Abstract
Starting with the first-in-class agent ibrutinib, the development of Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors has led to dramatic improvements in the management of B-cell malignancies. Subsequently, more-highly selective second-generation BTK inhibitors (including acalabrutinib, zanubrutinib, tirabrutinib and orelabrutinib) have been developed, primarily with an aim to reduce off-target toxicities. More recently, third-generation agents including the non-covalent BTK inhibitors pirtobrutinib and nemtabrutinib have entered later-stage clinical development. BTK inhibitors have shown strong activity in a range of B-cell malignancies, including chronic lymphocytic leukaemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, Waldenström’s macroglobulinaemia and marginal zone lymphoma. The agents have acceptable tolerability, with adverse events generally being manageable with dosage modification. This review article summarises the evidence supporting the role of BTK inhibitors in the management of B-cell malignancies, including highlighting some differential features between agents.
Plain Language Summary
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a key signalling molecule in the B-cell receptor pathway which is important for B-cell proliferation and survival. The development of drugs which inhibit BTK has led to dramatic improvements in the management of B-cell malignancies, difficult-to-treat diseases that primarily affect older populations. Following ibrutinib (the first-in-class BTK inhibitor), second-generation agents (including acalabrutinib, zanubrutinib, tirabrutinib and orelabrutinib) have been developed, primarily with an aim to improve drug tolerability. More recently, third-generation agents (including pirtobrutinib and nemtabrutinib) have entered later-stage clinical development, aiming to provide further treatment options. BTK inhibitors have shown strong activity in a range of B-cell malignancies. The agents have acceptable tolerability, with adverse events generally being manageable with dosage modification. This review article summarises the evidence supporting the role of BTK inhibitors in the management of B-cell malignancies, a rapidly developing field.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Digital Features for this Adis Disease Management article can be found at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.17056460. |
The development of BTK inhibitors has led to dramatic improvements in the management of B-cell malignancies |
Available evidence suggests that second-generation agents may have improved tolerability over the first-in-class agent ibrutinib |
Emerging evidence suggests that third-generation BTK inhibitors (currently in clinical development) may have a role in countering acquired resistance |
1 Introduction
The B-cell receptor (BCR) signalling pathway plays a key role in the proliferation, differentiation, development and survival of B cells [1]. With the understanding of the involvement of (aberrant) BCR signalling in the pathogenesis of B-cell malignancies [2], the targeting of BCR signalling pathway components, including the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK), has led to considerable advances in the management of these difficult-to-treat diseases. Following the approval of the first-in-class BTK inhibitor, ibrutinib, second-generation BTK inhibitors have been developed, primarily with an aim to reduce off-target toxicities. In this rapidly evolving field, third-generation BTK inhibitors are now in clinical development, aiming to provide further treatment options, in part to counter potential acquired resistance.
This article summarises the features, properties, therapeutic efficacy and tolerability of oral BTK inhibitors, approved or in later-stage clinical development, for use in the treatment of B-cell malignancies, including chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), Waldenström’s macroglobulinaemia (WM) and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL). BTK inhibitors which are no longer in development for B-cell malignancies, or the use or development of BTK inhibitors in other indications, are not discussed.
2 Drug Characteristics and Pharmacological Properties
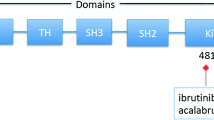
Despite being of the same drug class, currently approved BTK inhibitors and those in clinical development possess different characteristics and pharmacological properties (Table 1), including some which may have clinically relevant effects. All currently approved agents in the class are irreversible covalent BTK inhibitors and act through the formation of a covalent bond with a cysteine residue (Cys-481) within the BTK active site, resulting in potent and sustained inhibition of BTK enzymatic activity (Table 1). More recently, reversible, non-covalent BTK inhibitors have entered clinical development (Table 1).
Preclinical studies have shown that ibrutinib, the first-in-class BTK inhibitor, blocks BCR signalling and effectively inhibits malignant B-cell proliferation, migration and survival [2,3,4,5, 24], with subsequent clinical studies demonstrating high activity in a range of B-cell malignancies (Sect. 3). However, adverse events associated with ibrutinib (Sect. 4), some of which were proposed to be caused by off-target inhibition of other cysteine-containing kinases, led to the design and development of more selective BTK inhibitors, including acalabrutinib [6,7,8] and zanubrutinib [9, 10]. These second-generation BTK inhibitors have similar pleiotropic effects from BTK inhibition as ibrutinib [6,7,8,9,10]. However, acalabrutinib [6, 25, 26] and zanubrutinib [9] exhibit minimal inhibition of TEC, EGFR and Src family kinases, in contrast to ibrutinib (Table 1). Other examples of highly selective, irreversible covalent BTK inhibitors include tirabrutinib [14] and orelabrutinib [18] (Table 1). Metabolism of the currently approved covalent BTK inhibitors primarily involves CYP3A enzymes (Table 1), and there exists the potential for clinically significant drug interactions between the BTK inhibitor and CYP3A inhibitors or inducers [4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 17, 27, 28]. Furthermore, gastric acid-reducing agents have been shown to decrease the exposure of acalabrutinib, and its co-administration with proton pump inhibitors should be avoided [7, 8].
Non-covalent, reversible BTK inhibitors currently in clinical development in B-cell malignancies include pirtobrutinib [20] and nemtabrutinib [22] (Table 1). Pirtobrutinib was developed with pharmacokinetic properties designed to achieve high BTK inhibition regardless of BTK turnover [20]. Similar to the second-generation covalent BTK inhibitors, pirtobrutinib is highly selective, reducing the potential for off-target effects. Nemtabrutinib was developed following a different approach. Rather than aiming for high selectivity, nemtabrutinib development was based on the hypothesis that more robust responses might be achieved through a more global inhibition by targeting additional kinases (including Src family kinases and kinases related to ERK signalling) alongside BTK [22].
2.1 Acquired Resistance to BTK Inhibitors
Relapse or disease progression during treatment with BTK inhibitors in patients with B-cell malignancies is commonly associated with acquired resistance. The frequency with which acquired resistance develops varies between different B-cell malignancy subtypes but appears to be higher among patients with MCL and high-risk CLL/SLL [29]. The most commonly observed mutations conferring resistance to first- and second-generation BTK inhibitors are mutations at the Cys-481 residue in the BTK active site [30]. Mutations at Cys-481 disrupt the covalent binding between BTK and BTK inhibitors which act at this site (i.e. ibrutinib, acalabrutinib, zanubrutinib, tirabrutinib, orelabrutinib; Table 1), diminishing their inhibitory activity [31]. In contrast to the covalent inhibitors, the third-generation non-covalent BTK inhibitors pirtobrutinib and nemtabrutinib (in clinical development) do not rely on binding to Cys-481 in the BTK active site, with high activity against Cys-481-mutated BTK demonstrated for both of these agents [21, 22].
Other mutations leading to acquired resistance to BTK inhibitors include gain-of-function mutations resulting in the increased activity of downstream kinases (e.g. phospholipase C gamma 2) despite inhibition of BTK [29], with several other mechanisms of acquired resistance also observed (albeit less commonly) [32].
3 Therapeutic Efficacy of BTK Inhibitors
3.1 In Mantle Cell Lymphoma
3.1.1 Relapsed or Refractory Disease
The efficacy of ibrutinib [33,34,35], acalabrutinib [36,37,38] and zanubrutinib [39] (each as monotherapy) in the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) MCL after one or more prior therapies has been demonstrated in single-arm phase II clinical trials. Differences in trial design and patient populations limit the ability to compare data across trials, but all three drugs have clear efficacy in the treatment of R/R MCL with median progression-free survival (PFS) generally around 1–2 years (Table 2). Furthermore, the open-label randomised controlled phase III RAY trial demonstrated that, relative to the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus, ibrutinib prolongs PFS and is associated with a significantly higher overall response rate (ORR) in the treatment of R/R MCL (Table 2) [40, 41].
Currently available data from phase I and phase I/II trials also support the efficacy of tirabrutinib [14, 43], orelabrutinib [44, 45] and pirtobrutinib [20] as monotherapy in the treatment of R/R MCL (Table 2). Of note, the trials of tirabrutinib and pirtobrutinib involved heavily pretreated patients (both with a median three prior lines of therapy) with good activity observed, including in patients with resistance or intolerance to prior BTK inhibitor therapy [14, 20, 43].
Ibrutinib has also been evaluated in clinical trials in combination with other agents, including the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb) rituximab [46,47,48] and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax [49,50,51]. Currently available data (primarily from single-arm phase II trials) suggest that ibrutinib plus rituximab (± lenalidomide) and ibrutinib plus venetoclax (± obinutuzumab) have good activity in the treatment of R/R MCL. Accepting the limitations of indirect comparisons, ORRs and complete response (CR) rates in patients treated with ibrutinib combination therapy generally appear to be favourable relative to ibrutinib monotherapy (based on historical controls [33,34,35]), although randomised controlled trials are required to confirm any potential clinical benefits over monotherapy. In this regard, results from the ongoing randomised, double-blind phase III SYMPATICO trial [51] evaluating ibrutinib plus venetoclax versus ibrutinib plus placebo in the R/R MCL setting will be of particular interest. Of note, currently available data (although based on small patient numbers) suggest that responses to combination therapy involving ibrutinib and rituximab or venetoclax are observed independent of high-risk genetic markers (e.g. TP53 mutations) or other negative prognostic factors [47, 50].
Limited data are also available demonstrating activity of tirabrutinib plus entospletinib in the R/R MCL setting based on a subset of patients with MCL in a phase Ib trial in patients with previously treated B-cell lymphoma [52]. Clinical evaluation is also underway to investigate acalabrutinib in combination with bendamustine and rituximab in the treatment of R/R MCL (NCT02717624).
3.1.2 Treatment-Naïve Patients
Although data are currently limited, the potential role of BTK inhibitors in the treatment-naïve MCL setting is also being investigated, particularly as part of combination therapy. Among a separate cohort of treatment-naïve patients (n = 15) in the OAsIS trial, 14 patients responded to ibrutinib, obinutuzumab and venetoclax combination therapy and remained disease-free (median follow-up of 14 months) with 1-year PFS and overall survival (OS) rates of 93.3% and 100% [49]. Promising results were also reported from a single-arm phase II trial (NCT02427620) which evaluated chemotherapy-free induction treatment with ibrutinib plus rituximab followed by up to four cycles of cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin and dexamethasone (hyper-CVAD) plus methotrexate consolidation therapy [53]. In this trial of 131 patients aged ≤ 65 years, there was a 100% ORR on ibrutinib plus rituximab [88% CRs, 12% partial responses (PRs)] with 98% of patients achieving a CR by the time of last follow-up after completion of both induction and consolidation therapy. After a median follow-up of 37 months, median PFS and OS were not reached (3-year PFS and OS rates were 82% and 95%). At last follow-up, 22 patients (17%) had relapsed after treatment, including six patients who experienced disease transformation to aggressive MCL [53]. Another single-arm phase II trial evaluating continuous ibrutinib plus rituximab in 50 older patients (aged ≥ 65 years) found an ORR of 96% after a median follow-up of 36.2 months [54]. Further trials investigating BTK inhibitors in first-line treatment of MCL include the open-label phase II/III ENRICH trial (EudraCT no: 2015-000832-13), which is comparing ibrutinib plus rituximab versus standard chemotherapy plus rituximab; the double-blind phase III SHINE trial (NCT01776840), which is comparing ibrutinib versus placebo, each given in combination with bendamustine and rituximab; the open-label phase III TRIANGLE (NCT02858258) trial, which is evaluating chemoimmunotherapy with or without ibrutinib and/or with or without subsequent autologous stem cell transplant; and an open-label phase III trial (NCT04002297) [55] evaluating zanubrutinib plus rituximab versus bendamustine plus rituximab. There is also a new open-label arm of the ongoing SYMPATICO trial (Sect. 3.1.1) evaluating the efficacy of ibrutinib plus venetoclax in previously untreated patients aged ≥ 65 years and patients aged < 65 years with a TP53 mutation [56].
3.2 In Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
A pivotal trial in the evaluation of BTK inhibitors in the treatment of CLL/SLL, the phase Ib/II trial 1102 (together with the long-term extension study 1103) demonstrated that durable responses to ibrutinib monotherapy were achieved by a substantial proportion of patients, both in patients with R/R CLL/SLL (n = 101) and in elderly patients (aged ≥ 65 years; 74% aged ≥ 70 years) with previously untreated disease (n = 31) [57,58,59,60,61]. At the primary analysis (median follow-up of 26 months), the PFS rate was 75% and the OS rate was 83% [60]. With a median follow-up of 85 months, there was an ORR of 89% (including CRs in 10% of patients with R/R disease and 35% of previously untreated patients). Estimated 7-year PFS and OS rates were 34% and 55% in the R/R setting and 83% and 84% in the first-line setting, representing a significant advance in the treatment outcomes for patients with CLL/SLL relative to standard therapy at the time of the trial initiation. Subsequently, BTK inhibitors have been further evaluated (as monotherapy, or as part of combination therapy) in a range of phase III trials in CLL/SLL, in both the R/R disease (Sect. 3.2.1) and first-line treatment (Sect. 3.2.2) settings.
3.2.1 Phase III Trials in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Disease
Phase III data from the open-label RESONATE [62,63,64,65] and ASCEND [66, 67] trials have demonstrated robust efficacy for single-agent ibrutinib and acalabrutinib, respectively, in the treatment of R/R CLL/SLL. Furthermore, of particular interest are emerging data from ELEVATE-RR [68] and ALPINE [69], the first head-to-head phase III trials of BTK inhibitors in R/R CLL/SLL. Ibrutinib has also been shown to improve efficacy when added to bendamustine plus rituximab chemoimmunotherapy based on the findings of the double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III HELIOS trial [70, 71].
The RESONATE trial included patients with R/R CLL/SLL who were not eligible for purine analogue-based chemotherapy, with patients randomised to receive ibrutinib or the anti-CD20 mAb ofatumumab [65]. In the primary analysis (median follow-up of 9.4 months), ibrutinib significantly reduced the risk of progression or death by 78% versus ofatumumab (Table 3) and, based on an analysis in which data were censored at the time of crossover (from ofatumumab to ibrutinib following progression), significantly reduced the risk of death by 57% (p = 0.005). Ibrutinib treatment was also associated with a significantly higher ORR compared with ofatumumab (Table 3). With extended follow-up, ibrutinib efficacy was durable over the longer term [62,63,64]. Consistent with findings at the primary analysis [65], when analysed with censoring at crossover OS was found to be improved in ibrutinib recipients compared with ofatumumab recipients [hazard ratio (HR) 0.639; 95% CI 0.418–0.975] at the final analysis [64].
In the ASCEND trial, acalabrutinib monotherapy was found to significantly prolong independent review committee (IRC)-assessed PFS versus investigator’s choice of idelalisib plus rituximab or bendamustine plus rituximab [67]. With a median follow-up of 16.1 months, acalabrutinib monotherapy reduced the risk of progression or death by 69% compared with investigator’s choice (Table 3) [67]. ORR was similar between groups (81% vs 75%), although the median duration of response was significantly longer in the acalabrutinib group than in the investigator’s choice group (not reached vs 13.6 months; p < 0.0001). Final results from ASCEND (median follow-up of 22 months) supported the findings from the primary analysis (Table 3) [66]. The 18-month OS rate was 88% for both groups [66].
In a head-to-head comparison of two BTK inhibitors, the ongoing ELEVATE-RR study is a randomised, open-label trial to investigate the non-inferiority of acalabrutinib monotherapy to ibrutinib monotherapy in the treatment of patients with R/R CLL/SLL with del(17p) [45.2% of patients] and/or del(11q) [64.2% of patients] [68]. In the first results from the trial (median follow-up of 40.9 months), acalabrutinib was found to have non-inferior efficacy to ibrutinib based on IRC-assessed PFS (primary endpoint; 38.4 months in both groups) (Table 3). Median OS was not reached in either group at data cut-off [68].
In a second head-to-head comparison, the randomised, open-label ALPINE trial is comparing zanubrutinib and ibrutinib, with investigator-assessed ORR as the primary endpoint [69]. Based on a pre-planned interim analysis approximately 12 months after the first 415 out of 652 patients were enrolled (median follow-up of 15 months), the ORR was significantly higher in zanubrutinib recipients than in ibrutinib recipients (Table 3). Preliminary data also suggested a significant improvement in 12-month PFS rates for zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib (Table 3) [69]. Full results from this trial are awaited with interest for confirmation of these findings with longer-term follow-up.
In the HELIOS study, 578 patients with R/R CLL/SLL, most with high risk factors (e.g. unmutated IGHV, del(11q), bulky disease), were randomised to ibrutinib or placebo, each in combination with bendamustine and rituximab [71]. Patients with del(17p) were excluded based on a known poor response to bendamustine and rituximab. In the primary analysis (median follow-up of 17 months), the addition of ibrutinib to bendamustine plus rituximab immunotherapy reduced the risk of progression or death by 80% and was associated with a significant increase in the ORR (Table 3) [71]. There was no significant difference in OS between groups at the primary analysis, although a preplanned OS analysis adjusting for crossover did find a significant OS benefit for patients randomised to ibrutinib compared with placebo (HR 0.577; 95% CI 0.348–0.957; p = 0.033) [71]. Of note, a significant OS benefit was observed for the ibrutinib group with longer-term follow-up, even with extensive crossover from placebo to ibrutinib (by 63.3% of patients at the final analysis) [72] (Table 3).
3.2.2 Phase III Trials in Treatment-Naïve Patients
In the first-line treatment setting, ibrutinib monotherapy was superior to chemotherapy with single-agent chlorambucil based on significant improvements in IRC-assessed PFS (primary endpoint), OS and ORR in older patients (aged ≥ 65 years; median 73 years) with previously untreated CLL/SLL in the randomised, open-label phase III RESONATE-2 trial (Table 3) [73, 74, 79]. With a median follow-up of 18.4 months, ibrutinib reduced the risk of progression or death by 84% versus chlorambucil (Table 3). With crossover from chlorambucil to ibrutinib permitted after disease progression, 2-year OS rates were 98% with ibrutinib treatment versus 85% with chlorambucil treatment (p = 0.001). The long-term follow-up in this trial (to a median of 5 years) demonstrated sustained benefits for ibrutinib in the first-line setting, with a 5-year PFS rate among ibrutinib recipients of 70% [74].
Ibrutinib and acalabrutinib have also each been evaluated as first-line treatment for CLL/SLL in combination with the anti-CD20 mAb obinutuzumab [27, 75]. The randomised, open-label phase III iLLUMINATE [75] and ELEVATE-TN [27] trials, which evaluated ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab and acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab, respectively, versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab, each enrolled patients aged > 65 years or ≤ 65 years with comorbidities with previously untreated CLL/SLL.
Patients treated with ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab in iLLUMINATE (median follow-up of 31.3 months) or acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab in ELEVATE-TN (median follow-up of 28.3 months) had significantly prolonged IRC-assessed PFS compared with patients treated with chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in the respective trials (primary endpoint for both trials) (Table 3), indicating superior efficacy for the chemotherapy-free combination of a BTK inhibitor plus an anti-CD20 mAb over a standard chemoimmunotherapy regimen as first-line treatment for CLL/SLL [27, 75]. The ELEVATE-TN trial also included a group randomised to acalabrutinib monotherapy with this group also having significantly longer PFS versus the chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab group (Table 3). Furthermore, in a post-hoc analysis comparing acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab with acalabrutinib monotherapy, there appeared to an added benefit from obinutuzumab based on the hazard ratio for PFS (0.49; 95% CI 0.26–0.95) [27]. In both trials, no significant between-group differences were observed in OS at the primary analyses (Table 3).
The combination of a BTK inhibitor plus an anti-CD20 mAb as first-line treatment for CLL/SLL in older patients (aged ≥ 65 years) has also been evaluated in the randomised, open-label phase III Alliance 041202 trial [77]. This trial, which also included an ibrutinib monotherapy group, found that continuous ibrutinib, with or without rituximab, significantly reduced the risk of progression or death compared with six cycles of chemoimmunotherapy with bendamustine plus rituximab (Table 3). No significant difference in PFS was observed between patients treated with ibrutinib monotherapy and ibrutinib plus rituximab. At the primary analysis (at 2.5 years after the last patient enrolled), there were no significant between-group differences in OS [77]. Two-year OS rates were 90% for ibrutinib monotherapy, 94% for ibrutinib plus rituximab and 95% for bendamustine plus rituximab (p ≥ 0.65 for all pairwise comparisons) [77]. In the respective groups, ORRs were 93%, 94% and 81% and CR rates were 7%, 12% and 26%. A significantly higher proportion of patients treated with bendamustine plus rituximab (8%) than patients treated with ibrutinib monotherapy (1%) or ibrutinib plus rituximab (4%) had undetectable minimal residual disease (MRD) [77].
In another trial investigating the combination of a BTK inhibitor plus an anti-CD20 mAb, the randomised, open-label phase III E1912 trial evaluated ibrutinib plus rituximab (for six cycles followed by ibrutinib monotherapy) compared with six cycles of chemoimmunotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab [78]. Whereas other phase III studies of BTK inhibitors in treatment-naïve CLL/SLL generally enrolled older patients (aged ≥ 65 years), the E1912 trial enrolled patients ≤ 70 years old (mean age 56.7 years; 59.4% aged < 60 years). Patients with del(17p) were excluded due to a known poor response to the chemoimmunotherapy regimen [78]. Based on the results of a preplanned interim analysis (median follow-up of 33.6 months), ibrutinib plus rituximab was superior to the chemoimmunotherapy regimen with regard to PFS (primary endpoint) and OS (Table 3). Three-year PFS and OS rates showed a reduction in the risk of progression or death of 65% and a reduction in the risk of death of 83% for patients treated with ibrutinib plus rituximab versus the chemoimmunotherapy regimen (Table 3). In the respective groups, the ORRs were 98.5% versus 81.1%, the CR rates were 17.2% versus 30.3%, and (among evaluable patients) the rates of MRD-negativity at cycle 12 were 8.3% versus 59.2% [78].
Zanubrutinib is also under phase III clinical investigation in treatment-naïve patients with CLL/SLL, with limited data available from the SEQUOIA trial [80,81,82]. Of note, Arm C of the trial involves a non-randomised cohort of patients (n = 109) with del(17p) treated with zanubrutinib monotherapy [82]. After a median follow-up of 18.2 months, the ORR was 94.5% (with 4% of patients achieving a CR), suggesting good activity in this high-risk population. The 18-month PFS and OS rates were 88.6% and 95.1% [82]. Based on evidence that there may be added benefit from combining BTK inhibition with BCL2 inhibition, a further cohort (Arm D) is being included in the trial, involving treatment-naïve patients with CLL/SLL and del(17p) treated with zanubrutinib in combination with venetoclax [81].
3.2.3 Other Trials of Interest
Orelabrutinib [19], tirabrutinib [83, 84] and pirtobrutinib [20] have also been evaluated in earlier phase trials in patients with (R/R) CLL/SLL with overall promising results. High (≥ 89%) ORRs were observed in trials with patients treated with orelabrutinib monotherapy [19] or tirabrutinib with or without idelalisib or entospletinib [83, 84], including a 96% ORR in one trial involving 28 heavily pretreated patients (median four prior therapies) with R/R CLL/SLL who received tirabrutinib monotherapy [84]. Also of particular interest, an ORR of 62% was observed following pirtobrutinib monotherapy in 121 heavily pretreated patients (median four prior therapies) with R/R CLL/SLL who had received prior treatment with one or more covalent BTK inhibitors in the phase I/II BRUIN trial, including 79 patients with resistance to previous BTK inhibitor treatment (ORR 67%), 42 patients with BTK inhibitor intolerance (ORR 52%) and 24 patients with Cys-481-mutant BTK (ORR 71%) [20].
Another strategy that is receiving considerable attention in CLL/SLL (in both R/R and treatment-naïve patient settings) is combination therapy involving a BTK inhibitor and venetoclax (± an anti-CD20 mAb). Currently available data from phase II trials show that treatment with ibrutinib [85,86,87,88,89], acalabrutinib [90] or zanubrutinib [91] in combination with venetoclax (with [88, 90, 91] or without [85,86,87,88,89, 91] obinutuzumab) can produce deep responses, with good proportions (38–75% across trials) of patients achieving undetectable MRD. Several phase III trials investigating combinations of a BTK inhibitor and venetoclax (± obinutuzumab or rituximab) are underway (including with fixed-duration regimens), and results will be of particular interest.
3.3 In Waldenström’s Macroglobulinaemia
BTK inhibitors are highly active in WM, both in treatment-naïve patients and those with R/R disease, with phase II and/or phase III data available for ibrutinib, acalabrutinib, zanubrutinib, tirabrutinib and pirtobrutinib (Table 4). Although longer-term data are more limited, currently available evidence suggests that long-term disease control can be achieved [92, 93], with one study in patients with R/R WM showing more than half of all patients treated with ibrutinib monotherapy remaining progression-free after 5 years [92]. Furthermore, responses to BTK inhibition appear to deepen over time with continued treatment in WM [92, 93]. Also of note, there is evidence that MYD88 and CXCR4 mutation status can affect responses to BTK inhibitors [13, 92, 94, 95].
The largest randomised controlled trial of BTK inhibitor monotherapy in WM to date is the open-label phase III ASPEN trial comparing zanubrutinib and ibrutinib [96]. Despite failing to meet its primary endpoint of demonstrating superiority of zanubrutinib based on the proportions of patients achieving a CR or a very good partial response (VGPR), the ASPEN trial provides strong evidence for the efficacy of BTK inhibitors in WM. With a median follow-up of 19.4 months, a VGPR was achieved by 28% of zanubrutinib recipients and 19% of ibrutinib recipients, with the between-group difference not reaching statistical significance (p = 0.09). No patient in the trial achieved a CR [96]. High major response rates (MRR) and 18-month PFS rates were observed in both groups (Table 4). Longer-term follow-up of this head-to-head trial of two BTK inhibitors will be of particular interest.
In addition to the evaluation of BTK inhibitors as monotherapy, the combination of ibrutinib plus rituximab has been evaluated in the treatment of WM in the randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III iNNOVATE trial [95]. The trial, initiated based on the demonstrated activity of ibrutinib and rituximab as single agents (together with preclinical evidence of synergy), included 150 patients who were randomised to ibrutinib plus rituximab or placebo plus rituximab [95]. In the primary endpoint analysis (median follow-up of 26.5 months), the addition of ibrutinib to rituximab treatment was associated with an 80% reduction in the risk of progression or death (p < 0.001) (Table 4), with a 66% reduction for the subgroup of treatment-naïve patients (HR 0.34; 95% CI 0.12–0.95) and an 83% reduction for patients with R/R disease (HR 0.17; 95% CI 0.08–0.36) [95]. Ibrutinib plus rituximab was also associated with a significantly higher ORR and MRR than placebo plus rituximab (Table 4). Median OS was not reached in either group (30-month OS rates were 94% and 92%) [95].
Also of interest, included in the iNNOVATE trial was a single-arm, non-randomised substudy of 31 patients with rituximab-refractory WM who were treated with ibrutinib monotherapy [100]. Despite heavy pretreatment (median two prior therapies), ibrutinib was highly active in these patients, with an ORR of 90% and an MRR of 71% (median follow-up of 18.1 months); 18-month PFS and OS rates were 86% and 97% [100].
3.4 In Relapsed or Refractory Marginal Zone Lymphoma
Although data remain scarce overall, good activity has been demonstrated for BTK inhibitors in patients with R/R MZL, a clinical setting in which treatment options are limited [101,102,103]. Besides the trials on ibrutinib and zanubrutinib discussed below, small numbers of patients with MZL have been treated with other BTK inhibitors in early phase trials in patients with B-cell malignancies with moderate levels of activity observed [14, 20].
To test the hypothesis that BCR signalling is involved in MZL pathogenesis, a single-arm phase II trial of ibrutinib monotherapy was conducted in 63 patients with previously treated MZL who had received one or more anti-CD20-based therapies [103]. With a median follow-up of 19.4 months, the IRC-assessed ORR (primary endpoint) among 60 evaluable patients was 48%, including a CR in two patients (3%). Median duration of response was not reached and median PFS was 14.2 months. The ORR was largely consistent across subgroups based on baseline clinical parameters, including across extranodal (15/30 patients; 50%), splenic (7/13 patients; 54%) and nodal (7/17 patients; 41%) disease subtypes [103]. Extended follow-up (median 33.1 months) showed that responses were durable (median duration of 27.6 months) [102]. PFS and OS rates at month 33 were 32% and 72% [102].
Efficacy data are also available for zanubrutinib in R/R MZL from a phase I/II trial in 20 patients (median two prior therapies) and from a phase II trial in 66 patients who had previously received at least one anti-CD20-based therapy [10]. IRC-assessed ORRs for the respective trials were 80% (median follow-up of 31.4 months) and 56% (median follow-up of 8.3 months) with 20% of patients in each trial achieving a CR [10].
4 Tolerability of BTK Inhibitors
Overall, BTK inhibitors have acceptable tolerability in the treatment of B-cell malignancies. Among other adverse events (Table 5), BTK inhibitors may be associated with infections (including serious and opportunistic infections), skin disorders (including erythema multiforme and rash), bleeding, cytopenias and cardiac arrhythmias [4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 13, 20, 104]. Second primary malignancies have also been reported in patients treated with BTK inhibitors [4, 5, 7, 8, 10].
Although there is a large degree of overlap between different BTK inhibitors in terms of the most commonly observed adverse events (Table 5), there is evidence, most notably from head-to-head comparative randomised trials [68, 69, 96], suggesting some clinically important differences in the tolerability profiles of the different agents. In the ELEVATE-RR trial in R/R CLL/SLL (Sect. 3.2.1), the incidence of (all-grade) atrial fibrillation/flutter (secondary endpoint) was significantly (p = 0.02) lower in acalabrutinib (9.4%) versus ibrutinib (16.0%) recipients [68]. Among other adverse events with an incidence of ≥ 15% in either group, significantly more (p < 0.05; no adjustment for multiplicity) ibrutinib versus acalabrutinib recipients experienced diarrhoea (46% vs 35%), arthralgia (23% vs 16%), hypertension (23% vs 9%) and contusion (18% vs 12%), whereas significantly fewer ibrutinib versus acalabrutinib recipients experienced headache (20% vs 35%) and cough (21% vs 29%). Adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 21.3% and 14.7% of patients in the respective groups [68]. In the ASPEN trial (Sect. 3.3), which compared ibrutinib and zanubrutinib in patients with WM, significantly more (p ≤ 0.05; no adjustment for multiplicity) ibrutinib versus zanubrutinib recipients experienced diarrhoea (32% vs 21%), muscle spasms (24% vs 10%), peripheral oedema (19% vs 9%), atrial fibrillation/flutter (15% vs 2%) and pneumonia (12% vs 2%), whereas significantly fewer ibrutinib versus zanubrutinib recipients experienced neutropenia (13% vs 29%) [96]. Adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 9.2% and 4.0% of patients in the respective groups [96]. Based on interim data, the incidence of atrial fibrillation/flutter (prespecified endpoint) was also significantly (p = 0.0014) lower in zanubrutinib (2.5%) versus ibrutinib (10.1%) recipients in the ALPINE trial (Sect. 3.2.1) in patients with R/R CLL/SLL [69].
The cardiovascular toxicity of ibrutinib is believed to result from off-target inhibition of other kinases, such as TEC, HER2/ERBB2, HER4/ERBB4 and BMX [105]. HER2 (possibly in association with HER4) has been suggested as a lead candidate based on evidence of its expression in cardiomyocytes, its role in heart physiology and the pattern of its inhibition by ibrutinib but not by other BTK inhibitors at clinically relevant concentrations (Table 1) [105]. The higher incidence of diarrhoea reported with ibrutinib versus acalabrutinib [68] or zanubrutinib [96] is potentially due to off-target inhibition of EGFR by ibrutinib (Table 1), given the known link between EGFR inhibition and diarrhoea [106]. Off-target inhibition of EGFR is also considered likely to play a role in dermatological adverse events (including rash) associated with BTK inhibitors [107].
5 Current Clinical Position of BTK Inhibitors in B-Cell Malignancies
As monotherapy or in combination with other agents (notably anti-CD20 mAbs), BTK inhibitors have shown strong activity in a range of B-cell malignancies, including MCL, CLL/SLL, WM and MZL (Sect. 3). Of note, efficacy remains high in patients with or without high-risk factors, including in patients with del(17p) or TP53 mutations for whom responses to chemotherapy are generally poor [108]. BTK inhibitors have also been extensively studied in other B-cell malignancy subtypes, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma; however, although research is continuing, evidence for the benefit of BTK inhibitors in these diseases has so far been less conclusive. BTK inhibitors have acceptable tolerability, with adverse events generally being manageable with dosage modification. Some adverse events of special interest observed in patients receiving BTK inhibitor treatment include infections, bleeding events, cytopenias, cardiac arrhythmias and second primary malignancies (Sect. 4).
Ibrutinib remains the most well studied BTK inhibitor to date and has the advantages of having more longer-term data available and of having greater clinical (including real-world) experience. Ibrutinib is also approved (across different regulatory authorities) in a broad range of B-cell malignancy indications, including MCL, CLL/SLL, WM and MZL [4, 5]. The other approved covalent BTK inhibitors (Table 1) appear to have broadly similar efficacy to ibrutinib based on currently available data, although the level of data varies for different agents and across different B-cell malignancy subtypes (Sect. 3). Accepting the limitation of their open-label design, head-to-head trials have demonstrated the non-inferiority of acalabrutinib and the potential superiority (based on interim data) of zanubrutinib to ibrutinib in R/R CLL/SLL (Sect. 3.2.1). Another open-label head-to-head trial (ASPEN) in patients with WM found zanubrutinib to be associated a numerically greater CR/VGPR rate versus ibrutinib without reaching statistical significance (Sect. 3.3). Moreover, data from these head-to-head trials support the suggestion that the greater selectivity of these second-generation BTK inhibitors may result in tolerability benefits over ibrutinib, most notably relating to cardiovascular adverse events (Sect. 4). In note of this evidence, second-generation BTK inhibitors have been suggested to have particular benefit over ibrutinib in patients with a history of hypertension, atrial fibrillation or other cardiovascular conditions [109]. Further emerging evidence of the potential advantages of improved tolerability of second-generation BTK inhibitors over ibrutinib in B-cell malignancies is also available from phase II trials demonstrating the efficacy and tolerability of acalabrutinib [110] and zanubrutinib [111] in patients intolerant to ibrutinib.
Although data remain somewhat limited, third-generation BTK inhibitors potentially present another important advance in the management of B-cell malignancies. The agents remain in clinical development and have not yet reached registration (Table 1). However, with the approach of reversible BTK inhibition through non-covalent binding, third-generation BTK inhibitors may provide further treatment options and may be useful to combat acquired resistance to covalent BTK inhibitors (Sect. 2.1). Promising results have been observed so far in clinical trials, most notably the phase I/II BRUIN trial of pirtobrutinib in a range of B-cell malignancies, in which strong activity was demonstrated in a highly pretreated (including 76% of patients with prior BTK inhibitor treatment) population (Sect. 3.2.3) [20]. Phase III trials of pirtobrutinib are underway, and the results will be of particular interest.
In terms of other differentiating features, there are also some minor differences between BTK inhibitors in recommendations for their use in patients with hepatic or renal impairment and potential food effects (although information for the non-covalent agents still in clinical development is currently limited) (Table 5). There are also some differences between the different BTK inhibitors in pharmacokinetic properties (including differences in bioavailability and half-lives) (Table 1) and dosing schedules (i.e. once daily vs twice daily dosing) (Table 5) which could affect BTK occupancy, efficacy and tolerability; however, further study is required to confirm any potential clinically significant effects. Similarly, the reversible binding of non-covalent third-generation inhibitors (in contrast to covalent BTK inhibitors which bind irreversibly) has been suggested to potentially enable full BTK occupancy irrespective of BTK turnover [20, 112]. Again, any potential clinical benefits are yet to be demonstrated.
Current National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN®) guideline recommendations on the use of BTK inhibitors in B-cell malignancies broadly reflect the available clinical trial data [113,114,115]. Ibrutinib (± rituximab), acalabrutinib and zanubrutinib (alongside lenalidomide + rituximab) are each recommended as preferred regimens for R/R MCL, with regimens of ibrutinib, lenalidomide and rituximab or ibrutinib plus venetoclax recommended as being useful in certain circumstances [113]. Alongside venetoclax plus obinutuzumab, acalabrutinib (± obinutuzumab) and ibrutinib are each listed as preferred regimens for first-line treatment of CLL/SLL, with patients with del(17p)/TP53 mutations also having zanubrutinib recommended (for patients with a contraindication to ibrutinib/acalabrutinib) as an alternative regimen. In patients without del(17p)/TP53 mutations, ibrutinib plus rituximab is one of several alternative recommended regimens in patients aged < 65 years and without significant comorbidities, as is ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab in older patients or those with significant comorbidities [113]. In R/R CLL/SLL, ibrutinib and acalabrutinib are each listed as preferred regimens alongside venetoclax plus rituximab [or venetoclax alone in patients with del(17p)/TP53 mutations]; zanubrutinib (for patients with a contraindication to ibrutinib/acalabrutinib) is recommended as one of several alternative regimens [115]. In WM, ibrutinib (± rituximab) and zanubrutinib are recommended as the two category 1 preferred regimens; acalabrutinib is one of several recommended alternative regimens in R/R WM [114]. Finally, in R/R MZL, ibrutinib and zanubrutinib (after ≥ 1 prior anti-CD20 mAb-based regimen) are among the preferred regimen recommendations [113].
The development of BTK inhibitors as treatment options has led to dramatic improvements in the management of B-cell malignancies. The now-availability of chemotherapy-free treatment options may be particularly valuable in populations where patients are generally older and frequently have significant comorbidities. Areas of particular interest for the future include the coming availability of more longer-term data for second-generation BTK inhibitors, phase III data for third-generation agents, further investigation into potential combination therapies (including risk:benefit analyses), and more understanding towards the ideal positioning and sequencing of different therapies. With the growing number of treatment options available, there is also more potential to use understanding of prognostic factors in different B-cell malignancies (e.g. TP53 status, IGHV mutation status, blastoid morphology) to allow more targeted patient management [116, 117]. Furthermore, with the observation that mutations leading to acquired resistance can be present several months before disease progression, screening for such mutations may allow timely adaptation of treatment [118].
As indicated by guideline recommendations (discussed above), combination therapies are becoming more central to the treatment of B-cell malignancies. Besides potential synergy between agents helping towards (rapidly) achieving deep responses, combination therapy may also have benefits in terms of overcoming resistance [32]. Growing knowledge of the pharmacodynamic effects of different agents is also helping guide use of drug combinations where, for example, different anti-CD20 mAbs in combination with a BTK inhibitor can potentially have either synergistic or antagonistic effects [119].
Another area of interest around combination therapies involving BTK inhibitors is regarding the potential benefit of fixed-duration treatment. In most later-stage clinical trials on BTK inhibitors conducted to date, treatment has continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. This is reflected in currently approved indications [4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 17, 28], particularly given the observation that continued BTK inhibitor treatment appears to improve rates and depth of response over time (Sect. 3). However, given the potential for ongoing tolerability issues (as well as other factors, including cost), it has been raised whether fixed-duration (or response driven) BTK inhibitor treatment regimens could have an improved risk:benefit ratio [81, 88, 89]. Although deep responses allowing drug discontinuation are generally not rapidly achieved with BTK inhibitor monotherapy, combination therapies (e.g. BTK inhibitor + venetoclax ± an anti-CD20 mAb) can rapidly lead to deep responses (including undetectable MRD), thus making time-limited treatment more viable [32].
In conclusion, BTK inhibitors have become very valuable additions to the available treatment options for B-cell malignancies. Management of B-cell malignancies continues to be a rapidly developing field, and ongoing and future clinical trials (together with growing real-world experience) will continue to inform disease management decisions.
Change history
24 December 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-021-00864-9
References
Liu W, Tolar P, Song W, et al. Editorial: BCR signaling and B cell activation. Front Immunol. 2020;11:45.
Herman SEM, Gordon AL, Hertlein E, et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase represents a promising therapeutic target for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is effectively targeted by PCI-32765. Blood. 2011;117(23):6287–96.
Honigberg LA, Smith AM, Sirisawad M, et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 blocks B-cell activation and is efficacious in models of autoimmune disease and B-cell malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(29):13075–80.
European Medicines Agency. Imbruvica (ibrutinib): summary of product characteristics. 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu. Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
US FDA. Imbruvica (ibrutinib): US prescribing information. 2020. https://www.fda.gov. Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
Byrd JC, Harrington B, O’Brien S, et al. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(4):323–32.
European Medicines Agency. Calquence (acalabrutinib): summary of product characteristics. 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu. Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
US FDA. Calquence® (acalabrutinib): US prescribing information. 2019. https://www.fda.gov/. Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
Tam CS, Trotman J, Opat S, et al. Phase 1 study of the selective BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib in B-cell malignancies and safety and efficacy evaluation in CLL. Blood. 2019;134(11):851–9.
US FDA. Brukinsa® (zanubrutinib): US prescribing information. 2021. https://www.fda.gov. Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
Xu W, Yang S, Zhou K, et al. Treatment of relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma with the BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib: phase 2, single-arm, multicenter study. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):48.
Yu H, Truong H, Mitchell SA, et al. Homogeneous BTK occupancy assay for pharmacodynamic assessment of tirabrutinib (GS-4059/ONO-4059) target engagement. SLAS Discov. 2018;23(9):919–29.
Sekiguchi N, Rai S, Munakata W, et al. A multicenter, open-label, phase II study of tirabrutinib (ONO/GS-4059) in patients with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(9):3327–37.
Walter HS, Rule SA, Dyer MJS, et al. A phase 1 clinical trial of the selective BTK inhibitor ONO/GS-4059 in relapsed and refractory mature B-cell malignancies. Blood. 2016;127(4):411–9.
Liclican A, Serafini L, Xing W, et al. Biochemical characterization of tirabrutinib and other irreversible inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase reveals differences in on- and off-target inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020;1864(4):129531.
Munakata W, Ando K, Hatake K, et al. Phase I study of tirabrutinib (ONO-4059/GS-4059) in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies in Japan. Cancer Sci. 2019;110(5):1686–94.
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency-Japan. Velexbru tablets (tirabrutinib hydrochloride): report on the deliberation results. 2020. https://www.pmda.go.jp. Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
Zhang B, Zhao R, Liang R, et al. Orelabrutinib, a potent and selective Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor with superior safety profile and excellent PK/PD properties. Cancer Res. 2020;80(16 Suppl):CT132.
Xu W, Song Y, Wang T, et al. Updated results from the phase II study of orelabrutinib monotherapy in Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell leukemia. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):26–7.
Mato AR, Shah NN, Jurczak W, et al. Pirtobrutinib in relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (BRUIN): a phase 1/2 study. Lancet. 2021;397(10277):892–901.
Brandhuber B, Gomez E, Smith S, et al. LOXO-305, a next generation reversible BTK inhibitor, for overcoming acquired resistance to irreversible BTK inhibitors. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018;18(Suppl 1):S216.
Reiff SD, Mantel R, Smith LL, et al. The BTK inhibitor ARQ 531 targets ibrutinib-resistant CLL and Richter transformation. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(10):1300–15.
Woyach J, Stephens DM, Flinn I, et al. A phase 1 dose escalation study of ARQ 531 in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphoid malignancies [abstract plus poster no. PS1150]. In: EHA. 2019.
Ponader S, Chen SS, Buggy JJ, et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 thwarts chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival and tissue homing in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 2012;119(5):1182–9.
Patel V, Balakrishnan K, Bibikova E, et al. Comparison of acalabrutinib, a selective Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, with ibrutinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(14):3734–43.
Herman SEM, Montraveta A, Niemann CU, et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib demonstrates potent on-target effects and efficacy in two mouse models of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(11):2831–41.
Sharman JP, Egyed M, Jurczak W, et al. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzmab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE-TN): a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020;395(10232):1278–91.
InnoCare Pharma Ltd. Orelabrutinib: Chinese prescribing information. Beijing: Innocare Pharma Ltd. 2021.
Smith CIE, Burger JA. Resistance mutations to BTK inhibitors originate from the NF-κB but not from the PI3K-RAS-MAPK arm of the B cell receptor signaling pathway. Front Immunol. 2021;12:689472.
Woyach JA, Furman RR, Liu T-M, et al. Resistance mechanisms for the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(24):2286–94.
Furman RR, Cheng S, Lu P, et al. Ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(24):2352–4.
Furstenau M, Eichhorst B. Novel agents in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: new combination therapies and strategies to overcome resistance. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(6):1336.
Wang ML, Blum KA, Martin P, et al. Long-term follow-up of MCL patients treated with single-agent ibrutinib: updated safety and efficacy results. Blood. 2015;126(6):739–45.
Wang ML, Rule S, Martin P, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(6):507–16.
Wang M, Goy A, Martin P, et al. Efficacy and safety of single-agent ibrutinib in patients with mantle cell lymphoma who progressed after bortezomib therapy. Blood. 2014;124(21):4471.
Wang M, Rule S, Zinzani PL, et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: long-term efficacy and safety results from a phase 2 study. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):38–9.
Wang M, Rule S, Zinzani PL, et al. Durable response with single-agent acalabrutinib in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2019;33(11):2762–6.
Wang M, Rule S, Zinzani PL, et al. Acalabrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (ACE-LY-004): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10121):659–67.
Song Y, Zhou K, Zou D, et al. Treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma with zanubrutinib, a selective inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(16):4216–24.
Rule S, Jurczak W, Jerkeman M, et al. Ibrutinib versus temsirolimus: 3-year follow-up of patients with previously treated mantle cell lymphoma from the phase 3, international, randomized, open-label RAY study. Leukemia. 2018;32(8):1799–803.
Dreyling M, Jurczak W, Jerkeman M, et al. Ibrutinib versus temsirolimus in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma: an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2016;387(10020):770–8.
Song Y, Zhou K, Zou D, et al. Zanubrutinib (zanu) in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) mantle cell lymphoma (MCL): long-term efficacy and safety results from a phase 2 study [abstract no. EP789]. In: EHA2021. 2021.
Rule SA, Cartron G, Fegan C, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) treated with the selective Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor tirabrutinib (GS/ONO-4059). Leukemia. 2020;34(5):1458–61.
Song Y, Liu L, Zhang M, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of orelabrutinib monotherapy in Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a multicenter, open-label, phase II study. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):1.
Song Y, Liu L, Zhang M, et al. Safety and efficacy of orelabrutinib monotherapy in Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a multicenter, open-label, phase II study. Blood. 2019;134(Suppl 1):755.
Jain P, Romaguera J, Srour SA, et al. Four-year follow-up of a single arm, phase II clinical trial of ibrutinib with rituximab (IR) in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Br J Haematol. 2018;182(3):404–11.
Jerkeman M, Eskelund CW, Hutchings M, et al. Ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and rituximab in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (PHILEMON): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2018;5(3):e109–16.
Wang ML, Lee H, Chuang H, et al. Ibrutinib in combination with rituximab in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a single-centre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(1):48–56.
Le Gouill S, Morschhauser F, Chiron D, et al. Ibrutinib, obinutuzumab, and venetoclax in relapsed and untreated patients with mantle cell lymphoma: a phase 1/2 trial. Blood. 2021;137(7):877–87.
Tam CS, Anderson MA, Pott C, et al. Ibrutinib plus venetoclax for the treatment of mantle-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(13):1211–23.
Wang M, Ramchandren R, Chen R, et al. Concurrent ibrutinib plus venetoclax in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: the safety run-in of the phase 3 SYMPATICO study. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):179.
Morschhauser F, Dyer MJS, Walter HS, et al. Phase 1b study of tirabrutinib in combination with idelalisib or entospletinib in previously treated B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2020;35(7):2108–13.
Wang M, Jain P, Yao Y, et al. Ibrutinib plus rituximab (IR) followed by short course R-HCVAD/MTX in patients (age ≤ 65 years) with previously untreated mantle cell lymphoma-phase-II Window-1 clinical trial. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):35–6.
Jain P, Yao Y, Zhao S, et al. Combination of ibrutinib with rituximab (IR) in previously untreated older patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) -a phase II clinical trial. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):41–2.
Dreyling M, Tam CS, Wang M, et al. A phase III study of zanubrutinib plus rituximab versus bendamustine plus rituximab in transplant-ineligible, untreated mantle cell lymphoma. Future Oncol. 2021;17(3):255–62.
Wang ML, Jurczak W, Eckert K, et al. First-line ibrutinib plus venetoclax in MCL for older patients or those with a TP53 mutation: ongoing open-label arm of the PCYC-1143 phase 3 SYMPATICO study. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(Suppl 1):S259.
Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Ibrutinib treatment for first-line and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: final analysis of the pivotal phase Ib/II PCYC-1102 study. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(15):3918–27.
O’Brien S, Furman RR, Coutre S, et al. Single-agent ibrutinib in treatment-naïve and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a 5-year experience. Blood. 2018;131(17):1910–9.
Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Three-year follow-up of treatment-naive and previously treated patients with CLL and SLL receiving single-agent ibrutinib. Blood. 2015;125(16):2497–506.
Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(1):32–42.
O’Brien S, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma: an open-label, multicentre, phase 1b/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(1):48–58.
Brown JR, Hillmen P, O’Brien S, et al. Extended follow-up and impact of high-risk prognostic factors from the phase 3 RESONATE study in patients with previously treated CLL/SLL. Leukemia. 2018;32(1):83–91.
Byrd JC, Hillmen P, O’Brien S, et al. Long-term follow-up of the RESONATE phase 3 trial of ibrutinib vs ofatumumab. Blood. 2019;133(19):2031–42.
Munir T, Brown JR, O’Brien S, et al. Final analysis from RESONATE: up to six years of follow-up on ibrutinib in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(12):1353–63.
Byrd JC, Brown JR, O’Brien S, et al. Ibrutinib versus ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(3):213–23.
Ghia P, Pluta A, Wach M, et al. Acalabrutinib vs idelalisib plus rituximab (IDR) or bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in relapsed/ refractory (R/R) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): ASCEND final results. HemaSphere. 2020;4(Suppl 1):33.
Ghia P, Pluta A, Wach M, et al. ASCEND: phase III, randomized trial of acalabrutinib versus idelalisib plus rituximab or bendamustine plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(25):2849–61.
Byrd JC, Hillmen P, Ghia P, et al. Acalabrutinib versus ibrutinib in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results of the first randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.21.01210.
Hillmen P, Eichhorst B, Brown JR, et al. First interim analysis of ALPINE study: results of a phase 3 randomized study of zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma [abstract no. LB1900]. In: 25th European Hematology Association Annual Congress (EHA25). 2021.
Fraser G, Cramer P, Demirkan F, et al. Updated results from the phase 3 HELIOS study of ibrutinib, bendamustine, and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Leukemia. 2019;33(4):969–80.
Chanan-Khan A, Cramer P, Demirkan F, et al. Ibrutinib combined with bendamustine and rituximab compared with placebo, bendamustine, and rituximab for previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (HELIOS): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(2):200–11.
Fraser GAM, Chanan-Khan A, Demirkan F, et al. Final 5-year findings from the phase 3 HELIOS study of ibrutinib plus bendamustine and rituximab in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020;61(13):3188–97.
Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, et al. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2425–37.
Burger JA, Barr PM, Robak T, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of first-line ibrutinib treatment for patients with CLL/SLL: 5 years of follow-up from the phase 3 RESONATE-2 study. Leukemia. 2020;34(3):787–98.
Moreno C, Greil R, Demirkan F, et al. Ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (iLLUMINATE): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(1):43–56.
Sharman JP, Egyed M, Jurczak W, et al. Acalabrutinib ± obinutuzumab versus obinutuzumab + chlorambucil in treatment-naïve chronic lymphocytic leukemia: ELEVATE-TN four-year follow up. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15 Suppl):7509.
Woyach JA, Ruppert AS, Heerema NA, et al. Ibrutinib regimens versus chemoimmunotherapy in older patients with untreated CLL. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(26):2517–28.
Shanafelt TD, Wang XV, Kay NE, et al. Ibrutinib-rituximab or chemoimmunotherapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(5):432–43.
Barr PM, Robak T, Owen C, et al. Sustained efficacy and detailed clinical follow-up of first-line ibrutinib treatment in older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: extended phase 3 results from RESONATE-2. Haematologica. 2018;103(9):1502–10.
Hillmen P, Brown JR, Kahl BS, et al. Phase 3 zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) vs bendamustine + rituximab (BR) in patients (pts) with treatment-naïve (TN) chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL). J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15 suppl):TPS7581.
Tam CS, Flinn IW, Tedeschi A, et al. Zanubrutinib in combination with venetoclax for patients with treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma and del(17p): Arm D of the SEQUOIA (BGB-3111-304) trial. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):24–5.
Tam CS, Robak T, Ghia P, et al. Zanubrutinib monotherapy for patients with treatment naive chronic lymphocytic leukemia and 17p deletion. Haematologica. 2021;106(9):2354–63.
Danilov AV, Herbaux C, Walter HS, et al. Phase Ib study of tirabrutinib in combination with idelalisib or entospletinib in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(12):2810–8.
Walter HS, Jayne S, Rule SA, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with CLL treated with the selective Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ONO/GS-4059. Blood. 2017;129(20):2808–10.
Jain N, Keating M, Thompson P, et al. Ibrutinib and venetoclax for first-line treatment of CLL. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(22):2095–103.
Jain N, Keating M, Thompson P, et al. Ibrutinib plus venetoclax for first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a nonrandomized phase 2 trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021;10:10.
Jain N, Keating MJ, Thompson PA, et al. Combined ibrutinib and venetoclax for first-line treatment for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): focus on MRD results. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):42–3.
Rogers KA, Huang Y, Ruppert AS, et al. Three-year follow-up from a phase 2 study of combination obinutuzumab, ibrutinib, and venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):9–10.
Wierda WG, Allan JN, Siddiqi T, et al. Ibrutinib plus venetoclax for first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: primary analysis results from the minimal residual disease cohort of the randomized phase II CAPTIVATE study. J Clin Oncol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.21.00807.
Davids MS, Lampson BL, Tyekucheva S, et al. Acalabrutinib, venetoclax, and obinutuzumab as frontline treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a single-arm, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22(10):1391–402.
Soumerai J, Mato A, Carter J, et al. Initial results of a multicenter, investigator initiated study of MRD driven time limited therapy with zanubrutinib, obinutuzumab and venetoclax. HemaSphere. 2020;4(Suppl 1):35.
Treon SP, Meid K, Gustine J, et al. Long-term follow-up of ibrutinib monotherapy in symptomatic, previously treated patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(6):565–75.
Tam CSL, Opat S, Marlton P, et al. Three-year follow-up of treatment-naïve and previously treated patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) receiving single-agent zanubrutinib. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(15 suppl):8051.
Treon SP, Tripsas CK, Meid K, et al. Ibrutinib in previously treated Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(15):1430–40.
Dimopoulos MA, Tedeschi A, Trotman J, et al. Phase 3 trial of ibrutinib plus rituximab in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(25):2399–410.
Tam CS, Opat S, D’Sa S, et al. A randomized phase 3 trial of zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib in symptomatic Waldenström macroglobulinemia: the ASPEN study. Blood. 2020;136(18):2038–50.
Treon SP, Gustine J, Meid K, et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy in symptomatic, treatment-naïve patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(27):2755–61.
Owen RG, McCarthy H, Rule S, et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia: a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(2):e112–21.
An G, Zhou D, Zhao W, et al. Safety and efficacy of the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia from a phase 2 trial. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):42–3.
Dimopoulos MA, Trotman J, Tedeschi A, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with rituximab-refractory Waldenström’s macroglobulinaemia (iNNOVATE): an open-label substudy of an international, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(2):241–50.
Tedeschi A, Trotman J, Tam C, et al. Phase 1/2 study of single-agent zanubrutinib in patients with relapsed/refractory marginal zone lymphoma. HemaSphere. 2020;4(Suppl 1):542.
Noy A, de Vos S, Coleman M, et al. Durable ibrutinib responses in relapsed/refractory marginal zone lymphoma: long-term follow-up and biomarker analysis. Blood Adv. 2020;4(22):5773–84.
Noy A, de Vos S, Thieblemont C, et al. Targeting Bruton tyrosine kinase with ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory marginal zone lymphoma. Blood. 2017;129(16):2224–32.
Song Y, Xu W, Song Y, et al. Pooled analysis of safety data from clinical trials of orelabrutinib monotherapy in hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):43.
Estupiñán HY, Berglöf A, Zain R, et al. Comparative analysis of BTK inhibitors and mechanisms underlying adverse effects. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:630942.
Tao G, Chityala PK. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-induced diarrhea: clinical incidence, toxicological mechanism, and management. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021;10(3):476–86.
Sibaud V, Beylot-Barry M, Protin C, et al. Dermatological toxicities of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21(6):799–812.
Jones J, Mato A, Coutre S, et al. Evaluation of 230 patients with relapsed/refractory deletion 17p chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with ibrutinib from 3 clinical trials. Br J Haematol. 2018;182(4):504–12.
Shaw ML. Second-generation BTK inhibitors hit the treatment bullseye with fewer off-target effects. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(7):SP226–7.
Rogers KA, Thompson PA, Allan JN, et al. Phase II study of acalabrutinib in ibrutinib-intolerant patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 2021;106(9):2364–73.
Shadman M, Sharman JP, Levy MY, et al. Preliminary results of the phase 2 study of zanubrutinib in patients with previously treated B-cell malignancies intolerant to ibrutinib and/or acalabrutinib. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15 suppl):e19506.
Lasica M, Tam CS. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: beyond ibrutinib. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am. 2021;35(4):761–73.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN® Guidelines: B-cell lymphomas v5.2021. 2021. https://www.nccn.org/. Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN® Guidelines: Waldenström macroglobulinemia/lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma v1.2022. 2021. https://www.nccn.org/. Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN® Guidelines: chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma v1.2022. 2021. https://www.nccn.org/. Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
The International CLL-IPI working group. An international prognostic index for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL-IPI): a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(6):779–90.
Jain P, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Zhang S, et al. Long-term outcomes and mutation profiling of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who discontinued ibrutinib. Br J Haematol. 2018;183(4):578–87.
Woyach JA, Ruppert AS, Guinn D, et al. BTKC481S-mediated resistance to ibrutinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(13):1437–43.
Timofeeva N, Gandhi V. Ibrutinib combinations in CLL therapy: scientific rationale and clinical results. Blood Cancer J. 2021;11(4):79.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and conflict of interest
Matt Shirley is a salaried employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature, is responsible for the article content and declares no relevant conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent to publish, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
The manuscript was reviewed by: T. Robak, Department of Hematology, Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland; J. F. Seymour, Department of Haematology, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Royal Melbourne Hospital & University of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC, Australia; M. Šimkovič, Department of Internal Medicine-Hematology, Charles University, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic; S. Thangavadivel, Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH, USA.
The original version of this article was revised due to a retrospective Open Access order.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Shirley, M. Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in B-Cell Malignancies: Their Use and Differential Features. Targ Oncol 17, 69–84 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-021-00857-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-021-00857-8