Abstract
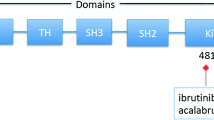
Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), a major kinase in the B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway, mediating B-cell proliferation and apoptosis, have substantially altered the management, clinical course, and outcome of patients with B-cell malignancies. This is especially true for patients with previously limited treatment options due to disease characteristics or coexisting diseases. Ibrutinib was the first orally available, nonselective and irreversible inhibitor of BTK approved for the treatment of patients with various B-cell malignancies. Newer and more selective BTK inhibitors are currently in clinical development, including acalabrutinib, which is currently US FDA approved for previously treated mantle cell lymphoma. Significant efforts are underway to investigate the optimal combinations, timing, and sequencing of BTK inhibitors with other regimens and targeted agents, and to capitalize on the immunomodulatory modes of action of BTK inhibitors to correct tumor-induced immune defects and to achieve long-lasting tumor control. This review describes the major milestones in the clinical development of BTK inhibitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other B-cell malignancies, highlights the most recent long-term follow-up results, and evaluates the role of BTK inhibitors and their combination with other agents in B-cell malignancies and other indications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischer K, Bahlo J, Fink AM, Goede V, Herling CD, Cramer P, et al. Long-term remissions after FCR chemoimmunotherapy in previously untreated patients with CLL: updated results of the CLL8 trial. Blood. 2016;127:208–15.
Thompson PA, Tam CS, O’Brien SM, Wierda WG, Stingo F, Plunkett W, et al. Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab treatment achieves long-term disease-free survival in IGHV-mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:303–9.
Rossi D, Terzi-di-Bergamo L, De Paoli L, Cerri M, Ghilardi G, Chiarenza A, et al. Molecular prediction of durable remission after first-line fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2015;126:1921–4.
Eichhorst B, Fink AM, Bahlo J, Busch R, Kovacs G, Maurer C, et al. First-line chemoimmunotherapy with bendamustine and rituximab versus fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL10): an international, open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:928–42.
Goede V, Fischer K, Busch R, Engelke A, Eichhorst B, Wendtner CM, et al. Obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in patients with CLL and coexisting conditions. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1101–10.
Zenz T, Gribben JG, Hallek M, Doehner H, Keating MJ, Stilgenbauer S. Risk categories and refractory CLL in the era of chemoimmunotherapy. Blood. 2012;119:4101–7.
Gribben JG. How and when I do allogeneic transplant in CLL. Blood. 2018;132:31–9.
Davids MS. How should we sequence and combine novel therapies in CLL? ASH Educ Program Book. 2017;2017:346–53.
Seda V, Mraz M. B-cell receptor signalling and its crosstalk with other pathways in normal and malignant cells. Eur J Haematol. 2015;94:193–205.
Pal Singh S, Dammeijer F, Hendriks RW. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:57.
Ten Hacken E, Burger JA. Microenvironment interactions and B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: implications for disease pathogenesis and treatment. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2016;1863:401–13.
Weber ANR, Bittner Z, Liu X, Dang TM, Radsak MP, Brunner C. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase: an emerging key player in innate immunity. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1454.
Dubovsky JA, Beckwith KA, Natarajan G, Woyach JA, Jaglowski S, Zhong Y, et al. Ibrutinib is an irreversible molecular inhibitor of ITK driving a Th1-selective pressure in T lymphocytes. Blood. 2013;122:2539–49.
Ren L, Campbell A, Fang H, Gautam S, Elavazhagan S, Fatehchand K, et al. Analysis of the effects of the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor ibrutinib on monocyte Fcgamma receptor (FcgammaR) function. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:3043–52.
Ping L, Ding N, Shi Y, Feng L, Li J, Liu Y, et al. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib exerts immunomodulatory effects through regulation of tumor-infiltrating macrophages. Oncotarget. 2017;8:39218–29.
Chen SS, Chang BY, Chang S, Tong T, Ham S, Sherry B, et al. BTK inhibition results in impaired CXCR4 chemokine receptor surface expression, signaling and function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2016;30:833–43.
Andersen MA, Eriksen CT, Brieghel C, Biccler JL, Cunha-Bang CD, Helleberg M, et al. Incidence and predictors of infection among patients prior to treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a Danish nationwide cohort study. Haematologica. 2018;103(7):e300–3.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration, C.f.D.E.a.R. Imbruvica® (ibrutinib), for oral use: highlights of prescribing information (2018). https://www.imbruvica.com/docs/librariesprovider7/default-document-library/prescribing-information.pdf. Accessed 30 Oct 2018.
Advani RH, Buggy JJ, Sharman JP, Smith SM, Boyd TE, Grant B, et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) has significant activity in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:88–94.
Noy A, de Vos S, Thieblemont C, Martin P, Flowers CR, Morschhauser F, et al. Targeting Bruton tyrosine kinase with ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory marginal zone lymphoma. Blood. 2017;129:2224–32.
Treon SP, Tripsas CK, Meid K, Warren D, Varma G, Green R, et al. Ibrutinib in previously treated Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1430–40.
Dimopoulos MA, Trotman J, Tedeschi A, Matous JV, Macdonald D, Tam C, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with rituximab-refractory Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinaemia (iNNOVATE): an open-label substudy of an international, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:241–50.
Treon SP, Gustine J, Meid K, Yang G, Xu L, Liu X, et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy in symptomatic, treatment-naive patients with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2755–61.
Wang ML, Rule S, Martin P, Goy A, Auer R, Kahl BS, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:507–16.
Rule S, Dreyling M, Goy A, Hess G, Auer R, Kahl BS, et al. Median 3.5-year follow-up of ibrutinib treatment in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a pooled analysis. Blood. 2017;130:151.
Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, Flinn IW, Burger JA, Blum KA, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:32–42.
Stauder R, Eichhorst B, Hamaker ME, Kaplanov K, Morrison VA, Osterborg A, et al. Management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in the elderly: a position paper from an international Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) Task Force. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:218–27.
O’Brien S, Furman RR, Coutre S, Flinn IW, Burger JA, Blum K, et al. Single-agent ibrutinib in treatment-naive and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a 5-year experience. Blood. 2018;131:1910–9.
Farooqui MZ, Valdez J, Martyr S, Aue G, Saba N, Niemann CU, et al. Ibrutinib for previously untreated and relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with TP53 aberrations: a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:169–76.
Ahn IE, Farooqui MZH, Tian X, Valdez J, Sun C, Soto S, et al. Depth and durability of response to ibrutinib in CLL: 5-year follow-up of a phase 2 study. Blood. 2018;131:2357–66.
O’Brien S, Jones JA, Coutre SE, Mato AR, Hillmen P, Tam C, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion (RESONATE-17): a phase 2, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:1409–18.
Byrd JC, Brown JR, O’Brien S, Barrientos JC, Kay NE, Reddy NM, et al. Ibrutinib versus ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:213–23.
O’Brien S, Furman RR, Coutre SE, Sharman JP, Burger JA, Blum KA, et al. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma: an open-label, multicentre, phase 1b/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:48–58.
Jones J, Mato A, Coutre S, Byrd JC, Furman RR, Hillmen P, et al. Evaluation of 230 patients with relapsed/refractory deletion 17p chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with ibrutinib from 3 clinical trials. Br J Haematol. 2018;182:504–12.
Dreyling M, Jurczak W, Jerkeman M, Silva RS, Rusconi C, Trneny M, et al. Ibrutinib versus temsirolimus in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma: an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2016;387:770–8.
Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, Robak T, Owen C, Ghia P, et al. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2425–37.
Barr PM, Robak T, Owen C, Tedeschi A, Bairey O, Bartlett NL, et al. Sustained efficacy and detailed clinical follow-up of first-line ibrutinib treatment in older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: extended phase 3 results from RESONATE-2. Haematologica. 2018;103:1502–10.
Woyach JA, Ruppert AS, Heerema NA, Zhao W, Booth AM, Ding W, et al. Ibrutinib regimens versus chemoimmunotherapy in older patients with untreated CLL. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2517–28.
Burger JA, Keating MJ, Wierda WG, Hartmann E, Hoellenriegel J, Rosin NY, et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib plus rituximab for patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:1090–9.
Jain P, Keating MJ, Wierda WG, Sivina M, Thompson PA, Ferrajoli A, et al. Long-term follow-up of treatment with ibrutinib and rituximab in patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:2154–8.
Shanafelt TD, Wang V, Kay NE, Hanson CA, O’Brien SM, Barrientos J, et al. A randomized phase III study of ibrutinib (PCI-32765)-based therapy vs. standard fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) chemoimmunotherapy in untreated younger patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): a trial of the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (E1912). Blood. 2018;132:LBA-4.
Dimopoulos MA, Tedeschi A, Trotman J, Garcia-Sanz R, Macdonald D, Leblond V, et al. Phase 3 trial of ibrutinib plus rituximab in Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2399–410.
Wang ML, Lee H, Chuang H, Wagner-Bartak N, Hagemeister F, Westin J, et al. Ibrutinib in combination with rituximab in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a single-centre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:48–56.
Jaglowski SM, Jones JA, Nagar V, Flynn JM, Andritsos LA, Maddocks KJ, et al. Safety and activity of BTK inhibitor ibrutinib combined with ofatumumab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a phase 1b/2 study. Blood. 2015;126:842–50.
Moreno C, Greil R, Demirkan F, Tedeschi A, Anz B, Larratt L, et al. Ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (iLLUMINATE): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;20:43–56.
Chanan-Khan A, Cramer P, Demirkan F, Fraser G, Silva RS, Grosicki S, et al. Ibrutinib combined with bendamustine and rituximab compared with placebo, bendamustine, and rituximab for previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (HELIOS): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:200–11.
Fraser G, Cramer P, Demirkan F, Silva RS, Grosicki S, Pristupa A, et al. Updated results from the phase 3 HELIOS study of ibrutinib, bendamustine, and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Leukemia. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-018-0276-9.
Ujjani C, Wang H, Skarbnik A, Trivedi N, Ramzi P, Khan N, Cheson BD. A phase 1 study of lenalidomide and ibrutinib in combination with rituximab in relapsed and refractory CLL. Blood Adv. 2018;2:762–8.
Jerkeman M, Eskelund CW, Hutchings M, Raty R, Wader KF, Laurell A, et al. Ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and rituximab in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (PHILEMON): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2018;5:e109–16.
Jain N, Keating M, Thompson PA, Ferrajoli A, Burger J, Borthakur G, et al. Combined ibrutinib and venetoclax in patients with treatment-naïve high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Blood. 2018;132:696.
Hillmen P, Rawstron A, Brock K, Munoz Vincente S, Yates F, Bishop RM, et al. Ibrutinib plus venetoclax in relapsed/refractory CLL: results of the bloodwise TAP Clarity Study. Blood. 2018;132:182.
Tam CS, Anderson MA, Pott C, Agarwal R, Handunnetti S, Hicks RJ, et al. Ibrutinib plus venetoclax for the treatment of mantle-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1211–23.
Rogers KA, Huang Y, Ruppert AS, Awan FT, Heerema NA, Hoffman C, et al. Phase 1b study of obinutuzumab, ibrutinib, and venetoclax in relapsed and refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2018;132:1568–72.
Rogers KA, Huang Y, Ruppert AS, Awan F, Hoffman C, Maddocks K, et al. Phase 2 study of combination obinutuzumab, ibrutinib, and venetoclax in treatment-naive and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2018;132:693.
Davids MS, Kim HT, Nicotra A, Savell A, Francoeur K, Hellman JM, et al. Umbralisib in combination with ibrutinib in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or mantle cell lymphoma: a multicentre phase 1-1b study. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6:e38–47.
Nastoupil LJ, Lunning MA, Vose JM, Schreeder MT, Siddiqi T, Flowers CR, et al. Tolerability and activity of ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a phase 1 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6:e100–9.
Fraietta JA, Beckwith KA, Patel PR, Ruella M, Zheng Z, Barrett DM, et al. Ibrutinib enhances chimeric antigen receptor T-cell engraftment and efficacy in leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:1117–27.
Herman SE, Mustafa RZ, Jones J, Wong DH, Farooqui M, Wiestner A. Treatment with ibrutinib inhibits BTK- and VLA-4-dependent adhesion of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:4642–51.
Wodarz D, Garg N, Komarova NL, Benjamini O, Keating MJ, Wierda WG, et al. Kinetics of CLL cells in tissues and blood during therapy with the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib. Blood. 2014;123:4132–5.
Burger JA, Li KW, Keating MJ, Sivina M, Amer AM, Garg N, et al. Leukemia cell proliferation and death in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients on therapy with the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib. JCI Insight. 2017;2:e89904.
Woyach JA, Smucker K, Smith LL, Lozanski A, Zhong Y, Ruppert AS, et al. Prolonged lymphocytosis during ibrutinib therapy is associated with distinct molecular characteristics and does not indicate a suboptimal response to therapy. Blood. 2014;123:1810–7.
Brown JR, Moslehi J, O’Brien S, Ghia P, Hillmen P, Cymbalista F, et al. Characterization of atrial fibrillation adverse events reported in ibrutinib randomized controlled registration trials. Haematologica. 2017;102:1796–805.
Wiczer TE, Levine LB, Brumbaugh J, Coggins J, Zhao Q, Ruppert AS, et al. Cumulative incidence, risk factors, and management of atrial fibrillation in patients receiving ibrutinib. Blood Adv. 2017;1:1739–48.
Reda G, Fattizzo B, Cassin R, Mattiello V, Tonella T, Giannarelli D, et al. Predictors of atrial fibrillation in ibrutinib-treated CLL patients: a prospective study. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11:79.
Guha A, Derbala MH, Zhao Q, Wiczer TE, Woyach JA, Byrd JC, et al. Ventricular arrhythmias following ibrutinib initiation for lymphoid malignancies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72:697–8.
Lipsky AH, Farooqui MZ, Tian X, Martyr S, Cullinane AM, Nghiem K, et al. Incidence and risk factors of bleeding-related adverse events in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib. Haematologica. 2015;100:1571–8.
Wang ML, Blum KA, Martin P, Goy A, Auer R, Kahl BS, et al. Long-term follow-up of MCL patients treated with single-agent ibrutinib: updated safety and efficacy results. Blood. 2015;126:739–45.
Caron F, Leong DP, Hillis C, Fraser G, Siegal D. Current understanding of bleeding with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2017;1:772–8.
Kazianka L, Drucker C, Skrabs C, Thomas W, Melchardt T, Struve S, et al. Ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation for monitoring of bleeding tendency in CLL treated with ibrutinib. Leukemia. 2017;31:1117–22.
Varughese T, Taur Y, Cohen N, Palomba ML, Seo SK, Hohl TM, Redelman-Sidi G. Serious infections in patients receiving ibrutinib for treatment of lymphoid malignancies. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67:687–92.
Ghez D, Calleja A, Protin C, Baron M, Ledoux MP, Damaj G, et al. Early-onset invasive aspergillosis and other fungal infections in patients treated with ibrutinib. Blood. 2018;131:1955–9.
Bercusson A, Colley T, Shah A, Warris A, Armstrong-James D. Ibrutinib blocks Btk-dependent NF-kB and NFAT responses in human macrophages during Aspergillus fumigatus phagocytosis. Blood. 2018;132:1985–8.
Rogers KA, Luay M, Zhao Q, Wiczer T, Levine L, Zeinab EB, et al. Incidence and type of opportunistic infections during ibrutinib treatment at a single academic center. Blood. 2017;130:830.
Maddocks KJ, Ruppert AS, Lozanski G, Heerema NA, Zhao W, Abruzzo L, et al. Etiology of ibrutinib therapy discontinuation and outcomes in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. JAMA Oncol. 2015;1:80–7.
Sun C, Tian X, Lee YS, Gunti S, Lipsky A, Herman SE, et al. Partial reconstitution of humoral immunity and fewer infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib. Blood. 2015;126:2213–9.
O’Brien SM, Jaglowski S, Byrd JC, Bannerji R, Blum KA, Fox CP, et al. Prognostic factors for complete response to ibrutinib in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a pooled analysis of 2 clinical trials. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:712–6.
Thompson PA, O’Brien SM, Xiao L, Wang X, Burger JA, Jain N, et al. beta2 -microglobulin normalization within 6 months of ibrutinib-based treatment is associated with superior progression-free survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer. 2016;122:565–73.
Barr PM, Brown JR, Hillmen P, O’Brien S, Barrientos JC, Reddy NM, et al. Impact of ibrutinib dose adherence on therapeutic efficacy in patients with previously treated CLL/SLL. Blood. 2017;129:2612–5.
Thompson PA, O’Brien SM, Wierda WG, Ferrajoli A, Stingo F, Smith SC, et al. Complex karyotype is a stronger predictor than del(17p) for an inferior outcome in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients treated with ibrutinib-based regimens. Cancer. 2015;121:3612–21.
Miller CR, Ruppert AS, Heerema NA, Maddocks KJ, Labanowska J, Breidenbach H, et al. Near-tetraploidy is associated with Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients receiving ibrutinib. Blood Adv. 2017;1:1584–8.
Woyach JA, Furman RR, Liu T-M, Ozer HG, Zapatka M, Ruppert AS, et al. Resistance mechanisms for the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2286–94.
Liu TM, Woyach JA, Zhong Y, Lozanski A, Lozanski G, Dong S, et al. Hypermorphic mutation of phospholipase C, gamma2 acquired in ibrutinib-resistant CLL confers BTK independency upon B-cell receptor activation. Blood. 2015;126:61–8.
Ahn IE, Underbayev C, Albitar A, Herman SE, Tian X, Maric I, et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2017;129:1469–79.
Woyach JA, Ruppert AS, Guinn D, Lehman A, Blachly JS, Lozanski A, et al. BTK(C481S)-mediated resistance to ibrutinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1437–43.
Burger JA, Landau DA, Taylor-Weiner A, Bozic I, Zhang H, Sarosiek K. Clonal evolution in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia developing resistance to BTK inhibition. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11589.
Landau DA, Sun C, Rosebrock D, Herman SE, Fein J, Sivina M, et al. The evolutionary landscape of chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib targeted therapy. Nat Commun. 2017;8:2185.
Scherer F, Kurtz DM, Newman AM, Stehr H, Craig AF, Esfahani MS, et al. Distinct biological subtypes and patterns of genome evolution in lymphoma revealed by circulating tumor DNA. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:364ra155.
Dubois S, Viailly PJ, Mareschal S, Bohers E, Bertrand P, Ruminy P, et al. Next-generation sequencing in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma highlights molecular divergence and therapeutic opportunities: a LYSA study. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:2919–28.
Xu L, Tsakmaklis N, Yang G, Chen JG, Liu X, Demos M, et al. Acquired mutations associated with ibrutinib resistance in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Blood. 2017;129:2519–25.
Paulus A, Akhtar S, Yousaf H, Manna A, Paulus SM, Bashir Y, et al. Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia cells devoid of BTK (C481S) or CXCR4 (WHIM-like) mutations acquire resistance to ibrutinib through upregulation of Bcl-2 and AKT resulting in vulnerability towards venetoclax or MK2206 treatment. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7:e565.
Zhao X, Lwin T, Silva A, Shah B, Tao J, Fang B, et al. Unification of de novo and acquired ibrutinib resistance in mantle cell lymphoma. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14920.
Lampson BL, Brown JR. Are BTK and PLCG2 mutations necessary and sufficient for ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia? Expert Rev Hematol. 2018;11:185–94.
Cheah CY, Chihara D, Romaguera JE, Fowler NH, Seymour JF, Hagemeister FB, et al. Patients with mantle cell lymphoma failing ibrutinib are unlikely to respond to salvage chemotherapy and have poor outcomes. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:1175–9.
Woyach JA. How I manage ibrutinib-refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2017;129:1270–4.
Ding W. Richter transformation in the era of novel agents. Hematology. 2018;2018:256–63.
Jones JA, Mato AR, Wierda WG, Davids MS, Choi M, Cheson BD, et al. Venetoclax for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia progressing after ibrutinib: an interim analysis of a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:65–75.
Mato AR, Hill BT, Lamanna N, Barr PM, Ujjani CS, Brander DM, et al. Optimal sequencing of ibrutinib, idelalisib, and venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from a multicenter study of 683 patients. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:1050–6.
Turtle CJ, Hay KA, Hanafi LA, Li D, Cherian S, Chen X, et al. Durable molecular remissions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor-modified t cells after failure of ibrutinib. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3010–20.
Robinson HR, Qi J, Cook EM, Nichols C, Dadashian EL, Underbayev C, et al. A CD19/CD3 bispecific antibody for effective immunotherapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the ibrutinib era. Blood. 2018;132:521–32.
Ding W, LaPlant BR, Call TG, Parikh SA, Leis JF, He R, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood. 2017;129:3419–27.
Byrd JC, Harrington B, O’Brien S, Jones JA, Schuh A, Devereux S, et al. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:323–32.
Wang M, Rule S, Zinzani PL, Goy A, Casasnovas O, Smith SD, et al. Acalabrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (ACE-LY-004): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2018;391:659–67.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration, C.f.D.E.a.R. CALQUENCE® (alabrutinib) capsules, for oral use: highlights of prescribing information. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/210259s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 30 Oct 2018.
Patel VK, Lamothe B, Ayres ML, Gay J, Cheung JP, Balakrishnan K, et al. Pharmacodynamics and proteomic analysis of acalabrutinib therapy: similarity of on-target effects to ibrutinib and rationale for combination therapy. Leukemia. 2018;32:920–30.
Niemann CU, Mora-Jensen HI, Dadashian EL, Krantz F, Covey T, Chen SS, et al. Combined BTK and PI3Kdelta inhibition with acalabrutinib and ACP-319 improves survival and tumor control in CLL mouse model. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:5814–23.
Walter HS, Rule SA, Dyer MJ, Karlin L, Jones C, Cazin B, et al. A phase 1 clinical trial of the selective BTK inhibitor ONO/GS-4059 in relapsed and refractory mature B-cell malignancies. Blood. 2016;127:411–9.
Walter HS, Jayne S, Rule SA, Cartron G, Morschhauser F, Macip S, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with CLL treated with the selective Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ONO/GS-4059. Blood. 2017;129:2808–10.
Tam C, Grigg AP, Opat S, Ku M, Gilbertson M, Anderson MA, et al. The BTK inhibitor, Bgb-3111, is safe, tolerable, and highly active in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies: initial report of a phase 1 first-in-human trial. Blood. 2015;126:832.
Brown JR, Harb WA, Hill BT, Gabrilove J, Sharman JP, Schreeder MT, et al. Phase I study of single-agent CC-292, a highly selective Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 2016;101:e295–8.
Cramer P, von Tresckow J, Bahlo J, Engelke A, Langerbeins P, Fink AM, et al. CLL2-BXX Phase II trials: sequential, targeted treatment for eradication of minimal residual disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Future Oncol. 2018;14:499–513.
Woyach JA. What is the optimal management of older CLL patients? Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2018;31:83–9.
Jaglowski SM, Blazar BR. How ibrutinib, a B-cell malignancy drug, became an FDA-approved second-line therapy for steroid-resistant chronic GVHD. Blood Adv. 2018;2:2012–9.
Ryan CE, Sahaf B, Logan AC, O’Brien S, Byrd JC, Hillmen P, et al. Ibrutinib efficacy and tolerability in patients with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia following allogeneic HCT. Blood. 2016;128:2899–908.
Grommes C, Pastore A, Palaskas N, Tang SS, Campos C, Schartz D, et al. Ibrutinib unmasks critical role of bruton tyrosine kinase in primary CNS lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:1018–29.
Gopal AK, Schuster SJ, Fowler NH, Trotman J, Hess G, Hou JZ, et al. Ibrutinib as treatment for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma: results from the open-label, multicenter, phase II DAWN study. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2405–12.
Campbell R, Chong G, Hawkes EA. Novel indications for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors, beyond hematological malignancies. J Clin Med. 2018;7:E62.
Maharaj K, Sahakian E, Pinilla-Ibarz J. Emerging role of BCR signaling inhibitors in immunomodulation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2017;1:1867–75.
Long M, Beckwith K, Do P, Mundy BL, Gordon A, Lehman AM, et al. Ibrutinib treatment improves T cell number and function in CLL patients. J Clin Investig. 2017;127:3052–64.
Niemann CU, Herman SE, Maric I, Gomez-Rodriguez J, Biancotto A, Chang BY, et al. Disruption of in vivo chronic lymphocytic leukemia tumor-microenvironment interactions by ibrutinib-findings from an investigator-initiated phase II study. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:1572–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No sources of funding were used to prepare this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Fabienne Lucas has no conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript. Jennifer A. Woyach receives research funding from Abbvie, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, Loxo, Karyopharm, Morphosys and has consulted for Janssen and Pharmacyclics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lucas, F., Woyach, J.A. Inhibiting Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase in CLL and Other B-Cell Malignancies. Targ Oncol 14, 125–138 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-019-00635-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-019-00635-7