Abstract
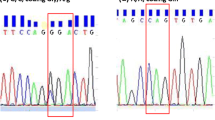
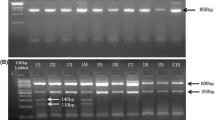
To understand the role of angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene (AGTR1) gene products in relation to hypotension we have analyzed the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with this gene. This can help us to understand the genetic variations that can alter the function of the gene products. In this present study, we report the polymorphic variant associated with AGTR1 and its weak interaction with angiotensin II (AngII) which leads to hypotension. Out of 1318 SNPs, six are found to be non-synonymous, of which rs1064533 shows significant damaging effect. A missense mutation (T1255G), i.e., from thymine to guanine for rs1064533 in AGTR1 gene results in amino acid substitution from cysteine (Cys) to tryptophan (Trp) in the receptor protein. A strong hydrogen bond exists between Cys289 of native AGTR1 protein and glutamine 167 of AngII. Interestingly, it is replaced by a weak hydrogen bond in the mutant protein between Trp289 (mutant residue) and serine 340. Such a substitution from small, hydrophilic to bulky, hydrophobic residue in AGTR1 protein results in reduced binding affinity of the receptor protein with AngII, leading to hypotension. The results presented from this in silico study will open up new prospect for genetic analysis of AGTR1 gene and will be beneficial to the researchers for understanding the role played by AGTR1 gene in hypotension disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anbarasu A, Anand S, Mathew L, Rao S (2006). Computation of noncovalent interactions in TNF proteins and interleukins. Cytokine, 35(5–6): 263–269
Anbarasu A, Anand S, Mathew L, Sethumadhavan R (2007). Influence of cation-π interactions on RNA-binding proteins. Int J Biol Macromol, 40(5): 479–483
Anbarasu A, Sethumadhavan R (2007). Exploring the role of cation-π interactions in glycoproteins lipid-binding proteins and RNA-binding proteins. J Theor Biol, 247(2): 346–353
Ausiello G, Cesareni G, Helmer-Citterich M (1997). ESCHER: a new docking procedure applied to the reconstruction of protein tertiary structure. Proteins, 28(4): 556–567
Benner S A, Cannarozzi G, Gerloff D, Turcotte M, Chelvanayagam G (1997). Bona fide predictions of protein secondary structure using transparent analyses of multiple sequence alignments. Chem Rev, 97(8): 2725–2844
Berry C, Touyz R, Dominiczak A F, Webb R C, Johns D G (2001). Angiotensin receptors: signaling, vascular pathophysiology, and interactions with ceramide. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 281(6): H2337–H2365
Cartegni L, Wang J, Zhu Z, Zhang M Q, Krainer A R (2003). ESEfinder: A web resource to identify exonic splicing enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res, 31(13): 3568–3571
Eswar N, Webb B, Marti-Renom M A, Madhusudhan M S, Eramian D, Shen M Y, Pieper U, Sali A (2007). Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Protein Sci, Chapter 2(9): 2, 9
Fairbrother W G, Yeh R F, Sharp P A, Burge C B (2002). Predictive identification of exonic splicing enhancers in human genes. Science, 297(5583): 1007–1013
Fairbrother W G, Yeo GW, Yeh R, Goldstein P, Mawson M, Sharp P A, Burge C B (2004). RESCUE-ESE identifies candidate exonic splicing enhancers in vertebrate exons. Nucleic Acids Res, 32(Web ServerWeb Server issue): W187–90
Fernandez-Recio J, Totrov M, Abagyan R (2002). Soft protein-protein docking in internal coordinates. Protein Sci, 11(2): 280–291
Fiser A, Sali A (2003). Modeller: generation and refinement of homology-based protein structure models. Methods Enzymol, 374: 461–491
Gallivan J P, Dougherty D A (1999). Cation-π interactions in structural biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 96(17): 9459–9464
Gavin A C, Superti-Furga G (2003). Protein complexes and proteome organization from yeast to man. Curr Opin Chem Biol, 7(1): 21–27
Gerken T A, Tep C, Rarick J (2004). Role of peptide sequence and neighboring residue glycosylation on the substrate specificity of the uridine 5′-diphosphate-alpha-N-acetylgalactosamine:polypeptide Nacetylgalactosaminyl transferases T1 and T2: kinetic modeling of the porcine and canine submaxillary gland mucin tandem repeats. Biochemistry, 43(30): 9888–9900
Griendling K K, Alexander RW (1993). The angiotensin (AT1) receptor. Semin Nephrol, 13(6): 558–566
Hansen J L, Haunsø S, Brann M R, Sheikh S P, Weiner D M (2004). Loss-of-function polymorphic variants of the human angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol, 65(3): 770–777
Hekkelman M L, Te Beek T A H, Pettifer S R, Thorne D, Attwood T K, Vriend G (2010). WIWS: a protein structure bioinformatics Web service collection. Nucleic Acids Res, 38(Web Server Web Server issue): W719–23
Higuchi S, Ohtsu H, Suzuki H, Shirai H, Frank G D, Eguchi S (2007). Angiotensin II signal transduction through the AT1 receptor: novel insights into mechanisms and pathophysiology. Clin Sci (Lond), 112(8): 417–428
Hogg P J (2003). Disulfide bonds as switches for protein function. Trends Biochem Sci, 28(4): 210–214
Hubbard T J P, Aken B L, Ayling S, Ballester B, Beal K, Bragin E, Brent S, Chen Y, Clapham P, Clarke L, Coates G, Fairley S, Fitzgerald S, Fernandez-Banet J, Gordon L, Graf S, Haider S, Hammond M, Holland R, Howe K, Jenkinson A, Johnson N, Kahari A, Keefe D, Keenan S, Kinsella R, Kokocinski F, Kulesha E, Lawson D, Longden I, Megy K, Meidl P, Overduin B, Parker A, Pritchard B, Rios D, Schuster M, Slater G, Smedley D, Spooner W, Spudich G, Trevanion S, Vilella A, Vogel J, White S, Wilder S, Zadissa A, Birney E, Cunningham F, Curwen V, Durbin R, Fernandez-Suarez X M, Herrero J, Kasprzyk A, Proctor G, Smith J, Searle S, Flicek P (2009). Ensembl 2009. Nucleic Acids Res, 37(Database Database issue): D690–D697
Jeffrey G A, Saenger W (1991) Hydrogen Bonding in Biological Structure. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, 459–486
Johnson M M, Houck J, Chen C (2005). Screening for deleterious non synonymous single-nucleotide polymorphisms in genes involved in steroid hormone metabolism and response. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 4(5): 1326–1329
Karchin R, Diekhans M, Kelly L, Thomas D J, Pieper U, Eswar N, Haussler D, Sali A (2005). LS-SNP: large-scale annotation of coding non-synonymous SNPs based on multiple information sources. Bioinformatics, 21(12): 2814–2820
Khan S, Vihinen M (2007). Spectrum of disease-causing mutations in protein secondary structures. BMC Struct Biol, 7(1): 56
Kuhn R M, Karolchik D, Zweig A S, Trumbower H, Thomas D J, Thakkapallayil A, Sugnet C W, Stanke M, Smith K E, Siepel A K, Rosenbloom K R, Rhead B, Raney B J, Pohl A, Pedersen J S, Hsu F, Hinrichs A S, Harte R A, Diekhans M, Clawson H, Bejerano G, Barber G P, Baertsch R, Haussler D, Kent W J (2007). The UCSC genome browser database: update 2007. Nucleic Acids Res, 35(Database Database issue): D668–D673
Lanver D, Mendoza-Mendoza A, Brachmann A, Kahmann R (2010). Sho1 and Msb2-related proteins regulate appressorium development in the smut fungus Ustilago maydis. Plant Cell, 22(6): 2085–2101
Leclerc P C, Lanctot P M, Auger-Messier M, Escher E, Leduc R, Guillemette G (2006). S-nitrosylation of cysteine 289 of the AT1 receptor decreases its binding affinity for angiotensin II. Br J Pharmacol, 148(3): 306–313
Lee P H, Shatkay H (2008). F-SNP: computationally predicted functional SNPs for disease association studies. Nucleic Acids Res, 36(Database Database issue): D820–D824
Lee P H, Shatkay H (2009). An integrative scoring system for ranking SNPs by their potential deleterious effects. Bioinformatics, 25(8): 1048–1055
Maekawa M, Kikuchi J, Kotani K, Nagao K, Odgerel T, Ueda K, Kawano M, Furukawa Y, Sakurabayashi I (2009). A novel missense mutation of ABCA1 in transmembrane alpha-helix in a Japanese patient with Tangier disease. Atherosclerosis, 206(1): 216–222
Mah J T L, Low E S H, Lee E (2011). In silico SNP analysis and bioinformatics tools: a review of the state of the art to aid drug discovery. Drug Discov Today, 16(17–18): 800–809
Meyer M, Wilson P, Schomburg D (1996). Hydrogen bonding and molecular surface shape complementarity as a basis for protein docking. J Mol Biol, 264(1): 199–210
Ng P C, Henikoff S (2003). SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res, 31(13): 3812–3814
Perodin J, Deraët M, Auger-Messier M, Boucard A A, Rihakova L, Beaulieu ME, Lavigne P, Parent J L, Guillemette G, Leduc R, Escher E (2002). Residues 293 and 294 are ligand contact points of the human angiotensin type 1 receptor. Biochemistry, 41(48): 14348–14356
Ramensky V, Bork P, Sunyaev S (2002). Human non-synonymous SNPs: server and survey. Nucleic Acids Res, 30(17): 3894–3900
Reumers J, Maurer-Stroh S, Schymkowitz J, Rousseau F (2006). SNPeffect v2.0: a new step in investigating the molecular phenotypic effects of human non-synonymous SNPs. Bioinformatics, 22(17): 2183–2185
Reumers J, Schymkowitz J, Ferkinghoff-Borg J, Stricher F, Serrano L, Rousseau F (2005). SNPeffect: a database mapping molecular phenotypic effects of human non-synonymous coding SNPs. Nucleic Acids Res, 33(Database issue): D527–D532
Reynolds C A, Hong M G, Eriksson U K, Blennow K, Bennet A M, Johansson B, Malmberg B, Berg S, Wiklund F, Gatz M, Pedersen N L, Prince J A (2009). A survey of ABCA1 sequence variation confirms association with dementia. Hum Mutat, 30(9): 1348–1354
Rosskopf D, Schürks M, Rimmbach C, Schäfers R (2007). Genetics of arterial hypertension and hypotension. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 374(5–6): 429–469
Rout C C, Rocke D A, Levin J, Gouws E, Reddy D (1993). A reevaluation of the role of crystalloid preload in the prevention of hypotension associated with spinal anesthesia for elective cesarean section. Anesthesiology, 79(2): 262–269
Ryan M, Diekhans M, Lien S, Liu Y, Karchin R (2009). LS-SNP/PDB: annotated non-synonymous SNPs mapped to Protein Data Bank structures. Bioinformatics, 25(11): 1431–1432
Satija R, Hein J, Lunter G A (2010). Genome-wide functional element detection using pairwise statistical alignment outperforms multiple genome footprinting techniques. Bioinformatics, 26(17): 2116–2120
Siepel A, Bejerano G, Pedersen J S, Hinrichs A S, Hou M, Rosenbloom K, Clawson H, Spieth J, Hillier L W, Richards S, Weinstock G M, Wilson R K, Gibbs R A, Kent W J, Miller W, Haussler D (2005). Evolutionarily conserved elements in vertebrate, insect, worm, and yeast genomes. Genome Res, 15(8): 1034–1050
Smith P J, Zhang C, Wang J, Chew S L, Zhang MQ, Krainer A R (2006). An increased specificity score matrix for the prediction of SF2/ASFspecific exonic splicing enhancers. Hum Mol Genet, 15(16): 2490–2508
Sugaya T, Nishimatsu S I, Tanimoto K, Takimoto E, Yamagishi T, Imamura K, Goto S, Imaizumi K, Hisada Y, Otsuka A, Sugiura M, Fukuta K, Fukamizu A, Murakami K (1995). Angiotensin II type 1a receptor-deficient mice with hypotension and hyperreninemia. J Biol Chem, 270(32): 18719–18722
Sugiyama F, Yagami K, Paigen B (2001). Mouse models of blood pressure regulation and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep, 3(1): 41–48
Tobin M D, Tomaszewski M, Braund P S, Hajat C, Raleigh S M, Palmer T M, Caulfield M, Burton P R, Samani N J (2008). Common variants in genes underlying monogenic hypertension and hypotension and blood pressure in the general population. Hypertension, 51(6): 1658–1664
Viklund H, Granseth E, Elofsson A (2006). Structural classification and prediction of reentrant regions in α-helical transmembrane proteins: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol, 361(3): 591–603
Wetzel R (1987). Harnessing disulfide-bonds using protein engineering. Trends Biochem Sci, 12: 478–482
Wheeler D L, Church DM, Lash A E, Leipe D D, Madden T L, Pontius J U, Schuler G D, Schriml L M, Tatusova T A, Wagner L, Rapp B A, Geer L Y, Helmberg W, Kapustin Y, Khovayko O, Landsman D, Lipman D J, Madden T L, Maglott D R, Miller V, Ostell J, Pruitt K D, Schuler G D, Shumway M, Sequeira E, Sherry S T, Sirotkin K, Souvorov A, Starchenko G, Tatusov R L, Tatusova T A, Wagner L, Yaschenko E (2002). Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information: 2002 update. Nucleic Acids Res, 30(1): 13–16
Xi H (2002). Linkage analysis on chromosome 2 in essential hypotension pedigrees. Chin Sci Bull, 47(18): 1538–1540
Xu D, Tsai C J, Nussinov R (1997). Hydrogen bonds and salt bridges across protein-protein interfaces. Protein Eng, 10(9): 999–1012
Yuan Z Q, Gottlieb B, Beitel L K, Wong N, Gordon P H, Wang Q, Puisieux A, Foulkes W D, Trifiro M (2002). Polymorphisms and HNPCC: PMS2-MLH1 protein interactions diminished by single nucleotide polymorphisms. Hum Mutat, 19(2): 108–113
Yue P, Melamud E, Moult J (2006). SNPs3D: candidate gene and SNP selection for association studies. BMC Bioinformatics, 7(1): 166–181
Zhang X H F, Kangsamaksin T, Chao M S P, Banerjee J K, Chasin L A (2005). Exon inclusion is dependent on predictable exonic splicing enhancers. Mol Cell Biol, 25(16): 7323–7332
Zhu Y, Hoffman A, Wu X, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Leaderer D, Zheng T (2008). Correlating observed odds ratios from lung cancer casecontrol studies to SNP functional scores predicted by bioinformatic tools. Mutat Res, 639(1–2): 80–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundu, A., Ramaiah, S. & Anbarasu, A. Mutation in angiotensin II type 1 receptor disrupts its binding to angiotensin II leading to hypotension: An insight into hydrogen bonding patterns. Front. Biol. 7, 477–484 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-012-1241-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-012-1241-z