Zhong H, Yan X, Ouyang C, Zhang L (2015) W6+ & Br− codoped Li4Ti5O12 anode with super rate performance for Li-ion batteries. J Mat Chem A 3:13706–13716
Zhu G-N, Wang Y-G, Xia Y-Y (2012) Ti-based compounds as anode materials for Li-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 5:6652–6667
Takamura T, Endo K, Fu L, Wu Y, Lee KJ, Matsumoto T (2007) Identification of nano-sized holes by TEM in the graphene layer of graphite and the high rate discharge capability of Li-ion battery anodes. Electrochim Acta 53:1055–1061
Geng H, Ang H, Ding X, Tan H, Guo G, Qu G, Yang Y, Zheng J, Yan Q, Gu H (2016) Metal coordination polymer derived mesoporous Co3O4 nanorods with uniform TiO2 coating as advanced anodes for lithium ion batteries. Nanoscale 8:2967–2973
Jiang S, Zhao B, Chen Y, Cai R, Shao Z (2013) Li4Ti5O12 electrodes operated under hurdle conditions and SiO2 incorporation effect. J Power Sources 238:356–365
Obrovac M, Christensen L (2004) Structural changes in silicon anodes during lithium insertion/extraction. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 7:A93
Parekh MH, Palanisamy M, Pol VG (2023) Reserve lithium-ion batteries: Deciphering in situ lithiation of lithium-ion free vanadium pentoxide cathode with graphitic anode. Carbon 203:561–570
Shobukawa H, Alvarado J, Yang Y, Meng YS (2017) Electrochemical performance and interfacial investigation on Si composite anode for lithium ion batteries in full cell. J Power Sources 359:173–181
Yin M, Feng X, Zhao D, Zhao Y, Li H, Zhou W, Liu H, Bai X, Wang H, Feng C (2019) Hierarchical Co9S8@carbon hollow microspheres as an anode for sodium ion batteries with ultralong cycling stability. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 7:6122–6130
Wang L, Jiang B, Vullum PE, Svensson AM, Erbe A, Selbach SM, Xu H, Vullum-Bruer F (2018) High interfacial charge storage capability of carbonaceous cathodes for Mg batteries. ACS Nano 12:2998–3009
Chao D, Zhu C, Yang P, Xia X, Liu J, Wang J, Fan X, Savilov SV, Lin J, Fan HJ (2016) Array of nanosheets render ultrafast and high-capacity Na-ion storage by tunable pseudocapacitance. Nat Commun 7:12122
Du X, He W, Zhang X, Yue Y, Liu H, Zhang X, Min D, Ge X, Du Y (2012) Enhancing the electrochemical performance of lithium ion batteries using mesoporous Li3V2(PO4)3/C microspheres. J Mater Chem 22:5960–5969
Shimizu M, Usui H, Sakaguchi H (2016) Functional ionic liquids for enhancement of Li-ion transfer: the effect of cation structure on the charge–discharge performance of the Li4Ti5O12 electrode. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:5139–5147
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52074353), and the Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate (No. CX20231105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huan Kuang: Writing- Original draft preparation. Li Xiao: Conceptualization, Methodology. Yuan Lai: Data analysis and prepared figures. Li Shen: Supervision, Validation. Anni Zhou: synthesized experimental LSiAC. Juan Wu: AC testing. Yirong Zhu: Writing- Reviewing and Editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All analyses were based on previous published studies, thus no ethical approval and patient consent are required.
Competing interests
I declare that the authors have no competing interests as defined by Springer, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kuang, H., Xiao, L., Lai, Y. et al. Effect of Si Doping and Active Carbon Surface Modifications on the Structure and Electrical Performance of Li4Ti5O12 Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Ionics 30, 1307–1317 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-05367-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-05367-3