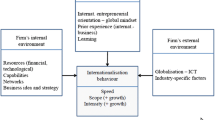
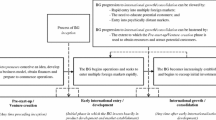
Abstract
Born globals (BG)’ post-entry evolution is a process characterized by superior growth opportunities, but also higher risks of failure. These concerns lead to the fundamental question regarding the factors that may play a role in BGs’ post-entry performance and survival. To provide a comprehensive picture on this issue, this paper critically examines 185 articles that have appeared in 39 academic journals over the past three decades. Drawing on complexity theory, we map a dynamic complex system comprising the interplay of six components relating to system inputs, managerial and firm-level capabilities – e.g., innovativeness, learning, and experience – , networks and system outputs – e.g., international growth and survival. Our review also suggests that strategic choices and orientations may act as change catalysts that bring BGs’ complex systems to the next stages of evolution, with further consequences on firm expansion. Our review contributes to the extant literature by taking stock of the present state of knowledge, and providing a taxonomy on the components of the dynamic system that influences the post-entry performance and survival of BGs. Furthermore, this paper and the resulting taxonomy unpacks the various sources of BGs’ heterogeneity, based on factors such as their different resources, capabilities, and strategies. In doing so, the paper uncovers significant gaps and contradictions in the literature, which opens important opportunities for future research. The paper concludes with a discussion of managerial and public policy implications.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The Edwards-Venn diagram counts the number of articles on each research theme. For example, it shows that seven articles examine the effects solely of networks, six examine networks and firm capabilities, three investigate networks and managers’ characteristics, and so on.
Although Kocak and Abimbola (2009) define learning orientation based on managers’ open-mindedness and commitment to learning, we have included this element within strategic orientations (and not managers’ characteristics) because these authors define and analyze it as an organizational feature. That is, they examine how managers render firm learning oriented through their activities and attitudes.
Furnari et al. (2021) suggest using a “fact-foil” approach to identify equifinal configurations. This approach involves that a set of factors theorized or observed to explain a phenomenon (“the fact”) is compared to a similar set of attributes that did not lead to that phenomenon (the “foil”), with the idea of the comparison being that a potential reason may be found where the causal histories of the fact and the foil differ. In other words, this process entails answering the question, ‘Why X [fact] rather than Y [foil]?’.
References
Aguilera, R. V., Crespí-Cladera, R., Infantes, P. M., & Pascual-Fuster, B. (2020). Business groups and internationalization: Effective identification and future agenda. Journal of World Business, 55(4), 101050.
Aguilera, R. V., Desender, K., Bednar, M. K., & Lee, J. H. (2015). Connecting the dots: Bringing external corporate governance into the corporate governance puzzle. Academy of Management Annals, 9(1), 483–573.
Altshuler, L., & Tarnovskaya, V. V. (2010). Branding capability of technology born globals. Journal of Brand Management, 18(3), 212–227.
Anderson, P. (1999). Perspective: Complexity theory and organization science. Organization Science, 10(3), 216–232.
Andersson, S., Awuah, G. B., Aagerup, U., & Wictor, I. (2020). How do mature born globals create customer value to achieve international growth? International Marketing Review.
Autio, E. (2017). Strategic entrepreneurial internationalization: A normative framework. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 11(3), 211–227.
Autio, E., Sapienza, H. J., & Almeida, J. G. (2000). Effects of age at entry, knowledge intensity, and imitability on international growth. Academy of Management Journal, 43(5), 909–924.
Bai, W., Liu, R., & Zhou, L. (2020). Enhancing the learning advantages of newness: The role of internal social capital in the international performance of young entrepreneurial firms. Journal of International Management, 26, 100733.
Baronchelli, G., & Cassia, F. (2014). Exploring the antecedents of born-global companies’ international development. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 10(1), 67–79.
Belhoste, N., Bocquet, R., Favre-Bonté, V., & Bally, F. (2019). How do SMEs use support services during their internationalisation process: A comparative study of French traditional SMEs and INVs in Asia. International Small Business Journal: Researching Entrepreneurship 37(8), 804–830. https://doi.org/10.1177/0266242619871165
Bembom, M., & Schwens, C. (2018). The role of networks in early internationalizing firms: A systematic review and future research agenda. European Management Journal, 36(6), 679–694.
Berg, M. S., Aspelund, A., & Sørheim, R. (2008). The hybrid structures of international new ventures: A social capital approach and research agenda. The International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation, 9(1), 33–42.
Blesa, A., & Ripollés, M. (2020). Critical capabilities for widening international new ventures’ geographical scope. European Management Journal.
Blomqvist, K., Hurmelinna-Laukkanen, P., Nummela, N., & Saarenketo, S. (2008). The role of trust and contracts in the internationalization of technology-intensive Born Globals. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 25(1–2), 123–135.
Bunz, T., Casulli, L., Jones, M. V., & Bausch, A. (2017). The dynamics of experiential learning: Microprocesses and adaptation in a professional service INV. International Business Review, 26(2), 225–238.
Cavusgil, S. T., & Knight, G. (2015). The born global firm: An entrepreneurial and capabilities perspective on early and rapid internationalization. Journal of International Business Studies, 46(1), 3–16.
Chiva, R., Ghauri, P., & Alegre, J. (2014). Organizational learning, innovation and internationalization: A complex system model. British Journal of Management, 25(4), 687–705.
Ciszewska-Mlinarič, M., Wójcik, P., & Obłój, K. (2020). Learning dynamics of rapidly internationalizing venture: Beyond the early stage of international growth in a CEE context. Journal of Business Research 108, 450–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.03.002
Clegg, J., Lin, H. M., Voss, H., Yen, I.-F., Shih, Y. T. (2016). The OFDI patterns and firm performance of Chinese firms: The moderating effects of multinationality strategy and external factors. International Business Review 25(4), 971–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2016.01.010
Connelly, B. L., Hoskisson, R. E., Tihanyi, L., & Certo, S. T. (2010). Ownership as a form of corporate governance. Journal of Management Studies, 47(8), 1561–1589.
Coviello, N., & Munro, H. (1997). Network relationships and the internationalisation process of small software firms. International Business Review, 6(4), 361–386.
Coviello, N. E. (2006). The network dynamics of international new ventures. Journal of International Business Studies, 37(5), 713–731.
Covin, J. G., & Miller, D. (2014). International entrepreneurial orientation: Conceptual considerations, research themes, measurement issues, and future research directions. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 38(1), 11–44.
Cyert, R. M., & March, J. G. (1963). A behavioral theory of the firm. Englewood Cliffs
Dillon, M. (2000). Poststructuralism, complexity and poetics. Theory, Culture and Society, 17(5), 1–26.
Efrat, K., & Shoham, A. (2012). Born global firms: The differences between their short-and long-term performance drivers. Journal of World Business, 47(4), 675–685.
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Martin, J. A. (2000). Dynamic capabilities: What are they? Strategic Management Journal, 21(10–11), 1105–1121.
Evers, N., Andersson, S., & Hannibal, M. (2012). Stakeholders and marketing capabilities in international new ventures: Evidence from Ireland, Sweden, and Denmark. Journal of International Marketing, 20(4), 46–71.
Fainshmidt, S., Witt, M. A., Aguilera, R. V., & Verbeke, A. (2020). The contributions of qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) to international business research. Journal of International Business Studies, 51(4), 455–466.
Falahat, M., Knight, G., & Alon, I. (2018). Orientations and capabilities of born global firms from emerging markets. International Marketing Review, 35, 936.
Falay, Z., Salimäki, M., Ainamo, A., & Gabrielsson, M. (2007). Design-intensive born globals: A multiple case study of marketing management. Journal of Marketing Management, 23(9–10), 877–899.
Fama, E. F., & Jensen, M. C. (1983). Separation of ownership and control. The Journal of Law and Economics, 26(2), 301–325.
Fariborzi, H., & Keyhani, M. (2018). Internationalize to live: A study of the post-internationalization survival of new ventures. Small Business Economics, 50(3), 607–624.
Faroque, A. R., Mostafiz, M. I., Faruq, M. O., & Bashar, M. F. B. (2020). Revisiting entrepreneurial capabilities and export market orientation: a multi-scale investigation in an emerging economy. International Journal of Emerging Markets.
Federo, R., Ponomareva, Y., Aguilera, R. V., Saz-Carranza, A., & Losada, C. (2020). Bringing owners back on board: A review of the role of ownership type in board governance. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 28(6), 348–371.
Felzensztein, C., Ciravegna, L., Robson, P., & Amorós, J. E. (2015). Networks, entrepreneurial orientation, and internationalization scope: Evidence from Chilean small and medium enterprises. Journal of Small Business Management, 53(sup1), 145–160.
Freeman, S., Hutchings, K., Lazaris, M., & Zyngier, S. (2010). A model of rapid knowledge development: The smaller born-global firm. International Business Review, 19(1), 70–84.
Freixanet, J. (2010). La evaluación del impacto de los programas de promoción de la internacionalización: una aplicación al caso de las empresas de Cataluña. Información Comercial Española, ICE: Revista de economía, (854), 105–121.
Freixanet, J. (2012). Export promotion programs: Their impact on companies’ internationalization performance and competitiveness. International Business Review, 21(6), 1065–1086.
Freixanet, J. (2022). Export promotion programs: A system-based systematic review and agenda for future research. Journal of World Business 57(4), 101344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2022.101344
Freixanet, J., Braojos, J., Rialp-Criado, A., & Rialp-Criado, J. (2020a). Does international entrepreneurial orientation foster innovation performance? The mediating role of social media and open innovation. The International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation, 1465750320922320.
Freixanet, J., & Renart, G. (2020). A capabilities perspective on the joint effects of internationalization time, speed, geographic scope and managers’ competencies on SME survival. Journal of World Business, 55(6), 101110.
Freixanet, J., Renart, G., & Rialp-Criado, A. (2018). The impact of managers’ global orientation on SME export and economic performance. Management International Review, 58(4), 571–604.
Freixanet, J., Rialp, A., & Churakova, I. (2020b). How do innovation, internationalization, and organizational learning interact and co-evolve in small firms? A complex systems approach. Journal of Small Business Management, 58(5), 1030–1063.
Freixanet, J., Monreal, J., & Sánchez-Marín., G. (2020c). Family firms’ selective learning-by-exporting: Product vs process innovation and the role of technological capabilities. Multinational Business Review 29(2), 210–236. https://doi.org/10.1108/MBR-01-2020-0011
Furnari, S., Crilly, D., Misangyi, V. F., Greckhamer, T., Fiss, P. C., & Aguilera, R. V. (2021). Capturing causal complexity: Heuristics for configurational theorizing. Academy of Management Review, 46(4), 778–799.
Gabrielsson, M., Gabrielsson, P., & Dimitratos, P. (2014). International entrepreneurial culture and growth of international new ventures. Management International Review, 54(4), 445–471.
Gabrielsson, M., & Kirpalani, V. M. (2004). Born globals: How to reach new business space rapidly. International Business Review, 13(5), 555–571.
Gabrielsson, P., & Gabrielsson, M. (2013). A dynamic model of growth phases and survival in international business-to-business new ventures: The moderating effect of decision-making logic. Industrial Marketing Management, 42(8), 1357–1373.
Gabrielsson, M., Kirpalani, V. H. M., Dimitratos, P., Solberg, C. A., Zucchella, A. (2008). Born globals: Propositions to help advance the theory. International Business Review 17(4), 385–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2008.02.015
Gassmann, O., & Keupp, M. M. (2007). The competitive advantage of early and rapidly internationalising SMEs in the biotechnology industry: A knowledge-based view. Journal of World Business, 42(3), 350–366.
Gaur, A., & Kumar, M. (2018). A systematic approach to conducting review studies: An assessment of content analysis in 25 years of IB research. Journal of World Business, 53(2), 280–289.
Gerschewski, S., Lew, Y. K., Khan, Z., & Park, B. I. (2018). Post-entry performance of international new ventures: The mediating role of learning orientation. International Small Business Journal, 36(7), 807–828.
Gerschewski, S., Rose, E. L., & Lindsay, V. J. (2015). Understanding the drivers of international performance for born global firms: An integrated perspective. Journal of World Business, 50(3), 558–575.
Gerschewski, S., & Xiao, S. S. (2015). Beyond financial indicators: An assessment of the measurement of performance for international new ventures. International Business Review, 24(4), 615–629.
Gresov, C., & Drazin, R. (1997). Equifinality: Functional equivalence in organization design. Academy of Management Review 22(2), 403–428. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.1997.9707154064
Greve, A., & Salaff, J. W. (2003). Social networks and entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 28(1), 1–22.
Habbershon, T. G. (2006). Commentary: A framework for managing the familiness and agency advantages in family firms. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 30(6), 879–886.
Hagen, B., & Zucchella, A. (2014). Born global or born to run? The long-term growth of born global firms. Management International Review, 54(4), 497–525.
Hallbäck, J., & Gabrielsson, P. (2013). Entrepreneurial marketing strategies during the growth of international new ventures originating in small and open economies. International Business Review, 22(6), 1008–1020.
Hambrick, D. C., & Mason, P. A. (1984). Upper echelons: The organization as a reflection of its top managers. Academy of Management Review, 9(2), 193–206.
Han, M. (2008). Achieving superior international new venture (INV) performance: exploting short-term duration of ties. Journal of Enterprising Culture 16(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218495808000028
Hashai, N. (2011). Sequencing the expansion of geographic scope and foreign operations by “born global” firms. Journal of International Business Studies, 42(8), 995–1015.
Hennart, J. F. (2007). The theoretical rationale for a multinationality-performance relationship. Management International Review, 47(3), 423–452.
Holcomb, T. R., Holmes, R. M., & Hitt, M. A. (2006). Diversification to achieve scale and scope: The strategic implications of resource management for value creation. Advances in Strategic Management: Ecology and Strategy, 23, 549–587.
Hughes, M., Cesinger, B., Cheng, C. F., Schuessler, F., & Kraus, S. (2019). A configurational analysis of network and knowledge variables explaining Born Globals’ and late internationalizing SMEs’ international performance. Industrial Marketing Management, 80, 172–187.
Hughes, M., Martin, S. L., Morgan, R. E., & Robson, M. J. (2010). Realizing product-market advantage in high-technology international new ventures: The mediating role of ambidextrous innovation. Journal of International Marketing, 18, 1–21.
Jain, N. K., Celo, S., & Kumar, V. (2019). Internationalization speed, resources and performance: Evidence from Indian software industry. Journal of Business Research, 95, 26–37.
Jiang, G., Kotabe, M., Hamilton, R. D., III., & Smith, S. W. (2016). Early internationalization and the role of immigration in new venture survival. International Business Review, 25(6), 1285–1296.
Jiang, G., Kotabe, M., Zhang, F., Hao, A. W., Paul, J., & Wang, C. L. (2020). The determinants and performance of early internationalizing firms: A literature review and research agenda. International Business Review, 29, 101662.
Jin, B., Chung, J. E., Yang, H., & Jeong, S. W. (2018). Entry market choices and post-entry growth patterns among born globals in consumer goods sectors. International Marketing Review, 35, 958.
Johanson, J., & Vahlne, J. E. (1977). The internationalization process of the firm – A model of knowledge development and increasing foreign market commitments. Journal of International Business Studies, 8(1), 23–32.
Johanson, J., & Vahlne, J.-E. (2003). Business relationship learning and commitment in the internationalisation process. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 1(1), 83–101.
Johanson, M., & Martín, O. M. (2015). The incremental expansion of Born Internationals: A comparison of new and old Born Internationals. International Business Review, 24(3), 476–496.
Jones, C., Hesterly, W. S., & Borgatti, S. P. (1997). A general theory of network governance: Exchange conditions and social mechanisms. Academy of Management Review, 22(4), 911–945.
Jones, M. V., & Coviello, N. E. (2005). Internationalisation: Conceptualising an entrepreneurial process of behaviour in time. Journal of International Business Studies, 36(3), 284–303.
Khan, Z., & Lew, Y. K. (2018). Post-entry survival of developing economy international new ventures: A dynamic capability perspective. International Business Review, 27(1), 149–160.
Khavul, S., Peterson, M., Mullens, D., & Rasheed, A. A. (2010). Going global with innovations from emerging economies: Investment in customer support capabilities pays off. Journal of International Marketing, 18(4), 22–42.
Kim, D., Basu, C., Naidu, G. M., & Cavusgil, E. (2011). The innovativeness of born-globals and customer orientation: Learning from Indian born-globals. Journal of Business Research, 64(8), 879–886.
Knight, G. A., & Cavusgil, S. T. (1996). The born global firm: A challenge to traditional internationalization theory. Advances in International Marketing, 8(1), 11–26.
Knight, G. A., & Cavusgil, S. T. (2004). Innovation, organizational capabilities, and the born-global firm. Journal of International Business Studies, 35(2), 124–141.
Kocak, A., & Abimbola, T. (2009). The effects of entrepreneurial marketing on born global performance. International Marketing Review, 26, 439.
Laanti, R., Gabrielsson, M., & Gabrielsson, P. (2007). The globalization strategies of business-to-business born global firms in the wireless technology industry. Industrial Marketing Management, 36(8), 1104–1117.
Lee, I. H., Paik, Y., & Uygur, U. (2016). Does gender matter in the export performance of international new ventures? Mediation effects of firm-specific and country-specific advantages. Journal of International Management, 22(4), 365–379.
Li, Q., & Deng, P. (2017). From international new ventures to MNCs: Crossing the chasm effect on internationalization paths. Journal of Business Research, 70, 92–100.
Liu, Y. (2017). Born global firms’ growth and collaborative entry mode: The role of transnational entrepreneurs. International Marketing Review.
Loane, S., Bell, J. D., & McNaughton, R. (2007). A cross-national study on the impact of management teams on the rapid internationalization of small firms. Journal of World Business, 42(4), 489–504.
Lumpkin, G. T., & Dess, G. G. (2001). Linking two dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation to firm performance: The moderating role of environment and industry life cycle. Journal of Business Venturing, 16(5), 429–451.
Madsen, T. K. (2013). Early and rapidly internationalizing ventures: Similarities and differences between classifications based on the original international new venture and born global literatures. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 11(1), 65–79.
Martin, S. L., & Javalgi, R. R. G. (2016). Entrepreneurial orientation, marketing capabilities and performance: The moderating role of competitive intensity on Latin American International new ventures. Journal of Business Research, 69(6), 2040–2051.
Martin, S. L., & Javalgi, R. R. G. (2019). Explaining performance determinants: A knowledge based view of international new ventures. Journal of Business Research, 101, 615–626.
Martin, S. L., Javalgi, R. R. G., & Ciravegna, L. (2018). Service advantage built on service capabilities: An empirical inquiry of international new ventures. Journal of Business Research, 88, 371–381.
Meschi, P. X., Ricard, A., & Moore, E. T. (2017). Fast and furious or slow and cautious? The joint impact of age at internationalization, speed, and risk diversity on the survival of exporting firms. Journal of International Management, 23(3), 279–291.
Miller, D., Steier, L., & Le Breton-Miller, I. (2003). Lost in time: Intergenerational succession, change, and failure in family business. Journal of Business Venturing, 18(4), 513–531.
Misangyi, V. F., Greckhamer, T., Furnari, S., Fiss, P. C., Crilly, D., & Aguilera, R. (2017). Embracing causal complexity: The emergence of a neo-configurational perspective. Journal of Management, 43(1), 255–282.
Mort, G. S., & Weerawardena, J. (2006). Networking capability and international entrepreneurship: How networks function in Australian born global firms. International Marketing Review, 23(5), 549–572.
Mudambi, R., & Zahra, S. A. (2007). The survival of international new ventures. Journal of International Business Studies, 38(2), 333–352.
Nadkarni, S., Herrmann, P., & Perez, P. D. (2011). Domestic mindsets and early international performance: The moderating effect of global industry conditions. Strategic Management Journal, 32(5), 510–531.
Nadler, D. A., & Tushman, M. L. (1980). A model for diagnosing organizational behavior. Organizational Dynamics, 9(2), 35–51.
Nemkova, E. (2017). The impact of agility on the market performance of born-global firms: An exploratory study of the ‘Tech City’ innovation cluster. Journal of Business Research, 80, 257–265.
Neuendorf, K. A. (2017). The content analysis guidebook. Sage.
Nguyen, Q. A., & Mort, G. S. (2020). Conceptualising organisational-level and microfoundational capabilities: An integrated view of born-globals’ internationalisation. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 17, 1–23.
Nonaka, I., Hirose, A., & Takeda, Y. (2016). ‘Meso’-foundations of dynamic capabilities: Team-level synthesis and distributed leadership as the source of dynamic creativity. Global Strategy Journal, 6(3), 168–182.
Nummela, N., Saarenketo, S., & Loane, S. (2016). The dynamics of failure in international new ventures: A case study of Finnish and Irish software companies. International Small Business Journal, 34(1), 51–69.
Oviatt, B. M., & McDougall, P. P. (1994). Toward a theory of international new ventures. Journal of International Business Studies, 25(1), 45–64.
Oviatt, B. M., & McDougall, P. P. (1995). Global start-ups: Entrepreneurs on a worldwide stage. Academy of Management Executive, 9(2), 30–43.
Parente, T. C., & Federo, R. (2019). Qualitative comparative analysis: Justifying a neo-configurational approach in management research. RAUSP Management Journal, 54, 399–412.
Park, T., & Rhee, J. (2012). Antecedents of knowledge competency and performance in born globals. Management Decision, 50, 1361.
Patel, P. C., Criaco, G., & Naldi, L. (2018). Geographic diversification and the survival of born-globals. Journal of Management, 44(5), 2008–2036.
Pellegrino, J. M., & McNaughton, R. B. (2015). The co-evolution of learning and internationalization strategy in international new ventures. Management International Review, 55(4), 457–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11575-015-0246-7
Pfeffer, J., & Salancik, G. R. (1978). A resource dependence perspective. In Intercorporate relations. The structural analysis of business. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Post, C., Sarala, S., Gatrell, C., & Prescott, J. E. (2020). Advancing Theory with Review Articles. Journal of Management Studies 57(2), 351–376. https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12549
Prashantham, S., & Birkinshaw, J. (2015). Choose your friends carefully: Home-country ties and new venture internationalization. Management International Review, 55(2), 207–234.
Prashantham, S., & Dhanaraj, C. (2010). The dynamic influence of social capital on the international growth of new ventures. Journal of Management Studies, 47(6), 967–994.
Prashantham, S., & Floyd, S. W. (2019). Navigating liminality in new venture internationalization. Journal of Business Venturing, 34(3), 513–527.
Prashantham, S., Kumar, K., & Bhattacharyya, S. (2019). International new ventures from emerging economies: Network connectivity and legitimacy building. Management and Organization Review, 15(3), 615–641.
Prashantham, S., & Young, S. (2011). Post–entry speed of international new ventures. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 35(2), 275–292.
Ragin, C. C. (2009). Redesigning social inquiry: Fuzzy sets and beyond. University of Chicago Press.
Rennie, M. (1993). Global competitiveness: Born global. Mckinsey Quarterly, 4, 45–52.
Ripollés, M., Blesa, A., & Monferrer, D. (2012). Factors enhancing the choice of higher resource commitment entry modes in international new ventures. International Business Review, 21(4), 648–666.
Rodríguez-Serrano, M. Á., & Martín-Armario, E. (2019). Born-global SMEs, performance, and dynamic absorptive capacity: Evidence from Spanish firms. Journal of Small Business Management, 57(2), 298–326.
Romanello, R., & Chiarvesio, M. (2017). Turning point: When born globals enter post-entry stage. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 15(2), 177–206.
Ryan, P., Evers, N., Smith, A., & Andersson, S. (2019). Local horizontal network membership for accelerated global market reach. International Marketing Review.
Sadeghi, A., Rose, E. L., & Chetty, S. (2018). Disentangling the effects of post-entry speed of internationalisation on export performance of INVs. International Small Business Journal, 36(7), 780–806.
Sapienza, H. J., Autio, E., George, G., & Zahra, S. A. (2006). A capabilities perspective on the effects of early internationalization on firm survival and growth. Academy of Management Review, 31(4), 914–933.
Sasi, V., & Arenius, P. (2008). International new ventures and social networks: Advantage or liability? European Management Journal, 26(6), 400–411.
Schleicher, D. J., Baumann, H. M., Sullivan, D. W., Levy, P. E., Hargrove, D. C., & Barros-Rivera, B. A. (2018). Putting the system into performance management systems: A review and agenda for performance management research. Journal of Management, 44(6), 2209–2245.
Schueffel, P., Amann, W., & Herbolzheimer, E. (2011). Internationalization of new ventures: Tests of growth and survival. Multinational Business Review.
Schwens, C., & Kabst, R. (2009). How early opposed to late internationalizers learn: Experience of others and paradigms of interpretation. International Business Review, 18(5), 509–522.
Schwens, C., Zapkau, F. B., Bierwerth, M., Isidor, R., Knight, G., & Kabst, R. (2018). International entrepreneurship: A meta–analysis on the internationalization and performance relationship. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 42(5), 734–768.
Sepulveda, F., & Gabrielsson, M. (2013). Network development and firm growth: A resource-based study of B2B Born Globals. Industrial Marketing Management, 42(5), 792–804.
Sharma, D. D., & Blomstermo, A. (2003). The internationalization process of born globals: A network view. International Business Review, 12(6), 739–753.
Sleuwaegen, L., & Onkelinx, J. (2014). International commitment, post-entry growth and survival of international new ventures. Journal of Business Venturing, 29(1), 106–120.
Sui, S., & Baum, M. (2014). Internationalization strategy, firm resources and the survival of SMEs in the export market. Journal of International Business Studies, 45(7), 821–841.
Taylor, M., & Jack, R. (2013). Understanding the pace, scale and pattern of firm internationalization: An extension of the ‘born global’ concept. International Small Business Journal, 31(6), 701–721.
Terjesen, S., O’Gorman, C., & Acs, Z. J. (2008). Intermediated mode of internationalization: New software ventures in Ireland and India. Entrepreneurship and Regional Development, 20(1), 89–109.
Tolstoy, D. (2010). Network development and knowledge creation within the foreign market: A study of international entrepreneurial firms. Entrepreneurship and Regional Development, 22(5), 379–402.
Trudgen, R., & Freeman, S. (2014). Measuring the performance of born-global firms throughout their development process: The roles of initial market selection and internationalisation speed. Management International Review, 54(4), 551–579.
Tsoukas, H., & Dooley, K. J. (2011). Introduction to the special issue: Towards the ecological style: Embracing complexity in organizational research. Organization Studies, 32(6), 729–735.
Turcan, R. V., & Juho, A. (2014). What happens to international new ventures beyond start-up: An exploratory study. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 12(2), 129–145.
Ughetto, E. (2016). Growth of born globals: The role of the entrepreneur’s personal factors and venture capital. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 12(3), 839–857.
Weerawardena, J., Mort, G. S., Liesch, P. W., & Knight, G. (2007). Conceptualizing accelerated internationalization in the born global firm: A dynamic capabilities perspective. Journal of World Business 42(3), 294–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2007.04.004
Wood, E., Khavul, S., Perez-Nordtvedt, L., Prakhya, S., Velarde Dabrowski, R., & Zheng, C. (2011). Strategic commitment and timing of internationalization from emerging markets: Evidence from China, India, Mexico, and South Africa. Journal of Small Business Management, 49(2), 252–282.
World Economic Forum. (2021). https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2021/11/here-are-the-top-countries-enjoying-the-largest-growth-in-small-businesses-and-why-that-matters/
Wu, A., & Voss, H. (2015). When does absorptive capacity matter for international performance of firms? Evidence from China. International Business Review, 24(2), 344–351.
Xie, E., Huang, Y., Peng, M. W., & Zhuang, G. (2016). Resources, aspirations, and emerging multinationals. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 23(2), 144–161.
Yamakawa, Y., Peng, M. W., & Deeds, D. L. (2008). What drives new ventures to internationalize from emerging to developed economies? Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 32(1), 59–82.
Yang, M., & Gabrielsson, P. (2017). Entrepreneurial marketing of international high-tech business-to-business new ventures: A decision-making process perspective. Industrial Marketing Management, 64, 147–160.
Yang, T., & Aldrich, H. E. (2017). “The liability of newness” revisited: Theoretical restatement and empirical testing in emergent organizations. Social Science Research, 63, 36–53.
Zaheer, S., & Mosakowski, E. (1997). The dynamics of the liability of foreignness: A global study of survival in financial services. Strategic Management Journal, 18(6), 439–463.
Zahra, S. A. (2014). Public and corporate governance and young global entrepreneurial firms. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 22(2), 77–83.
Zain, M., & Ng, S. I. (2006). The impacts of network relationships on SMEs’ internationalization process. Thunderbird International Business Review, 48(2), 183–205.
Zettinig, P., & Benson-Rea, M. (2008). What becomes of international new ventures? A coevolutionary approach. European Management Journal, 26(6), 354–365.
Zhang, M., & Tansuhaj, P. S. (2007). Organizational culture, information technology capability, and performance: The case of born global firms. Multinational Business Review.
Zhou, L., & Wu, A. (2014). Earliness of internationalization and performance outcomes: Exploring the moderating effects of venture age and international commitment. Journal of World Business, 49(1), 132–142.
Zhou, L., Wu, W. P., & Luo, X. (2007). Internationalization and the performance of born-global SMEs: The mediating role of social networks. Journal of International Business Studies, 38(4), 673–690.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Freixanet, J., Federo, R. When Born Globals Grow Up: A Review and Agenda for Research on the Performance of Maturing Early Internationalizers. Manag Int Rev 62, 817–857 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11575-022-00485-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11575-022-00485-y