Abstract
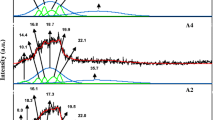
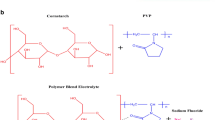
The present work deals with the preparation and characterization of polymer blend electrolyte films. Glutaraldehyde is used as a cross-linker to cross-link polymers polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and starch for the proper film formation. Structural characterizations such as X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) have been performed. X-ray diffraction is done to investigate the amorphous nature of the sample. FTIR study confirms about the complexation of salt with the polymer and interaction of thiocyanate ion with the polymer matrix. Electrical characterizations were done using impedance spectroscopy. DC and AC ionic conductivity was obtained at varying salt concentration in the films which shows maximum ionic conductivity of the polymer electrolyte containing 30 wt% of salt content. The AC conductivity behaviour of the polymer electrolyte follows Jonscher’s power law. Dielectric parameters such as dielectric constant, dielectric loss and loss tangent have been determined. Relaxation time is obtained and decreases to lower value with the increase in the salt concentration in the polymer electrolyte.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shreekanth T, Reddy MJ, Subramanyam S, Rao UVS (1999) Ion conducting polymer electrolyte films based on (PEO+KNO3) system and its application as an electrochemical cell. Mater Sci Eng B 64:107–112. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.01.030
Polu AR, Kumar R (2013) Preparation and characterization of PVA based solid polymer electrolytes for electrochemical cell applications. Chin J Polym Sci 31:641–648. doi:10.1007/s10118-013-1246-3
Hatta FF, Yahya MZA, Ali AMM, Subban RHY, Harun MK, Mohamad AA (2005) Electrical conductivity studies on PVA/PVP-KOH alkaline solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics 11:418–422
Mahendran O, Rajendran S (2003) Ionic conductivity studies in PMMA/PVDF polymer blend electrolyte with lithium salts. Ionics 9:282–288
Lenz RW (1993) Biodegradable polymers. Adv Polym Sci 107:1–40
Avella M, Vlieger JDJ, Errico MA, Fischer S, Vacca P, Volpe MG (2005) Biodegradable starch/clay nanocomposite films for food packaging applications. Food Chem 93:467–474. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.10.024
Tang X, Alavi S (2011) Recent advances in starch, polyvinyl alcohol based polymer blends, nanocomposites and their biodegradability. Carbohydr Polym 85:7–16. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.01.030
Azahari A, Othman N, Ismail H (2011) Biodegradation studies of polyvinyl alcohol/corn starch blend films in solid and solution media. J Phys Sci 22:15–31
Tudorachi N, Cascaval CN, Rusu Z, Pruteanu M (2000) Testing of polyvinyl alcohol and starch mixtures as biodegradable polymeric materials. Polym Test 19:785–799. doi:10.1016/S0142-9418(99)00049-5
Yang SY, Liu CI, Wu JY, Kuo JC, Huang CY (2008) Improving the processing ability and mechanical strength of starch/poly(vinyl alcohol) blends through plasma and acid modification. Macromol Symp 272:150–155. doi:10.1002/masy.200851222
Park HR, Chough SH, Yun YH, Yoon SD (2005) Properties of starch: PVA blend films containing citric acid as additive. J Polym Environ 13:375–382. doi:10.1007/s10924-005-5532-1
Lawton JW, Fanta GF (1994) Glycerol-plasticized films prepared from poly(vinyl alcohol) mixtures: effect of poly(ethylene-co-acrylic acid). Carbohydr Polym 23:275–280
Ramaraj B (2007) Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) and starch composite films. II. Physicomechanical, thermal properties and swelling studies. J Appl Polym Sci 103:906–916. doi:10.1002/app.25237
Sreedhar B, Sairam M, Chattopadhyay DK, Rathnam PAS, Rao DVM (2005) Thermal, mechanical, and surface characterization of starch-poly(vinyl alcohol) blends and borax-crosslinked films. J Appl Polym Sci 96:1313–1322. doi:10.1002/app.21439
Yoon S, Chough S, Park H (2007) Preparation of resistant starch/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend films with added plasticizer and crosslinking agents. J Appl Polym Sci 106:2485–2493. doi:10.1002/app.26755
Agrawal SL, Rai N, Natarajan TS, Chand N (2013) Electrical characterization of PVA-based nanocomposite electrolyte nanofibre mats doped with a multiwalled carbon nanotube. Ionics 19:145–154. doi:10.1007/s11581-012-0713-0
Kulshrestha N, Chatterjee B, Gupta PN (2014) Characterization and electrical properties of polyvinyl alcohol based polymer electrolyte films doped with ammonium thiocyanate. Mater Sci Eng B 184:49–57. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2014.01.012
Khandale AP, Bhoga SS, Gedam SK (2013) Study on ammonium acetate salt-added polyvinyl alcohol-based solid proton-conducting polymer electrolytes. Ionics 19:1619–1626. doi:10.1007/s11581-013-0899-9
Khiar ASA, Arof AK (2010) Conductivity studies of starch-based polymer electrolytes. Ionics 16:123–129. doi:10.1007/s11581-009-0356-y
Yusof YM, Shukur MF, Illias HAand Kadir MFZ (2014) Conductivity and electrical properties of corn starch–chitosan blend biopolymer electrolyte incorporated with ammonium iodide. Phys Scr 89:035701–035710. doi:10.1088/0031-8949/89/03/035701
Ramya CS, Selvasekarapandian S, Savitha T, Hirankumar G, Angelo PC (2007) Vibrational and impedance spectroscopic study on PVP–NH4SCN based polymer electrolytes. Physica B 393:11–17. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2006.11.021
Hafiza MN, Isa MIN (2014) Ionic conductivity and conduction mechanism studies of CMC/chitosan biopolymer blend electrolytes. Res J Recent Sci 3:50–56
Chatterjee B, Kulshrestha N, Gupta PN (2015) Electrical properties of starch-PVA biodegradable polymer blend. Phys Scr 90:025805–025813. doi:10.1088/0031-8949/90/2/025805
Prajapati GK, Gupta PN (2011) Comparative study of the electrical and dielectric properties of PVA–PEG–Al2O3–MI (M=Na, K, Ag) complex polymer electrolytes. Physica B 406:3108–3113. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2011.05.019
Ibrahim S, Yasin SMM, Nee NM, Ahmad R, Johan MR (2012) Conductivity and dielectric behaviour of PEO-based solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Solid State Commun 152:426–434. doi:10.1016/j.ssc.2011.11.037
Majid SR, Arof AK (2007) Electrical behavior of proton-conducting chitosan-phosphoric acid-based electrolytes. Physica B 390:209–215. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2006.08.038
Tripathi SK, Gupta A, Kumari M (2012) Studies on electrical conductivity and dielectric behaviour of PVdF–HFP–PMMA–NaI polymer blend electrolyte. Bull Mater Sci 35:969–975
Ravi M, Bhavani S, Pavani Y, Rao VVRN (2013) Investigation of electrical and dielectric properties of PVP:KClO4 polymer electrolyte films. Ind J Pure Appl Phys 51:362–366
Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Samantaray BK (2009) Studies of dielectric and electrical properties of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Mater Chem Phys 11:557–561. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.01.008
Venkateswarlu M, Satyanarayana N (1998) AC conductivity studies of silver based fast ion conducting glassy materials for solid state batteries. Mater Sci Eng B 54:189–195. doi:10.1016/S0921-5107(98)00156-1
Ravi M, Song S, Gu K, Tang J, Zhan Z (2015) Electrical properties of biodegradable poly(caprolactone): lithiumthiocyanate complexed polymer electrolyte films. Mater Sci Eng B 195:74–83. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2015.02.003
Jonscher AK (1972) Frequency-dependence of conductivity in hopping systems. J Non-Cryst Solids 8–10:293–315. doi:10.1016/0022-3093(72)90151-2
Acknowledgments
One of the authors, N. Kulshrestha, is thankful to UGC for the award of Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) under University with Potential of Excellence Scheme (UPE). The authors are thankful to Mr. M. Gupta for kind help in the experimental observations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulshrestha, N., Gupta, P.N. Structural and electrical characterizations of 50:50 PVA:starch blend complexed with ammonium thiocyanate. Ionics 22, 671–681 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1588-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1588-7