Abstract
Early childhood educators’ (ECEs) well-being has attracted worldwide attention given its importance to many individual, organizational, and child outcomes. ECEs’ well-being is a multidimensional construct that encompasses a number of elements. These elements are interrelated and represent a complex psychological network. Scant research has examined the features of this network and whether the network would be upheld for ECEs across career stages. This study uses a network analysis to identify pervasive and robust features of well-being in ECEs from diverse career developmental phases. Participants were 1,188 ECEs (1,008 females, Mage = 32.19 years) recruited from four cities in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. They reported mental (i.e., subjective well-being and psychological well-being), occupational (i.e., job stress, job satisfaction, job burnout, and work engagement), and physical (i.e., physical health and role functioning of health) well-being. The results showed that emotional exhaustion was the most central element in the network whilst some other eudaimonic elements from the occupational aspect (e.g., vigor, dedication, and depersonalization) also occupied relatively important places. Further invariance analyses suggested that the above network was largely equivalent across ECEs at the novice, advanced beginner, and competent career stages. Theoretically, this study informs which elements are playing the fundamental role in the holistic well-being network among Chinese ECEs. Practically, the findings also provide implications for prevention and intervention strategies and career counselling to enhance Chinese ECEs’ different aspects of well-being.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
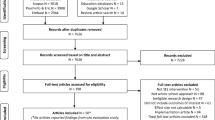
Since the minimum sample size for a network analysis with 20 node or less requires at least 250 participants (Constantin, 2018), we excluded Hong Kong from the city comparison test because the number of Hong Kong participants was lower than the required minimum sample size.
References
Abacioglu, C. S., Isvoranu, A. M., Verkuyten, M., Thijs, J., & Epskamp, S. (2019). Exploring multicultural classroom dynamics: A network analysis. Journal of School Psychology, 74, 90–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2019.02.003
Ahuvia, A. C. (2002). Individualism/collectivism and cultures of happiness: A theoretical conjecture on the relationship between consumption, culture and subjective well-being at the national level. Journal of Happiness Studies, 3, 23–36. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015682121103
Ansari, A., & Pianta, R. C. (2019). Teacher-child interaction quality as a function of classroom age diversity and teachers’ beliefs and qualifications. Applied Developmental Science, 23, 294–304. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2018.1439749
Bakker, A., & Demerouti, E. (2013). The spillover-crossover model. In J. G. Grzywacz, & E. Demerouti (Eds.), Current issues in work and organizational psychology. New frontiers in work and family research (pp. 55–70). New York, NY, US: Psychology Press
Bauer, J. J., McAdams, D. P., & Pals, J. L. (2008). Narrative identity and eudaimonic well-being. Journal of Happiness Studies, 9, 81–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-006-9021-6
Berger, E., Reupert, A., Campbell, T. C., Morris, Z., Hammer, M., Diamond, Z., Hine, R., Patrick, P., & Fathers, C. (2022). A systematic review of evidence-based wellbeing initiatives for schoolteachers and early childhood educators. Educational Psychology Review, 34(4), 2919–2969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-022-09690-5
Blasco-Belled, A., & Alsinet, C. (2022). The architecture of psychological well-being: A network analysis study of the Ryff Psychological Well-Being Scale. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 63(3), 199–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjop.12795
Blase, J. J. (1982). A social-psychological grounded theory of teacher stress and Burnout. Educational Administration Quarterly, 18, 93–113. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013161x82018004008
Blustein, D. L. (2008). The role of work in psychological health and well-being: A conceptual, historical, and public policy perspective. American Psychologist, 63(4), 228–240. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.63.4.228
Booth, J., Coldwell, M., Müller, L. M., Perry, E., & Zuccollo, J. (2021). Mid-career teachers: A mixed methods scoping study of professional development, career progression and retention. Education Sciences, 11, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11060299
Borsboom, D. (2008). Psychometric perspectives on diagnostic systems. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 64, 1089–1108. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.20503
Borsboom, D., & Cramer, A. O. J. (2013). Network analysis: An integrative approach to the structure of psychopathology. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 9, 91–121. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185608
Borsboom, D., Deserno, M. K., Rhemtulla, M., Epskamp, S., Fried, E. I., McNally, R. J., Robinaugh, D. J., Perugini, M., Dalege, J., Costantini, G., Isvoranu, A.-M., Wysocki, A. C., van Borkulo, C. D., van Bork, R., & Waldorp, L. J. (2021). Network analysis of multivariate data in psychological science. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 1, 58. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-021-00055-w
Brough, P., Biggs, A. (2014). Comparing the impact of occupation-specific and generic work characteristics. In: Dollard, M., Shimazu, A., Bin Nordin, R., Brough, P., Tuckey, M. (eds) Psychosocial Factors at Work in the Asia Pacific. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-8975-2_7
Çelik, O. T., & Kahraman, Ü. (2018). The Relationship among teachers’ general self-efficacy perceptions, job burnout and life satisfaction. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 6, 2721–2729. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2018.061204
Census and Statistics Department of Hong Kong. (2023). Fertility trend in Hong Kong 1991 to 2021. Retrieved from https://www.censtatd.gov.hk/en/data/stat_report/product/FA100090/att/B72302FA2023XXXXB0100.pdf
Chen, F. F., Jing, Y., Hayes, A., & Lee, J. M. (2013). Two concepts or two approaches? A bifactor analysis of psychological and subjective well-being. Journal of Happiness Studies, 14, 1033–1068. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-012-9367-x
Chen, C., Li, F., Liu, C., Li, K., Yang, Q., & Ren, L. (2022). The relations between mental well-being and burnout in medical staff during the COVID-19 pandemic: A network analysis. Frontiers in Public Health, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.919692
Cheung, A. C. K., Chao, G. C. N., Lau, E., Leung, A. N. M., & Chui, H. (2022). Cultivating the psychological well-being of early childhood education teachers: The importance of quality work life. Applied Research in Quality of Life, 17, 1533–1553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-021-09959-x
Constantin, M., & Cramer, A. (2018). Sample size recommendation for estimating cross-sectional network models. 10.17605/OSF.IO/ZKAXU
Constitutional and Mainland Affairs Bureau. (September 2023). Overview of the Greater Bay Area. Retrieved from https://www.bayarea.gov.hk/en/about/overview.html
Cumming, T. (2017). Early childhood educators’ well-being: An updated review of the literature. Early Childhood Education Journal, 45, 583–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-016-0818-6
Cumming, T., & Wong, S. (2019). Towards a holistic conceptualisation of early childhood educators’ work-related well-being. Contemporary Issues in Early Childhood, 20, 265–281. https://doi.org/10.1177/14639491187725
Day, C., Stobart, G., Sammons, P., & Kington, A. (2006). Variations in the work and lives of teachers: Relative and relational effectiveness. Teachers and Teaching, 12, 169–192. https://doi.org/10.1080/13450600500467381
Department of Education of Guangdong Province. (2021). 2020 statistical bulletin of the development of education in Guangdong province. Retrieved from http://edu.gd.gov.cn/zwgknew/sjfb/content/post_3776040.html
Diener, E., Emmons, R. A., Larsen, R. J., & Griffin, S. (1985). The satisfaction with life scale. Journal of Personality Assessment, 49, 71–75. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa4901_13
Diener, E., Lucas, R. E., & Oishi, S. (2002). Subjective well-being: The science of happiness and life satisfaction. In S. J. Lopez & C. R. Snyder (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Positive Psychology (2nd ed., pp. 187–194). Oxford University Press.
Diener, E., Oishi, S., & Lucas, R. E. (2003). Personality, culture, and subjective well-being: Emotional and cognitive evaluations of life. Annual Review of Psychology, 54, 403–425. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.54.101601.145056
Diener, E., Wirtz, D., Tov, W., Kim-Prieto, C., Choi, D., Oishi, S., & Biswas-Diener, R. (2009). New measures of well-being: Flourishing and positive and negative feelings. Social Indicators Research, 39, 247–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-009-9493-y
Dreyfus, S. E. (2004). The five-stage model of adult skill acquisition. Bulletin of Science, Technology & Society, 24(3), 177–181. https://doi.org/10.1177/0270467604264992
Duffy, R. D., Foley, P. F., Raque-Bogdan, T. L., Reid, L., Dik, B. J., Castano, M. C., & Adams, C. (2012). Counseling psychologists who view their careers as a calling: A qualitative study. Journal of Career Assessment, 20, 293–308. https://doi.org/10.1177/1069072711436145
Duffy, R. D., England, J. W., Douglass, R. P., Autin, K. A., & Allan, B. A. (2017). Perceiving a calling and well-being: Motivation and access to opportunity as moderators. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 98, 127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2016.11.003
Education Bureau. (2023). Figures and statistics of kindergarten education. Retrieved from https://www.edb.gov.hk/en/about-edb/publications-stat/figures/index.html
Epskamp, S., Cramer, A. O. J., Waldorp, L. J., Schmittmann, V. D., & Borsboom, D. (2012). qgraph: Network visualizations of relationships in psychometric data. Journal of Statistical Software, 48, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v048.i04
Epskamp, S., Borsboom, D., & Fried, E. I. (2018). Estimating psychological networks and their accuracy: A tutorial paper. Behavior Research Methods, 50, 195–212. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-017-0862-1
Epskamp, S. (2022). Package 'mlVAR'. Retrieved from https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/mlVAR/mlVAR.pdf
Erikson, E. H. (1963). Childhood and society (2nd ed.). Norton.
Erikson, E. H. (1968). Identity: Youth and crisis. Norton.
Fináncz, J., Nyitrai, Á., Podráczky, J., & Csima, M. (2020). Connections between professional well-being and mental health of early childhood educators. International Journal of Instruction, 13, 731–746. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2020.13445a
Fredrickson, B. L. (2001). The role of positive emotions in positive psychology: The broaden-and-build theory of positive emotions. American Psychologist, 56, 218–226. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.56.3.218
Fried, E. I., van Borkulo, C. D., Cramer, A. O., Boschloo, L., Schoevers, R. A., & Borsboom, D. (2017). Mental disorders as networks of problems: A review of recent insights. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 52, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-016-1319-z
Gaston-Breton, C., Lemoine, J. E., Voyer, B. G., & Kastanakis, M. N. (2021). Pleasure, meaning or spirituality: Cross-cultural differences in orientations to happiness across 12 countries. Journal of Business Research, 134, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.05.013
Germani, A., Delvecchio, E., Li, J. B., Lis, A., Nartova-Bochaver, S. K., Vazsonyi, A. T., & Mazzeschi, C. (2021). The link between individualism–collectivism and life satisfaction among emerging adults from four countries. Applied Psychology: Health and Well-Being, 13, 437–453. https://doi.org/10.1111/aphw.12259
Granziera, H., Collie, R., & Martin, A. (2021). Understanding teacher wellbeing through job demands-resources theory. In C. F. Mansfield (Ed.), Cultivating teacher resilience: International approaches, applications and impact (pp. 229–244). Springer.
Hall-Kenyon, K. M., Bullough, R. V., MacKay, K. L., & Marshall, E. E. (2014). Preschool teacher well-being: A review of the literature. Early Childhood Education Journal, 42, 153–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-013-0595-4
Hanson, G. C., Rameshbabu, A., Bodner, T. E., Hammer, L. B., Rohlman, D. S., Olson, R., Wipfli, B., Kuel, K., Perrin, N. A., Alley, L., Schue, A., Thompson, S. V., & Parish, M. (2021). A comparison of safety, health, and well-being risk factors across five occupational samples. Frontiers in Public Health, 9, 614725. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.614725
Harada, N. D., Chiu, V., & Stewart, A. L. (1999). Mobility-related function in older adults: Assessment with a 6-minute walk test. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 80, 837–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-9993(99)90236-8
Hascher, T., & Waber, J. (2021). Teacher well-being: A systematic review of the research literature from the year 2000–2019. Educational Research Review, 34, 100411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100411
Heshmati, S., Oravecz, Z., Brick, T. R., & Roeser, R. W. (2022). Assessing psychological well-being in early adulthood: Empirical evidence for the structure of daily well-being via network analysis. Applied Developmental Science, 26, 207–225. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2020.1766356
Hofstede, G., Hofstede, G. J., & Minkov, M. (2010). Cultures and organizations: Software of the mind (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
Hong Kong Federation of Education Workers. (2019). 「幼師工作現狀」問卷調查 [Survey of “Kindergarten teachers work status”]. Retrieved from https://hkfew.org.hk/images/content_file/%E3%80%8C%E5%B9%BC%E5%B8%AB%E5%B7%A5%E4%BD%9C%E7%8F%BE%E7%8B%80%E3%80%8D%E5%95%8F%E5%8D%B7%E8%AA%BF%E6%9F%A5%E7%B5%90%E6%9E%9C.pdf
Hong Kong Financial Times. (2022). Teachers' Salary 2022. Retrieved from https://www.businesstimes.com.hk/articles/141156/
Huberman, M. (1989). The professional life cycle of teachers. Teachers College Record, 91(1), 31–57. https://doi.org/10.1177/016146818909100107
Hutteman, R., Hennecke, M., Orth, U., Reitz, A. K., & Specht, J. (2014). Developmental tasks as a framework to study personality development in adulthood and old age. European Journal of Personality, 28(3), 267–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/per.1959
HyseniDuraku, Z., Jahiu, G., & Geci, D. (2022). The interplay of individual and organizational factors with early childhood teachers’ level of work motivation, job satisfaction, and burnout. International Journal of Educational Reform. https://doi.org/10.1177/10567879221114891
Innstrand, S. T. (2016). Occupational differences in work engagement: A longitudinal study among eight occupational groups in Norway. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 57, 338–349. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjop.12298
Jayawickreme, E., Forgeard, M. J. C., & Seligman, M. E. P. (2012). The engine of well-being. Review of General Psychology, 16(4), 327–342. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027990
Jeon, L., Buettner, C. K., Grant, A. A., & Lang, S. N. (2019). Early childhood teachers’ stress and children’s social, emotional, and behavioral functioning. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 61, 21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2018.02.002
Joshanloo, M. (2016). Revisiting the empirical distinction between hedonic and eudaimonic aspects of well-being using exploratory structural equation modeling. Journal of Happiness Studies, 17, 2023–2036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-015-9683-z
Joshanloo, M. (2019). Investigating the relationships between subjective well-being and psychological well-being over two decades. Emotion, 19, 183–187. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000414
Kamtsios, S. (2018). Burnout syndrome and stressors in different stages of teachers’ professional development: The mediating role of coping strategies. Hellenic Journal of Psychology, 15, 229–253.
Kim, S. Y., Fouad, N., Maeda, H., Xie, H., & Nazan, N. (2018). Midlife work and psychological well-being: A test of the psychology of working theory. Journal of Career Assessment, 26, 413–424. https://doi.org/10.1177/1069072717714538
Klassen, A. F., Miller, A., & Fine, S. (2004). Health-related quality of life in children and adolescents who have a diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics, 114, e541–e547. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2004-0844
Kwon, K. A., Ford, T. G., Jeon, L., Malek-Lasater, A., Ellis, N., Randall, K., Kile, M., & Salvatore, A. L. (2021). Testing a holistic conceptual framework for early childhood teacher well-being. Journal of School Psychology, 86, 178–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2021.03.006
Levinson, D. J. (1986). A conception of adult development. American Psychologist, 41(1), 3–13. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.41.1.3
Li, Z., & Li, J. B. (2019). The association between job stress and emotional problems in Mainland Chinese kindergarten teachers: The mediation of self-control and the moderation of perceived social support. Early Education and Development, 31, 491–506. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2019.1669127
Li, S., Li, Y., Lv, H., Jiang, R., Zhao, P., Zheng, X., Wang, L., Li, J., & Mao, F. (2020). The prevalence and correlates of burnout among Chinese preschool teachers. BMC Public Health, 20, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-8287-7
Li, J. B., Leung, I. T. Y., & Li, Z. (2021a). The pathways from self-control at school to performance at work among novice kindergarten teachers: The mediation of work engagement and work stress. Children and Youth Services Review, 121, 105881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105881
Li, X., Chen, J., & Zhang, L. (2023). Review of research on early childhood education teacher well-being from 1993 to 2022: A descriptive analysis. Educational Review.
Li, J. B., Yang, A., Zhang, R., Leung, T. Y., & Li, Z. (2021b). Occupational well-being in beginning early childhood educators of Hong Kong and the prediction of job-related factors: Variable-centered and person-centered approaches. Frontiers in Psychology, 5371. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.746123
Li, H. (2014). Compensation of chinese early childhood teachers: A preliminary study in Hong Kong, Shenzhen, Singapore, and Taipei. International Journal of Child Care and Education Policy, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40723-014-0002-7
Locke, E. A. (1976). The nature and causes of job satisfaction. In M. D. Dunnette (Ed.), Handbook of industrial and organizational psychology (pp. 1297–1343). Rand McNally.
Løvgren, M. (2016). Emotional exhaustion in day-care workers. European Early Childhood Education Research Journal, 24, 157–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/1350293X.2015.1120525
Mancinelli, E., Ruocco, E., Napolitano, S., & Salcuni, S. (2022). A network analysis on self-harming and problematic smartphone use: The role of self-control, internalizing and externalizing problems in a sample of self-harming adolescents. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 112, 152285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2021.152285
Maree, J. G. (2021). The psychosocial development theory of Erik Erikson: Critical overview. Early Child Development and Care, 191, 1107–1121. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430.2020.1845163
Markowitz, A. J., & Bassok, D. (2022). Understanding the wellbeing of early educators in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic: Lessons from Louisiana. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 61, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2022.05.001
Maslach, C., Schaufeli, W. B., & Leiter, M. P. (2001). Job burnout. Annual Review of Psychology, 52, 397–422. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.397
McKee-Ryan, F., Song, Z., Wanberg, C. R., & Kinicki, A. J. (2005). Psychological and physical well-being during unemployment: A meta-analytic study. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90, 53–76. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.90.1.53
Moshier, S. J., Bovin, M. J., Gay, N. G., Wisco, B. E., Mitchell, K. S., Lee, D. J., Sloan, D. M., Weathers, F. W., Schnurr, P. P., Keane, T. M., & Marx, B. P. (2018). Examination of posttraumatic stress disorder symptom networks using clinician-rated and patient-rated data. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 127, 541–547. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000368
Ntim, S. Y., Qin, J., Antwi, C. O., Aboagye, M. O., Chen, S., & Mensah, E. T. (2023). Early childhood educators’ emotional labor and burnout in an emerging economy: The mediating roles of affective states. Heliyon, 9(3), e14053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14053
Oishi, S. (2018). Culture and subjective well-being: Conceptual and measurement issues. In E. Diener, S. Oishi, & L. Tay (Eds.), Handbook of well-being (pp. 834–848). DEF Publishers.
Opsahl, T., Agneessens, F., & Skvoretz, J. (2010). Node centrality in weighted networks: Generalizing degree and shortest paths. Social Networks, 32, 245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socnet.2010.03.006
Otten, J. J., Bradford, V. A., Stover, B., Hill, H. D., Osborne, C., Getts, K., & Seixas, N. (2019). The culture of health in early care and education: Worker wages, health, and job characteristics. Health Affairs, 38, 709–720. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05493
Peele, M., & Wolf, S. (2021). Depressive and anxiety symptoms in early childhood education teachers: Relations to professional well-being and absenteeism. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 55, 275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2020.11.008
Peng, J., He, Y., Jing, D., Zheng, L., Chang, Y., & Liu, X. (2019). Emotional labor strategies and job burnout in preschool teachers: Psychological capital as a mediator and moderator. Work: A Journal of Prevention. Assessment, & Rehabilitation, 63, 335–345. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-192939
Penttinen, V., Pakarinen, E., von Suchodoletz, A., & Lerkkanen, M. K. (2020). Relations between kindergarten teachers’ occupational well-being and the quality of teacher-child interactions. Early Education and Development, 31, 994–1010. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2020.1785265
Purper, C. J., Thai, Y., Frederick, T. V., & Farris, S. (2022). Exploring the Challenge of Teachers’ Emotional Labor in Early Childhood Settings. Early Childhood Education Journal, 51, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-022-01345-y
R Core Team (2022). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria. https://www.r-project.org/
Randall, K., Ford, T. G., Kwon, K. A., Sisson, S. S., Bice, M. R., Dinkel, D., & Tsotsoros, J. (2021). Physical activity, physical well-being, and psychological well-being: Associations with life satisfaction during the COVID-19 pandemic among early childhood educators. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18, 9430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189430
Rouquette, A., Pingault, J.-B., Fried, E. I., Orri, M., Falissard, B., Kossakowski, J. J., Vitaro, F., Tremblay, R., Cote, S. M., & Borsboom, D. (2018). Emotional and behavioral symptom network structure in elementary school girls and association with anxiety disorders and depression in adolescence and early adulthood: A network analysis. JAMA Psychiatry, 75, 1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2119
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2001). On happiness and human potentials: A review of research on hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. Annual Review of Psychology, 52, 141–166. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.141
Ryff, C. D. (1989). Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological wellbeing. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 57, 1069–1081. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.57.6.1069
Santos, H. P., Jr., Kossakowski, J. J., Schwartz, T. A., Beeber, L., & Fried, E. I. (2018). Longitudinal network structure of depression symptoms and self-efficacy in low-income mothers. PLoS ONE, 13, e0191675. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191675
Schaack, D. D., Le, V. N., & Stedron, J. (2020). When fulfillment is not enough: Early childhood teacher occupational burnout and turnover intentions from a job demands and resources perspective. Early Education and Development, 31, 1011–1030. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2020.1791648
Schaufeli, W. B., Salanova, M., González-romá, V., & Bakker, A. B. (2002). The measurement of engagement and burnout: A two sample confirmatory factor analytic approach. Journal of Happiness Studies, 3, 71–92. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1015630930326
Schmittmann, V. D., Cramer, A. O., Waldorp, L. J., Epskamp, S., Kievit, R. A., & Borsboom, D. (2013). Deconstructing the construct: A network perspective on psychological phenomena. New Ideas in Psychology, 31, 43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.newideapsych.2011.02.007
Statistics Bureau of Guangdong Province. (2022). Guangdong statistical yearbook 2022: Main population indicators. Retrieved from http://stats.gd.gov.cn/gdtjnj/content/post_4035145.html
Steigleder, J., Buhr, L., Ehm, J. H., Gawrilow, C., & von Suchodoletz, A. (2023). Changes in subjective stress experiences and self-efficacy beliefs of preschool teachers in Germany: A longitudinal study during 12 months of the COVID-19 pandemic. Teaching and Teacher Education, 124, 104015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2023.104015
Stochl, J., Soneson, E., Wagner, A. P., Khandaker, G. M., Goodyer, I., & Jones, P. B. (2019). Identifying key targets for interventions to improve psychological wellbeing: Replicable results from four UK cohorts. Psychological Medicine, 49, 2389–2396. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291718003288
Tanaka, R. N., Boyce, L. K., Chinn, C. C., & Murphy, K. N. (2020). Improving early care and education professionals’ teaching self-efficacy and well-being: A mixed methods exploratory study. Early Education and Development, 31, 1089–1111. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2020.1794246
Tsui, A. S., Egan, T. D., & O’Reilly, C. A., III. (1992). Being different: Relational demography and organizational attachment. Administrative Science Quarterly, 37, 549–579. https://doi.org/10.2307/2393472
van Borkulo, C. D., van Bork, R., Boschloo, L., Kossakowski, J. J., Tio, P., Schoevers, R. A., Borsboom, D., & Waldorp, L. J. (2022). Comparing network structures on three aspects: A permutation test. Psychological Methods. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000476
Wang, T., Jia, Y., You, X. Q., & Huang, X. T. (2021). Exploring well-being among individuals with different life purposes in a Chinese context. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 16, 60–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760.2019.1663253
Ware, J. E., & Sherbourne, C. D. (1992). The MOS 36-ltem Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36). Medical Care, 30, 473–483. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002
Waterman, A. S. (1993). Two conceptions of happiness: Contrasts of personal expressiveness (eudaimonia) and hedonic enjoyment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 64, 678–691. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.64.4.678
Wei, M. H. (2013). Multiple abilities and subjective well-being of Taiwanese kindergarten teachers. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 41, 7–16. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2013.41.1.7
Van de Weijer, M., Landvreugd, A., Pelt, D., & Bartels, M. (2021, November 27). Connecting the dots: Using a network approach to study the well-being spectrum. Psyarxiv, https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/9u6vt
Whitaker, R. C., Becker, B. D., Herman, A. N., & Gooze, R. A. (2013). The physical and mental health of head start staff: The Pennsylvania head start staff wellness survey, 2012. Preventing Chronic Disease, 10, E181. https://doi.org/10.5888/pcd10.130171
Wong, S., Cumming, T., MacQuarrie, A., Bull, R., Robertson, C., Saha, M., McFarland, L., & Logan, H. (2022). Holistic measurement of early childhood educators’ well-being: a protocol. International Journal of Research & Method in Education, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/1743727X.2022.2128746
Yuen, M., Lau, P. S. Y., Shek, D. T. L., & Lam, M. P. (2002). Confirmatory factor analysis and reliability of the Chinese version of the Maslach Burnout Inventory among guidance teachers in Hong Kong. Psychological Reports, 91, 1081–1086. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.2002.91.3f.1081
Zeiler, M., Philipp, J., Truttmann, S., Waldherr, K., Wagner, G., & Karwautz, A. (2021). Psychopathological symptoms and well-being in overweight and underweight adolescents: a network analysis. Nutrients, 13, 4096. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114096
Zeng, G., Peng, K., & Hu, C. P. (2019). The network structure of adolescent well-being traits: Results from a large-scale Chinese sample. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 2783. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02783
Zhang, L., Yu, S., & Jiang, L. (2020). Chinese preschool teachers’ emotional labor and regulation strategies. Teaching and Teacher Education, 92, 103024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2020.103024
Zhou, Y., & Li, D. Y. (2011). 农村幼儿教师专业发展与生存状态研究——广州市农村幼儿教师专业发展与生存状态的调查报告[Research on professional development and living status of rural kindergarten teachers: A report on the professional development and living status of kindergarten preschool teachers in Guangzhou]. Journal of Educational Development, 11, 5–9.
Funding
This study is supported by the Research Impact Cluster Fund from the Department of Early Childhood Education and the Internal Research Grant from Committee on Research and Development (RG 20/2021-2022R), the Education University of Hong Kong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, JB., Deng, J., Xu, Y. et al. Which Well-Being Elements Are Fundamental for Early Childhood Educators in the Chinese Context? A Network Analysis. Applied Research Quality Life 19, 103–134 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-023-10233-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-023-10233-5