Abstract
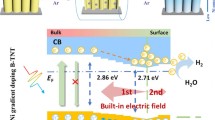
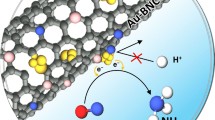
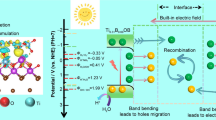
The large-scale production of ammonia mainly depends on the Haber-Bosch process, which will lead to the problems of high energy consumption and carbon dioxide emission. Electrochemical nitrogen fixation is considered to be an environmental friendly and sustainable process, but its efficiency largely depends on the activity and stability of the catalyst. Therefore, it is imperative to develop high-efficient electrocatalysts in the field of nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR). In this paper, we developed a BiVO4/TiO2 nanotube (BiVO4/TNT) heterojunction composite with rich oxygen vacancies as an electrocatalytic NRR catalyst. The heterojunction interface and oxygen vacancy of BiVO4/TNT can be the active site of N2 dynamic activation and proton transition. The synergistic effect of TiO2 and BiVO4 shortens the proton transport path and reduces the over potential of chemical reaction. BiVO4/TNT has high ammonia yield of 8.54 µg·h−1·cm−2 and high Faraday efficiency of 7.70% in −0.8 V vs. RHE in 0.1 M Na2SO4 solution.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Bhattacharya, D. E. Prokopchuk, and M. T. Mock, Exploring the role of pendant amines in transition metal complexes for the reduction of N2 to hydrazine and ammonia, Coord. Chem. Rev. 334, 67 (2017)
J. R. Christianson, D. Zhu, R. J. Hamers, and J. R. Schmidt, Mechanism of N2 reduction to NH3 by aqueous solvated electrons, J. Phys. Chem. B 118(1), 195 (2014)
B. Qin, Y. Li, Q. Zhang, G. Yang, H. Liang, and F. Peng, Understanding of nitrogen fixation electro catalyzed by molybdenum-iron carbide through the experiment and theory, Nano Energy 68, 104374 (2020)
W. Zhao, S. Dou, K. Zhang, L. Wu, Q. Wang, D. Shang, and Q. Zhong, Promotion effect of S and N co-addition on the catalytic performance of V2O5/TiO2 for NH3-SCR of NOx, Chem. Eng. J. 364, 401 (2019)
J. Zhao, Q. Ouyang, Q. Chen, and H. Lin, Simultaneous determination of amino acid nitrogen and total acid in soy sauce using near infrared spectroscopy combined with characteristic variables selection, Food Sci. Technol. Int. 19(4), 305 (2013)
B. Cui, J. Zhang, S. Liu, X. Liu, W. Xiang, L. Liu, H. Xin, M. J. Lefler, and S. Licht, Electrochemical synthesis of ammonia directly from N2 and water over iron-based catalysts supported on activated carbon, Green Chem. 19(1), 298 (2017)
W. Qiu, X. Y. Xie, J. Qiu, W. H. Fang, R. Liang, X. Ren, X. Ji, G. Cui, A. M. Asiri, G. Cui, B. Tang, and X. Sun, High-performance artificial nitrogen fixation at ambient conditions using a metal-free electrocatalyst, Nat. Commun. 9(1), 3485 (2018)
Z. Cui, W. Du, C. Xiao, Q. Li, R. Sa, C. Sun, and Z. Ma, Enhancing hydrogen evolution of MoS2 Basal planes by combining single-boron catalyst and compressive strain, Front. Phys. 15(6), 63502 (2020)
X. Chen, X. Zhao, Z. Kong, W. J. Ong, and N. Li, Unravelling the electrochemical mechanisms for nitrogen fixation on single transition metal atoms embedded in defective graphitic carbon nitride, J. Mater. Chem. A 6(44), 21941 (2018)
Z. X. Xu, H. Song, X. Q. Deng, Y. Y. Zhang, M. Xue-Qin, S. Q. Tong, Z. X. He, Q. Wang, Y. W. Shao, and X. Hu, Dewatering of sewage sludge via thermal hydrolysis with ammonia-treated Fenton iron sludge as skeleton material, J. Hazard. Mater. 379, 120810 (2019)
C. Liu, Q. Li, C. Wu, J. Zhang, Y. Jin, D. R. MacFarlane, and C. Sun, Single-boron catalysts for nitrogen reduction reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141(7), 2884 (2019)
Q. Li, C. Liu, S. Qiu, F. Zhou, L. He, X. Zhang, and C. Sun, Exploration of iron borides as electrochemical catalysts for the nitrogen reduction reaction, J. Mater. Chem. A 7(37), 21507 (2019)
Q. Li, S. Qiu, L. He, X. Zhang, and C. Sun, Impact of H-termination on the nitrogen reduction reaction of molybdenum carbide as an electrochemical catalyst, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20(36), 23338 (2018)
H. Cheng, L. X. Ding, G. F. Chen, L. Zhang, J. Xue, and H. Wang, Molybdenum carbide nanodots enable efficient electrocatalytic nitrogen fixation under ambient conditions, Adv. Mater. 30(46), 1803694 (2018)
X. Ren, J. Zhao, Q. Wei, Y. Ma, H. Guo, Q. Liu, Y. Wang, G. Cui, A. M. Asiri, B. Li, B. Tang, and X. Sun, High-performance N2-to-NH3 conversion electrocatalyzed by Mo2C nanorod, ACS Cent. Sci. 5(1), 116 (2019)
Z. Sun, R. Huo, C. Choi, S. Hong, T. S. Wu, J. Qiu, C. Yan, Z. Han, Y. Liu, Y. L. Soo, and Y. Jung, Oxygen vacancy enables electrochemical N2 fixation over WO3 with tailored structure, Nano Energy 62, 869 (2019)
P. Chen, N. Zhang, S. Wang, T. Zhou, Y. Tong, C. Ao, W. Yan, L. Zhang, W. Chu, C. Wu, and Y. Xie, Interfacial engineering of cobalt sulfide/graphene hybrids for highly efficient ammonia electrosynthesis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 116(14), 6635 (2019)
M. Kitano, Y. Inoue, Y. Yamazaki, F. Hayashi, S. Kanbara, S. Matsuishi, T. Yokoyama, S. W. Kim, M. Hara, and H. Hosono, Ammonia synthesis using a stable electride as an electron donor and reversible hydrogen store, Nat. Chem. 4(11), 934 (2012)
F. Zhou, L. M. Azofra, M. Ali, M. Kar, A. N. Simonov, C. McDonnell-Worth, C. Sun, X. Zhang, and D. R. Mac-Farlane, Electro-synthesis of ammonia from nitrogen at ambient temperature and pressure in ionic liquids, Energy Environ. Sci. 10(12), 2516 (2017)
D. Wang, L. M. Azofra, M. Harb, L. Cavallo, X. Zhang, B. H. R. Suryanto, and D. R. MacFarlane, Energy-efficient nitrogen reduction to ammonia at low overpotential in aqueous electrolyte under ambient conditions, Chem.Sus.Chem. 11(19), 3416 (2018)
A. R. Singh, B. A. Rohr, J. A. Schwalbe, M. Cargnello, K. Chan, T. F. Jaramillo, I. Chorkendorff, and J. K. Nørskov, Electrochemical ammonia synthesis — The selectivity challenge, ACS Catal. 7(1), 706 (2017)
S. Z. Andersen, V. Čolić, S. Yang, J. A. Schwalbe, A. C. Nielander, J. M. McEnaney, K. Enemark-Rasmussen, J. G. Baker, A. R. Singh, B. A. Rohr, M. J. Statt, S. J. Blair, S. Mezzavilla, J. Kibsgaard, P. C. K. Vesborg, M. Cargnello, S. F. Bent, T. F. Jaramillo, I. E. L. Stephens, J. K. Nørskov, and I. Chorkendorff, A rigorous electrochemical ammonia synthesis protocol with quantitative isotope measurements, Nature 570(7762), 504 (2019)
J. Kibsgaard, J. K. Nørskov, and I. Chorkendorff, The Difficulty of Proving Electrochemical Ammonia Synthesis, ACS Energy Lett. 4(12), 2986 (2019)
T. Chen, S. Liu, H. Ying, Z. Li, and J. Hao, Reactive ionic liquid enables the construction of 3D Rh particles with nanowire subunits for electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction, Chem. Asian J. 15(7), 1081 (2020)
H. Xie, Q. Geng, X. Zhu, Y. Luo, L. Chang, X. Niu, X. Shi, A. M. Asiri, S. Gao, Z. Wang, and X. Sun, PdP2 nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide for electrocatalytic N2 conversion to NH3 under ambient conditions, J. Mater. Chem. A 7(43), 24760 (2019)
Z. Zhang, K. Yao, L. Cong, Z. Yu, L. Qu, and W. Huang, Facile synthesis of a Ru-dispersed N-doped carbon framework catalyst for electrochemical nitrogen reduction, Catal. Sci. Technol. 10(5), 1336 (2020)
X. Zhao, Z. Yang, A. V. Kuklin, G. V. Baryshnikov, H. Ågren, W. Wang, X. Zhou, and H. Zhang, Potassium ions promote electrochemical nitrogen reduction on nano-Au catalysts triggered by bifunctional boron supramolecular assembly, J. Mater. Chem. A 8(26), 13086 (2020)
D. Deng, K. S. Novoselov, Q. Fu, N. Zheng, Z. Tian, and X. Bao, Catalysis with two-dimensional materials and their heterostructures, Nat. Nanotechnol. 11(3), 218 (2016)
D. Gao, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhou, F. Cai, X. Zhao, W. Huang, Y. Li, J. Zhu, P. Liu, F. Yang, G. Wang, and X. Bao, Enhancing CO2 electroreduction with the metal-oxide interface, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139(16), 5652 (2017)
Y. Guo, J. Zou, X. Shi, P. Rukundo, and Z. Wang, A Ni/CeO2-CDC-SiC catalyst with improved Coke resistance in CO2 reforming of methane, ACS Sustain. Chem. & Eng. 5(3), 2330 (2017)
S. Xie, Y. Liu, J. Deng, J. Yang, X. Zhao, Z. Han, K. Zhang, Y. Lu, F. Liu, and H. Dai, Carbon monoxide oxidation over rGO-mediated gold/cobalt oxide catalysts with strong metal-support interaction, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(28), 31467 (2020)
H. C. Song, G. R. Lee, K. Jeon, H. Lee, S. W. Lee, Y. S. Jung, and J. Y. Park, Engineering nanoscale interfaces of metal/oxide nanowires to control catalytic activity, ACS Nano 14(7), 8335 (2020)
J. Lv, S. Wu, Z. Tian, Y. Ye, J. Liu, and C. Liang, Construction of PdO-Pd interfaces assisted by laser irradiation for enhanced electrocatalytic N2 reduction reaction, J. Mater. Chem. A 7(20), 12627 (2019)
B. Xu, L. Xia, F. Zhou, R. Zhao, H. Chen, T. Wang, Q. Zhou, Q. Liu, G. Cui, X. Xiong, F. Gong, and X. Sun, Enhancing Electrocatalytic, N2 reduction to NH3 by CeO2 nanorod with oxygen vacancies, ACS Sustain. Chem. & Eng. 7(3), 2889 (2019)
W. Fu, P. Zhuang, M. OliverLam Chee, P. Dong, M. Ye, and J. Shen, Oxygen vacancies in Ta2O5 nanorods for highly efficient electrocatalytic N2 reduction to NH3 under ambient conditions, ACS Sustain. Chem. & Eng. 7(10), 9622 (2019)
Y. Tong, H. Guo, D. Liu, X. Yan, P. Su, J. Liang, S. Zhou, J. Liu, G. Q. Lu, and S. X. Dou, Vacancy engineering of iron-doped W18O49 nanoreactors for low-barrier electrochemical nitrogen reduction, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59(19), 7356 (2020)
T. Wu, X. Zhu, Z. Xing, S. Mou, C. Li, Y. Qiao, Q. Liu, Y. Luo, X. Shi, Y. Zhang, and X. Sun, Greatly improving electrochemical N2 reduction over TiO2 nanoparticles by iron doping, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58(51), 18449 (2019)
T. Wu, W. Kong, Y. Zhang, Z. Xing, J. Zhao, T. Wang, X. Shi, Y. Luo, and X. Sun, Greatly enhanced electrocatalytic N2 reduction on TiO2 via V doping, Small Methods 3(11), 1900356 (2019)
S. Cheng, Y. J. Gao, Y. L. Yan, X. Gao, S. H. Zhang, G. L. Zhuang, S. W. Deng, Z. Z. Wei, X. Zhong, and J. G. Wang, Oxygen vacancy enhancing mechanism of nitrogen reduction reaction property in Ru/TiO2, J. Energ. Chem. 39, 144 (2019)
Z. Han, C. Choi, S. Hong, T. S. Wu, Y. L. Soo, Y. Jung, J. Qiu, and Z. Sun, Activated TiO2 with tuned vacancy for efficient electrochemical nitrogen reduction, Appl. Catal. B 257, 117896 (2019)
B. Li, X. Zhu, J. Wang, R. Xing, Q. Liu, X. Shi, Y. Luo, S. Liu, X. Niu, and X. Sun, Ti3+ self-doped TiO2−x nanowires for efficient electrocatalytic N2 reduction to NH3, Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 56(7), 1074 (2020)
Y. T. Liu, X. Chen, J. Yu, and B. Ding, Carbon-nanoplated CoS@TiO2 nanofibrous membrane: An interface-engineered heterojunction for high-efficiency electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58(52), 18903 (2019)
M. M. Shi, D. Bao, B. R. Wulan, Y. H. Li, Y. F. Zhang, J. M. Yan, and Q. Jiang, Au sub-nanoclusters on TiO2 toward highly efficient and selective electrocatalyst for N2 conversion to NH3 at ambient conditions, Adv. Mater. 29(17), 1606550 (2017)
J. Zhang, Y. Tian, T. Zhang, Z. Li, X. She, Y. Wu, Y. Wang, and J. Wu, Confinement of intermediates in blue TiO2 nanotube arrays boosts reaction rate of nitrogen electrocatalysis, Chem. Cat. Chem. 12(10), 2760 (2020)
P. Zhao, L. Zhang, J. Song, S. Wen, and Z. Cheng, Phosphorus cation substitution in TiO2 nanorods toward enhanced N2 electroreduction, Appl. Surf. Sci. 523, 146517 (2020)
Q. Hao, C. Liu, G. Jia, Y. Wang, H. Arandiyan, W. Wei, and B. J. Ni, Catalytic reduction of nitrogen to produce ammonia by bismuth-based catalysts: State of the art and future prospects, Mater. Horiz. 7(4), 1014 (2020)
L. Li, C. Tang, B. Xia, H. Jin, Y. Zheng, and S. Z. Qiao, Two-dimensional mosaic bismuth nanosheets for highly selective ambient electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction, ACS Catal. 9(4), 2902 (2019)
J. M. Wu, Y. Chen, L. Pan, P. Wang, Y. Cui, D. Kong, L. Wang, X. Zhang, and J. J. Zou, Multi-layer mono-clinic BiVO4 with oxygen vacancies and V4+ species for highly efficient visible-light photoelectrochemical applications, Appl. Catal. B 221, 187 (2018)
J. X. Yao, D. Bao, Q. Zhang, M. M. Shi, Y. Wang, R. Gao, J. M. Yan, and Q. Jiang, Tailoring oxygen vacancies of BiVO4 toward highly efficient noble-metal-free electro-catalyst for artificial N2 fixation under ambient conditions, Small Methods 3(6), 1800333 (2019)
C. Ling, Y. Zhang, Q. Li, X. Bai, L. Shi, and J. Wang, New mechanism for N2 reduction: The essential role of surface hydrogenation, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141(45), 18264 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51802126 and 52072152), the Jiangsu University Jinshan Professor Fund and Jiangsu Specially-Appointed Professor Fund, Open Fund from Guangxi Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Energy Materials. The authors also acknowledged the financial support by Guangdong Innovation Research Team for Higher Education (No. 2017KCXTD030) and High-level Talents Project of Dongguan University of Technology (No. KCYKYQD2017017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Special Topic
Heterojunction and Its Applications (Ed. Chenghua Sun). This article can also be found at http://journal.hep.com.cn/fop/EN/10.1007/s11467-021-1067-8.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Deng, P., Wu, R. et al. BiVO4/TiO2 heterojunction with rich oxygen vacancies for enhanced electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reaction. Front. Phys. 16, 53503 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-021-1067-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-021-1067-8