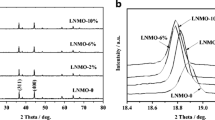
Abstract
The pristine LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 (LNMO) and Mo-F co-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel materials were prepared via a rheological phase method. The four samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Compared with the pristine LNMO sample, Mo-F co-doped LNMO materials could increase the lattice parameters, reduce particle sizes, and significantly improve the electrochemical performances of LNMO. The doped material exhibited optimum electrochemical properties when the Mo and F doping amounts were 1% and 3%, respectively, denoted as Mo/F-2. The discharge capacity retention of Mo/F-2 is 95.6%, which is higher than the pristine sample (87.7%) after 100 cycles at 1C and room temperature. Furthermore, the discharge-specific capacity of the Mo/F-2 sample reaches 113.4 mAh g−1 at 5C, while the pristine sample reaches only 61.9 mAh g−1. After CV and EIS analysis, it was found that the Mo-F co-doped LNMO materials had better Li+ diffusion kinetics than the pristine LNMO sample. Thus, Mo-F co-doping is considered an effective modification method for LNMO cathode material.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qin X, Zhou MS, Zong B, Guo JL, Gong JJ, Wang L, Liang GC (2018) Urea-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of a hollow hierarchical LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material with tunable morphology characteristics. Rsc Adv 8(53):30087–30097
Qureshi ZA, Tariq HA, Shakoor RA, Kahraman R, AlQaradawi S (2022) Impact of coatings on the electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials: a focused review. Ceram Int 48(6):7374–7392
Amin A, Muralidharan R, Petla RK, Yahia HB, Al-Hai SAJ, Essehli R, Darrel C, Khaleel NA, Belharouak I (2020) Research advances on cobalt-free cathodes for Li-ion batteries - the high voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as an example. J Power Sources 467:228318
Liu GQ, Wen L, Liu YM (2010) Spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 and its derivatives as cathodes for high-voltage Li-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 14(12):2191–2202
Lin FC, Wu HM, Chen TC, Zhou DF, Yan W, Guo JB (2022) The action of Y-F co-doping in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 positive electrode materials. Powder Technol 409:117182
Chen JX, Huang Z, Zeng WH, Cao F, Ma JJ, Tian WX, Mu SC (2021) Synthesis, modification, and lithium-storage properties of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. ChemElectroChem 8(4):608–624
Cabana J, Casas-Cabanas M, Omenya FO, Zeng DL, Whittingham MS, Grey CP (2012) Composition-structure relationships in the Li-Ion battery electrode material LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. Chem Mater 24(15):2952–2964
Wang LP, Li H, Huang XJ, Baudrin E (2011) A comparative study of Fd-3m and P4332 “LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4”. Solid State Ionics 193(1):32–38
Sun HB, Hu AY, Spence S, Kuai CG, Hou D, Mu LQ, Liu J, Li LX, Sun CG, Sainio S, Nordlund D, Luo W, Huang YH, Lin F (2022) Tailoring disordered/ordered phases to revisit the degradation mechanism of high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel cathode materials. Adv Funct Mater 32:2112279
Patoux S, Daniel L, Bourbon C, Lignier H, Pagano C, Cras FL, Jouanneau MS (2009) High voltage spinel oxides for Li-ion batteries: from the material research to the application. J Power Sources 189(1):344–352
Xiao J, Chen XL, Sushko PV, Sushko ML, Kovarik L, Feng JJ, Deng ZQ, Zhang JM, Graff GL, Nie ZM, Choi DW, Liu J, Zhang JG, Whittingham MS (2012) High-performance LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel controlled by Mn3+ concentration and site disorder. Adv Mater 24(16):2109–2116
Amin R, Belharouk I (2017) Part I: electronic and ionic transport properties of the ordered and disordered LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel cathode. J Power Sources 348:311–317
Atanasov M, Barras JL, Benco L, Daul C (2000) Electronic structure, chemical bonding, and vibronic coupling in Mn-IV/Mn-III mixed valent LixMn2O4 spinels and their effect on the dynamics of intercalated Li: a cluster study using DFT. J Am Chem Soc 122(19):4718–4728
Park OK, Cho Y, Lee S, Yoo HC, Song HK, Cho J (2011) Who will drive electric vehicles, olivine or spinel? Energy Environ Sci 4(5):1621–1633
Zhan C, Wu TP, Lu J, Amine K (2018) Dissolution, migration, and deposition of transition metal ions in Li-ion batteries exemplified by Mn-based cathodes - a critical review. Energy Environ Sci 11:243–257
Song YM, Han JG, Park S, Lee KT, Choi NS (2014) A multifunctional phosphite-containing electrolyte for 5 V-class LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes with superior electrochemical performance. J Mater Chem A 2(25):9506–9513
Liang G, Peterson VK, See KW, Guo ZP, Pang WK (2020) Developing high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes for high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries: current achievements and future prospects. J Mater Chem A 8:15373–15398
Piao JY, Sun YG, Duan SY, Yang XQ, Goodenough JB, Wan LJ (2018) Stabilizing cathode materials of lithium-ion batteries by controlling interstitial sites on the surface. Chem 4:1685–1695
Mao J, Dai KH, Xuan MJ, Shao GS, Qiao RM, Yang WL, Battaglia VS, Liu G (2016) Effect of chromium and niobium doping on the morphology and electrochemical performance of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(14):9116–9124
Zheng XT, Liu WJ, Qu QT, Zheng HH, Huang YH (2019) Bi-functions of titanium and lanthanum co-doping to enhance the electrochemical performance of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode. J Mater 5(2):156–163
Cui XL, Shi XM, Li GX, Li SY, Xu XL, Li YL, Mao LP, Ye XS (2013) Electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 doped with la and its compatibility with new electrolyte system. Russian J Electrochem. https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319351310011X
Ji X, Dai XY, Wu FZ, Mai Y, Chen HJ, Gu YJ (2021) In situ Sr2+ - doped spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for Li-ion batteries with high electrochemical performance and its impact on morphology. Ceram Int 47:32043–32052
Bini M, Boni P, Mustarelli P, Quinzeni I, Bruni G (2018) Silicon-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as a high-voltage cathode for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 320:1–6
Kim WK, Han DW, Ryu WH, Lim SJ, Eom JY, Kwon HS (2014) Effects of Cl doping on the structural and electrochemical properties of high voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. J Alloy Compd 592:48–52
Luo Y, Li HY, Lu TL, Zhang TX, Mao SS, Liu Z, Wen W, Xie JY, Yan LQ (2017) Fluorine gradient-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel with improved high voltage stability for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 238:237–245
Kim DW, Zettsu N, Shiiba H, Santolino GS, Ishikwa R, Ikuhara Y, Teshima K (2020) Metastable oxysulfide surface formation on LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 single crystal particles by carbothermal reaction with sulfur-doped heterocarbon nanoparticles: new insight into their structural and electrochemical characteristics, and their potential applications. J Mater Chem A 8(42):22302–22314
Li J, Li SF, Xu SJ, Huang S, Zhu JX (2017) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials with Cr3+ and F- composite doping for lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale Res Lett 12:414
Liu JJ, Yuan ML, Li Z, Xie S, Wang TX, Yan JQ, Peng J (2022) Improving the electrochemical performance of single crystal LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials by Y-Ti doping and unannealing process. Ceram Int 48(24):36490–36499
Wei AJ, Li W, Chang Q, Bai X, He R, Zhang LH, Liu ZF, Wang YJ (2019) Effect of Mg2+/F- co-doping on electrochemical performance of LiNi05Mn15O4 for 5 V lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 323:134692
Wei AJ, Mu JP, He R, Bai X, Li XH, Zhang LH, Wang YJ, Liu ZF, Wang SN (2021) Enhanced electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 composite cathodes for lithium-ion batteries by selective doping of K+/Cl and K+/F. Nanomaterials 11(9):2323
Wei AJ, Mu JP, He R, Bai X, Li XH, Wang YJ, Liu ZF, Wang SN (2021) Li+ and Cl- co-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material with truncated octahedral shape and enhanced electrochemical performance for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 371:115753
Zeng FF, Zhang Y, Shao ZC (2023) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Mo-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material. Mater Manuf Process 38(2):197–205
Kim DW, Shiiba H, Zettsu N, Yamada T, Kimijima T et al (2017) Full picture discovery for mixed-fluorine anion effects on high-voltage spinel lithium nickel manganese oxide cathodes. NPG Asia Mater 9:e398
Yi TF, Han X, Chen B, Zhu YR, Xie Y (2017) Porous sphere-like LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 - CeO2 composite with high cycling stability as cathode material for lithium-ion battery. J Alloy Compd 703:103–113
Chen TC, Lin FC, Wu HM, Zhou DF, Song JL, Guo JB (2023) Zn-Y co-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials with high electrochemical performance. J Alloys Compds 941:168825
Liu GQ, Wen L, Wang X, Ma BY (2011) Effect of the impurity LixNi1-xO on the electrochemical properties of 5 V cathode material LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. J Alloys Compds 509(38):9377–9381
Chen MF, Chen P, Yang F, Song HY, Liao SJ (2016) Ni, Mo Co-doped lithium manganate with significantly enhanced discharge capacity and cycling stability. Electrochim Acta 206:356–365
Hagh NM, Amatucci GG (2014) Effect of cation and anion doping on microstructure and electrochemical properties of the LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4δ spinel. J Power Sources 256:457–469
Potapenko AV, Kirillov SA (2014) Lithium manganese spinel materials for high-rate electrochemical applications. J Energy Chem 23(5):543–558
Lin FC, Guo JB, Wang LY, Zhou Y, Wu HM, Zhou DF (2021) Synergistic effect of Mg and Y co-dopants on enhancement of electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel. Electrochim Acta 399:139433
Kunduraci M, Amatucci GG (2006) Synthesis and characterization of nanostructured 47 V LixNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinels for high-power lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 153(7):A1345–A1352
Yang JG, Han XP, Zhang XL, Cheng FY, Chen J (2013) Spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries: nano vs micro, ordered phase (P4332) vs disordered phase (Fd3m). Nano Res 6(9):679–87
Liu RR, Deng X, Liu XR, Yan HJ, Cao AM, Wang D (2014) Facet dependent SEI formation on the LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode identified by in situ single particle atomic force microscopy. Chem Commun 50(99):15756–15759
Miyashiro H, Seki S, Kobayashi Y, Ohno Y, Mita Y, Usami A (2005) All-solid-state lithium polymer secondary battery with LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by mixing of Li3PO4. Electrochem Commun 7(11):1083–1086
Yi TF, Chen B, Zhu YR, Li XY, Zhu RS (2014) Enhanced rate performance of molybdenum-doped spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for lithium ion battery. J Power Sources 247:778–785
Lin MX, Ben LB, Sun Y, Wang H, Yang ZZ, Gu L, Yu XQ, Yang XQ, Zhao HF, Yu RC, Armand M, Huang XJ (2015) Insight into the atomic structure of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material in the first cycle. Chem Mater 27(1):292–303
Yan SP, Sun XL, Zhang Y, Fu SX, Lang YQ, Wang L, Liang GC (2022) From coating to doping: effect of post-annealing temperature on the alumina coating of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material. J Solid State Chem 306:122765
Yi TF, Xie Y, Zhu YR, Zhu RS, Ye MF (2012) High rate micron-sized niobium-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as ultra high power positive-electrode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 211:59–65
Zhou DF, Lin FC, Song JL, Guo JB (2022) Exploring the action of rare-earth yttrium dopant on enhancing electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 material. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33(20):16621–16637
Yang HP, Zhang HL, Zhao WT (2023) Improvement of electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 by LaF3 coating at high cut-off voltage. Ionics 29:1335–1345
Deng JC, Xu YL, Xiong LL, Li L, Sun XF, Zhang Y (2016) Improving the fast discharge performance of high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel by Cu2+, Al3+, Ti4+ tri-doping. J Alloy Compd 677:18–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL has done the synthesis experiments, assembled the coin cells and tested the electrochemical properties. HL has designed the research program and evaluation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No human and/or animal studies have been included in this paper. Also, no other ethical problems are involved.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, Y., Zhang, H. Enhancement of the electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for Li-ion battery by Mo-F co-doping. Ionics 30, 1885–1895 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-05366-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-05366-4