Abstract
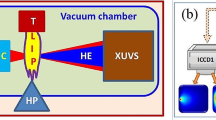
Gold disk targets were irradiated using focusing and beam smoothing methods on Xingguang (XG-II) laser facilities with 350 nm wavelength, 0.6 ns pulse width and 20–80 Joules energies. Laser absorption, light scattering and X-ray conversion were experimentally investigated. The experimental results showed that laser absorption and scattered light were about 90% and 10%, respectively, under focusing irradiation, but the laser absorption increased 5%–10% and the scattered light about 1% under the condition of beam smoothing. Compared with the case of focusing irradiation, the laser absorption was effectively improved and the scattered light remarkably dropped under uniform irradiation; then due to the decrease in laser intensity, X-ray conversion increased. This is highly advantageous to the inertial confinement fusion. However, X-ray conversion mechanism basically did not change and X-ray conversion efficiency under beam smoothing and focusing irradiation was basically the same.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindl J, Amendt P, Berger R, et al. The physics basis for ignition using indirect-drive targets on the National Ignition Facility. Phys Plasm, 2004, 11(2): 339–491
Chang T Q, Zhang J, Zhang J T, et al. Laser Plasma Interaction and Laser Fusion (in Chinese). Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1991
Lindl J. Development of the indirect-drive approach to inertial confinement fusion and the target physics basis for ignition and gain. Phys Plasm, 1995, 2(11): 3933–4024
Zhang J, Chang T Q. Fundaments of the Targets Physics for Laser Fusion (in Chinese). Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2004
Zhang J T. Laser Plasma Interaction Physics and Simulation (in Chinese). Zhengzhou: Henan Science and Technology Press, 1999
Kruer W. The Physics of Laser Plasma Interactions. New York: Addison-Wesley, 1988
Sakaiya T, Azechi H, Matsuoka M, et al. Ablative Rayleigh-Taylor instability at short wavelengths observed with Moiré interferometry. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 88(14): 145003
Rubenchik A, Witkowski S. Handbook of Physics of Laser Plasma. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishing, 1991
Batani D, Strati F, Stabile H, et al. Hugoniot data for carbon at megabar pressures. Phys Lett Rev, 2004, 92(6): 065503
Koenig M, Faral B, Boudenne J, et al. Optical smoothing technique for shock wave generation in laser-produced plasmas. Phys Rev E, 1994, 50(5): R3314–R3317
Delamater N, Lindman E, Magelssen G, et al. Observation of reduced beam deflection using smoothed beams in gas-filled hohlraum symmetry experiments at Nova. Phys Plasm, 2000, 7(5): 1609–1613
Kato Y, Mima K, Miyanaga N, et al. Random phasing of high-power lasers for uniform target acceleration and plasma-instability suppression. Phys Rev Lett, 1984, 53(11): 1057–1060
Dixit S, Lawson J, Manes K, et al. Kinoform phase plates for focal plane irradiance profile control. Opt Lett, 1994, 19(6): 417–419
Deng X, Liang X, Chen Z. Uniform illumination of large targets using a lens array. Appl Opt, 1986, 25(3): 377–380
Stevenson M, Norman M, Bett T, et al. Binary-phase zone plate arrays for the generation of uniform focal profiles. Opt Lett, 1994, 19(6): 363–365
Obenschain S, Grun J, Herbst J, et al. Laser-target interaction with induced spatial incoherence. Phys Rev Lett, 1986, 56(26): 2807–2810
Skupsky S, Short R, Kessler T, et al. Improved laser-beam uniformity using the angular dispersion of frequency-modulated light. J Appl Phys, 1989, 66(8): 3456–3462
Nakano H, Tsukakimoto K, Miyanaga N, et al. Spectrally dispersion amplified spontaneous emission for improving irradiation uniformity into high power Nd:glass laser system. J Appl Phys, 1993, 75(5): 2122–2131
Veron D, Ayral H, Gouedard C, et al. Optical spatial smoothing of Nd-glass laser beam. Opt Comm, 1988, 65(1): 42–48
Moody J, Baldis H, Montgomery D, et al. Beam smoothing effects on the stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) instability in Nova exploding foil plasmas. Phys plasm, 1995, 2(11): 4285–4296
Glenzer S, Berger R, Divol L, et al. Reduction of stimulated scattering losses from hohlraum plasmas with laser beam smoothing. Phys Plasm, 2001, 8(5): 1692–1696
Glenzer S, Suter L, Berger R, et al. Hohlraum energetics with smoothed laser beams. Phys Plasm, 2000, 7(6): 2585–2593
Batani D, Nazarov W, Hall T, et al. Foam-induced smoothing studied through laser-driven shock waves. Phys Rev E, 2000, 62(6): 8573–8582
Stevenson R, Oades K, Thomas B, et al. Evidence for high-efficiency laser-heated Hohlraum performance at 527 nm. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 94(5): 055006
Fujioka S, Shiraga H, Nishikino M, et al. First observation of density profile in directly laser-driven polystyrene targets for ablative Rayleigh-Taylor instability research. Phys Plasm, 2003, 10(12): 4784–4789
Batani D, Morelli A, Tomasin M, et al. Equation of state data for iron at pressures beyond 10 Mbar. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 83(23): 235502
Obenschain S, Pawley C J, Mostovych A, et al. Reduction of Raman scatting in a plasma to convective levels using induced spatial incoherence. Phys Rev Lett, 1989, 62(7): 768–771
Mostovych A, Obenschain S, Gardner J, et al. Brilluin-scattering measurements from plasmas irradiated with spatially and temporally incoherent laser light. Phys. Rev. Lett., 1987, 59(11): 1193–1196
Fu S Z, Sun R Q, Huang X G, et al. Optimazative design of uniform illumination system on ’shenguang-II’ laser facilities. Chin J Lasers, 2003, 30(2): 129–133
Mead W, Stover K, Kauffman R, et al. Modeling, measurements, and analysis of X-ray from 0.26-μm-laser-irradiated gold disks. Phys Rev A, 1988, 38(10): 5275–5288
Chakera J, Arora V, Sailaja S, et al. Dependence of soft X-ray conversion on atomic composition in laser produced plasma of gold-copper mix-Z targets. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83(1): 27–29
Baldis H, Labaune C, Moody J, et al. Localization of stimulated Brillouin scattering in random phase plate speckles. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 80(9): 1900–1903
Moody J, MacGowan B, Rothenberg J, et al. Backscatter reduction using combined Spatial, temporal, and polarization beam smoothing in a long-scale-length laser plasma. Phys Rev Lett, 2001, 86(13): 2810–2813
Bodner S, Colombant D, Gardner J, et al. Direct-drive laser fusion: Status and prospects. Phys Plasm, 1998, 5(5): 1901–1918
Yang J M, Ding Y K, Yi R Q. et al. Quantitative measurement of soft X-ray spectrum using transmission grating spectrometer. Acta Phys Sin (in Chinese), 2001, 50(9): 1723–1728
Sun K X, Yang J M, Zheng Z J. A sub-keV X-ray spectrometer used in laser plasma interaction experiments. High Power Laser Part Beams (in Chinese), 1990, 2(1): 16–22
Liu S Y, Teng H, Ding Y K, et al. Experimental investigation on absorption and scattering of gold disk irradiated by laser with 0.351 μm. Acta Phys Sin (in Chinese), 1997, 46(10): 1917–1925
Colombant D, Tonon G. X-ray emission in laser-produced plasmas. J Appl Phys, 1973, 44(8): 3524–3537
Rosen M, Phillion D, Rupert V, et al. The interaction of 1.06 μm laser radiation with high Z disk targets. Phys Fluids, 1979, 22(10): 2020–2031
Qi L Y, Jiang X H, Zhao X W, et al. Study on mechanism aoubt generation and restraining of hot electron produced by laser with short wavelength. Acta Phys Sin (in Chinese), 2000, 49(3): 492–496
Young P, Berger R, Estabrook K, et al. Measurements of backscattered light from the interaction of 0.35 μm laser light with high-Z targets. Phys Fluids B, 1992, B4(8): 2605–2613
Drake R, Kauffman R, Lasinski B, et al. The angular dependence of the absorption of 0.35 μm laser-produced plasmas. Phys Fluids, 1991, B3(12): 3477–3484
Afshar-rad T, Coe S, Willi O, et al. Evidence of stimulated Raman scattering occurring in laser filaments in long-scaled-length plasmas. Phys Fluids, 1992, B4(5): 1301–1322
Bosch R, Gabl E, Kania D, et al. Effects of induced spatial incoherence on laser light absorption and X-ray conversion at 0.53 μm. Phys Rev A, 1991, 43(2): 953–960
Fuchs J, Labaune C, Depierreux S, et al. Modification of spatial and temporal gains of stimulated Brillouin and Raman Scattering by polarization smoothing. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 84(14): 3089–3092
Sigel R, Eidmann K, Lavarenne F, et al. Conversion of laser light into soft X-ray. Part I: Dimensional analysis. Phys Fluids B, 1990, 2(1): 199–207
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Zhang, B., Liu, S. et al. Experiments and analysis of gold disk targets irradiated by smoothing beams of Xingguang II facilities with 350 nm wavelength. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. Astron. 50, 716–730 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-007-0069-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-007-0069-z