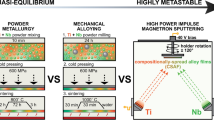
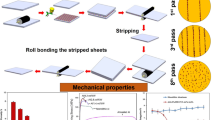
Abstract
Metallic materials have historic and served as critical enablers of human progress, wealth, and wellbeing over millennia. Recently, the global demand for the development of environment-friendly and energy-saving technology has been increasing, with the aim to support the sustainability of metallic materials. Twin-roll strip casting (TRC) is one of the most cutting-edge technologies and a near-net-shape manufacturing method in the steel industry, which conforms to the green fabrication trend of next-generation high-performance metallic materials. By utilizing the dominant characteristics of sub-rapid solidification, and integration of solidification, solid-state transformation, and deformation; TRC has become a meaningful way to deal with the most challenging issues in the processing of metallic materials, and made a significant contribution to materials manufacturing. Hence, we review the TRC process of various metallic materials, including plain carbon steels, stainless steels, Fe-Si electrical steels, high-strength steels, clad steels, aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, metallic glasses, and so on This paper offers an outlook of future opportunities for various advanced metallic materials development through the TRC process, and inspires more in-depth research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plummer J. Metallurgy is key. Nat Mater, 2016, 15: 699–700
Raabe D, Tasan C C, Olivetti E A. Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals. Nature, 2019, 575: 64–74
Kim S H, Kim H, Kim N J. Brittle intermetallic compound makes ultrastrong low-density steel with large ductility. Nature, 2015, 518: 77–79
Nolli P. Initial solidification phenomena: Factors affecting heat transfer in strip casting. Dissertation for Doctoral Degree. Pittsburgh: Carnegie Mellon University, 2007
Zhu C, Wang W, Lu C. Sub-rapid solidification and its related interfacial heat-transfer behaviors in strip casting process. J Sust Metall, 2019, 5: 378–390
Campbell P, Blejde W, Mahapatra R, et al. Recent progress on commercialization of castrip® direct strip casting technology at Nucor Crawfordsville. Metallurgist, 2004, 48: 507–514
Dai Y, Xu Z, Luo Z, et al. Phase formation kinetics, hardness and magnetocaloric effect of sub-rapidly solidified LaFe11.6Si1.4 plates during isothermal annealing. J Magn Magn Mater, 2018, 454: 356–361
Girgensohn A, Büchner A R. Twin roll strip casting of low carbon steels. Ironmak Steelmak, 2013, 27: 317–323
Ge S, Isac M, Guthrie R I L. Progress of strip casting technology for steel: Historical developments. ISIJ Int, 2012, 52: 2109–2122
Park J Y, Oh K H, Ra H Y. Texture and deformation behaviour through thickness direction in strip-cast 4.5wt% Si steel sheet. ISIJ Int, 2000, 40: 1210–1215
Yamamoto K, Matsuura M, Sugimoto S. Microstructure formation in strip-cast RE-Fe-B alloys for magnets. Metall Mat Trans A, 2017, 48: 3482–3489
Mizoguchi T, Miyazawa K. Formation of solidification structure in twin roll casting process of 18Cr-8Ni stainless steel. ISIJ Int, 1995, 35: 771–777
Chen H, Xu W, Tang C, et al. Intragranular glass/crystal conjugated particles in strip cast Nd-Fe-B flakes. J Magn Magn Mater, 2020, 495: 165863
Daamen M, Güvenç O, Bambach M, et al. Development of efficient production routes based on strip casting for advanced high strength steels for crash-relevant parts. CIRP Ann, 2014, 63: 265–268
Zhang W, Yu Y, Fang Y, et al. Determination of interfacial heat flux of stainless steel solidification on copper substrate during the first 0.2 s. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Sci), 2011, 16: 65–70
Dou W X, Yuan G, Lan M F, et al. The significance of microstructure and texture on magnetic properties of non-oriented silicon steel: Strip casting versus conventional process. Steel Res Int, 2020, 91: 1900286
Wang W, Zhu C, Lu C, et al. Study of the heat transfer behavior and naturally deposited films in strip casting by using droplet solidification technique. Metall Mat Trans A, 2018, 49: 5524–5534
Wu Y, Zhang L, Chen S, et al. A multiple twin-roller casting technique for producing metallic glass and metallic glass composite strips. Materials, 2019, 12: 3842
Guo J, Liu Y, Liu L, et al. 3D stress simulation and parameter design during twin-roll casting of 304 stainless steel based on the Anand model. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2014, 21: 666–673
Vidoni M, Ackermann R, Richter S, et al. Production of clad steel strips by twin-roll strip casting. Adv Eng Mater, 2015, 17: 1588–1597
Kikuchi D, Harada Y, Kumai S. Surface quality and microstructure of Al-Mg alloy strips fabricated by vertical-type high-speed twin-roll casting. J Manuf Process, 2019, 37: 332–338
Chen M, Hu X D, Han B, et al. Study on the microstructural evolution of AZ31 magnesium alloy in a vertical twin-roll casting process. Appl Phys A, 2016, 122: 91
Zapuskalov N. Comparison of continuous strip casting with conventional technology. ISIJ Int, 2003, 43: 1115–1127
Ge S, Isac M, Guthrie R I L. Progress in strip casting technologies for steel: Technical developments. ISIJ Int, 2013, 53: 729–742
Maleki A, Taherizadeh A, Hosseini N. Twin roll casting of steels: An overview. ISIJ Int, 2017, 57: 1–14
Zhao J, Jiang Z. Thermomechanical processing of advanced high strength steels. Prog Mater Sci, 2018, 94: 174–242
Dong H. Year 2020: 200th anniversary for alloy steel-preword of special issue for alloy steel (in Chinese). Acta Metall Sin, 2020, 56: 1–IV
Guillet A, Es-Sadiqi E, L’EspÉRance G, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of strip cast 1008 steel after simulated coiling, cold rolling and batch annealing. ISIJ Int, 1996, 36: 1190–1198
Tavares R P, Isac M, Guthrie R I L. Roll-strip interfacial heat fluxes in twin-roll casting of low-carbon steels and their effects on strip microstructure. ISIJ Int, 1998, 38: 1353–1361
Laleh M, Hughes A E, Xu W, et al. Unexpected erosion-corrosion behaviour of 316L stainless steel produced by selective laser melting. Corrosion Sci, 2019, 155: 67–74
Wang Y M, Voisin T, McKeown J T, et al. Additively manufactured hierarchical stainless steels with high strength and ductility. Nat Mater, 2018, 17: 63–71
Yasunaka H, Taniguchi K, Kokita M, et al. Surface quality of stainless steel type 304 cast by twin-roll type strip caster. ISIJ Int, 1995, 35: 784–789
Choo D K, Moon H K, Kang T, et al. Analysis and prevention of cracking during strip casting of AISI 304 stainless steel. Metall Mat Trans A, 2001, 32: 2249–2258
Ha M, Choi J, Jeong S, et al. Analysis and prevention of microcracking phenomenon occurring during strip casting of an AISI 304 stainless steel. Metall Mat Trans A, 2002, 33: 1487–1497
Hunter A, Ferry M. Texture enhancement by inoculation during casting of ferritic stainless steel strip. Metall Mat Trans A, 2002, 33: 1499–1507
Hunter A, Ferry M. Evolution of microstructure and texture during casting of AISI 304 stainless steel strip. Metall Mat Trans A, 2002, 33: 3747–3754
Liu H T, Liu Z Y, Qiu Y Q, et al. Characterization of the solidification structure and texture development of ferritic stainless steel produced by twin-roll strip casting. Mater Charact, 2009, 60: 79–82
Strezov L, Herbertson J. Experimental studies of interfacial heat transfer and initial solidification pertinent to strip casting.. ISIJ Int, 1998, 38: 959–966
Spinelli J E, Tosetti J P, Santos C A, et al. Microstructure and solidification thermal parameters in thin strip continuous casting of a stainless steel. J Mater Processing Tech, 2004, 150: 255–262
Strezov L, Herbertson J, Belton G R. Mechanisms of initial melt/substrate heat transfer pertinent to strip casting. Metall Materi Trans B, 2000, 31: 1023–1030
Zhu C, Wang W, Zeng J, et al. Interactive relationship between the superheat, interfacial heat transfer, deposited film and microstructure in strip casting of duplex stainless steel. ISIJ Int, 2019, 59: 880–888
Zhao Y, Zhang W, Liu X, et al. Development of TRIP-aided lean duplex stainless steel by twin-roll strip casting and its deformation mechanism. Metall Mat Trans A, 2016, 47: 6292–6303
Hao Y, Cao G, Li C, et al. The aging precipitation behavior of 20Cr-24Ni-6Mo super-austenitic stainless steel processed by conventional casting and twin-roll strip casting. Mater Charact, 2019, 147: 21–30
Hao Y, Cao G, Li C, et al. Solidification structures of Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo-N super-austenitic stainless steel processed by twin-roll strip casting and ingot casting and their segregation evolution behaviors. ISIJ Int, 2018, 58: 1801–1810
Wang Z J, Huang X M, Li Y W, et al. Ultra-fine microstructure and excellent mechanical properties of high borated stainless steel sheet produced by twin-roll strip casting. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2019, 747: 185–196
Sha Y H, Sun C, Zhang F, et al. Strong cube recrystallization texture in silicon steel by twin-roll casting process. Acta Mater, 2014, 76: 106–117
Li H Z, Liu H T, Liu Z Y, et al. Microstructure, texture evolution and magnetic properties of strip-casting non-oriented 6.5 wt% Si electrical steel doped with cerium. Mater Charact, 2015, 103: 101–106
Li H Z, Liu H T, Liu Z Y, et al. Characterization of microstructure, texture and magnetic properties in twin-roll casting high silicon non-oriented electrical steel Mater Charact, 2014, 88: 1–6
Li H Z, Liu H T, Liu Y, et al. Effects of warm temper rolling on microstructure, texture and magnetic properties of strip-casting 6.5 wt% Si electrical steel. J Magn Magn Mater, 2014, 370: 6–12
Xu Y, Jiao H, Qiu W, et al. Effect of cold rolling process on microstructure, texture and properties of strip cast Fe-2.6%Si steel. Materials, 2018, 11: 1161
Li H Z, Wang X L, Liu H T, et al. Microstructure, texture evolution, and magnetic properties of strip-casting nonoriented 6.5 wt.% Si electrical steel sheets with different thickness. IEEE Trans Magn, 2015, 51: 1–4
Xu Y B, Zhang Y X, Wang Y, et al. Evolution of cube texture in strip-cast non-oriented silicon steels. Scripta Mater, 2014, 87: 17–20
Liu H T, Li H Z, Li H L, et al. Effects of rolling temperature on microstructure, texture, formability and magnetic properties in strip casting Fe-6.5 wt% Si non-oriented electrical steel. J Magn Magn Mater, 2015, 391: 65–74
Chen A, Li H. Microstructure and texture of 0.75%Si non-oriented electrical steel fabricated by strip casting process. Metallogr Microstruct Anal, 2016, 5: 428–434
Liu H T, Wang Y P, An L Z, et al. Effects of hot rolled microstructure after twin-roll casting on microstructure, texture and magnetic properties of low silicon non-oriented electrical steel. J Magn Magn Mater, 2016, 420: 192–203
Jiao H, Xu Y, Xu H, et al. Influence of hot deformation on texture and magnetic properties of strip cast non-oriented electrical steel. J Magn Magn Mater, 2018, 462: 205–215
Xu Y, Jiao H, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of pre-annealing prior to cold rolling on the precipitation, microstructure and magnetic properties of strip-cast non-oriented electrical steels. J Mater Sci Tech, 2017, 33: 1465–1474
Wang Y Q, Zhang X M, Zu G Q, et al. Effect of hot band annealing on microstructure, texture and magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical steel processed by twin-roll strip casting. J Magn Magn Mater, 2018, 460: 41–53
Fang F, Xu Y B, Zhang Y X, et al. Evolution of recrystallization microstructure and texture during rapid annealing in strip-cast non-oriented electrical steels. J Magn Magn Mater, 2015, 381: 433–439
Liu H T, Li H L, Schneider J, et al. Effects of coiling temperature after hot rolling on microstructure, texture, and magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical steel in strip casting processing route. Steel Res Int, 2016, 87: 1256–1263
Song H Y, Liu H T, Lu H H, et al. Fabrication of grain-oriented silicon steel by a novel way: Strip casting process. Mater Lett, 2014, 137: 475–478
Wang Y, Xu Y B, Zhang Y X, et al. Development of microstructure and texture in strip casting grain oriented silicon steel. J Magn Magn Mater, 2015, 379: 161–166
Fang F, Zhang Y, Lu X, et al. Inhibitor induced secondary re-crystallization in thin-gauge grain oriented silicon steel with high permeability Mater Des, 2016, 105: 398–403
Song H Y, Liu H T, Liu W Q, et al. Effects of two-stage cold rolling schedule on microstructure and texture evolution of strip casting grain-oriented silicon steel with extra-low carbon Metall Mat Trans A, 2016, 47: 1770–1781
Song H Y, Liu H T, Lu H H, et al. Effect of hot rolling reduction on microstructure, texture and ductility of strip-cast grain-oriented silicon steel with different solidification structures. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2014, 605: 260–269
Song H Y, Lu H H, Liu H T, et al. Microstructure and texture of strip cast grain-oriented silicon steel after symmetrical and asymmetrical hot rolling. Steel Res Int, 2014, 85: 1477–1482
Song H Y, Liu H T, Wang Y P, et al. Microstructure and texture evolution of ultra-thin grain-oriented silicon steel sheet fabricated using strip casting and three-stage cold rolling method. J Magn Magn Mater, 2017, 426: 32–39
Wang Y P, Liu H T, Song H Y, et al. Ultra-thin grain-oriented silicon steel sheet fabricated by a novel way: Twin-roll strip casting and two-stage cold rolling. J Magn Magn Mater, 2018, 452: 288–296
Fang F, Lu X, Zhang Y X, et al. Influence of cold rolling direction on texture, inhibitor and magnetic properties in strip-cast grain-oriented 3% silicon steel J Magn Magn Mater, 2017, 424: 339–346
Fang F, Lu X, Lan M, et al. Effect of rolling temperature on the microstructure, texture, and magnetic properties of strip-cast grain-oriented 3% Si steel J Mater Sci, 2018, 53: 9217–9231
Wang Y, Xu Y B, Zhang Y X, et al. Effect of annealing after strip casting on texture development in grain oriented silicon steel produced by twin roll casting. Mater Charact, 2015, 107: 79–84
Fang F, Lan M F, Lu X, et al. The impact of niobium on the microstructure, texture and magnetic properties of strip-cast grain oriented silicon steel J Magn Magn Mater, 2017, 442: 1–7
Lu X, Xu Y B, Fang F, et al. Characterization of microstructure and texture in grain-oriented high silicon steel by strip casting. Acta Metall Sin (Engl Lett), 2015, 28: 1394–1402
Lu X, Xu Y, Fang F, et al. Microstructure, texture and precipitate of grain-oriented 4.5wt% Si steel by strip casting. J Magn Magn Mater, 2016, 404: 230–237
Lu X, Fang F, Zhang Y X, et al. Microstructure and magnetic properties of strip-cast grain-oriented 4.5%Si steel under isochronal and isothermal secondary annealing. J Mater Sci, 2017, 53: 2928–2941
Lu X, Fang F, Zhang Y X, et al. Evolution of microstructure and texture in grain-oriented 6.5%Si steel processed by strip-casting. Mater Charact, 2017, 126: 125–134
Kuziak R, Kawalla R, Waengler Advanced high strength steels for automotive industry. Arch Civil Mech Eng, 2008, 8: 103–117
Xiong Z P, Kostryzhev A G, Stanford N E, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of dual phase steel produced by laboratory simulated strip casting. Mater Des, 2015, 88: 537–549
Xiong Z P, Kostryzhev A G, Stanford N E, et al. Effect of deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of dual phase steel produced via strip casting simulation. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2016, 651: 291–305
Xiong Z P, Saleh A A, Kostryzhev A G, et al. Strain-induced ferrite formation and its effect on mechanical properties of a dual phase steel produced using laboratory simulated strip casting. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 721: 291–306
Xiong Z, Kostryzhev A G, Zhao Y, et al. Microstructure evolution during the production of dual phase and transformation induced plasticity steels using modified strip casting simulated in the laboratory Metals, 2019, 9: 449
Wang H, Yuan G, Kang J, et al. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of dual phase steel produced by strip casting Mater Sci Eng-A, 2017, 703: 486–495
Xiong Z P, Kostryzhev A G, Saleh A A, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of TRIP steel produced by strip casting simulated in the laboratory Mater Sci Eng-A, 2016, 664: 26–42
Xiong Z P, Kostryzhev A G, Chen L, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of strip cast TRIP steel subjected to thermomechanical simulation. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2016, 677: 356–366
Wang H S, Yuan G, Zhang Y X, et al. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of duplex TRIP steel produced by strip casting. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2017, 692: 43–52
Xiong Z P, Saleh A A, Marceau R K W, et al. Site-specific atomic-scale characterisation of retained austenite in a strip cast TRIP steel. Acta Mater, 2017, 134: 1–15
Daamen M, Wietbrock B, Richter S, et al. Strip casting of a high-manganese steel (FeMn22C0.6) compared with a process chain consisting of ingot casting and hot forming. Steel Res Int, 2011, 82: 70–75
Daamen M, Nessen W, Pinard P T, et al. Deformation Behavior of High-manganese TWIP steels produced by twin-roll strip casting. Procedia Eng, 2014, 81: 1535–1540
Daamen M, Haase C, Dierdorf J, et al. Twin-roll strip casting: A competitive alternative for the production of high-manganese steels with advanced mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2015, 627: 72–81
Song C, Lu W, Xie K, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of sub-rapidly solidified Fe-18 wt%Mn-C alloy strip. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2014, 610: 145–153
Yang Y, Zhang J, Hu C, et al. Structures and properties of Fe-(8–16) Mn-9Al-0.8C low density steel made by a centrifugal casting in near-rapid solidification. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2019, 748: 74–84
Wang H, Zhang Y, Ran R, et al. A medium-Mn steel processed by novel twin-roll strip casting route. Mater Sci Tech, 2019, 35: 1227–1238
Wang Z, Carpenter K, Chen Z, et al. The effect of cooling rate and coiling temperature on the niobium retention in Ultra-Thin Cast Strip steel. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2017, 700: 234–240
Felfer P J, Killmore C R, Williams J G, et al. A quantitative atom probe study of the Nb excess at prior austenite grain boundaries in a Nb microalloyed strip-cast steel. Acta Mater, 2012, 60: 5049–5055
Dorin T, Wood K, Taylor A, et al. Effect of coiling treatment on microstructural development and precipitate strengthening of a strip cast steel. Acta Mater, 2016, 115: 167–177
Stanford N, Dorin T, Hodgson P D. The effect of Nb micro-alloying on the bainitic phase transformation under strip casting conditions. Metall Mat Trans A, 2018, 49: 1021–1025
Dorin T, Wood K, Taylor A, et al. Quantitative examination of carbide and sulphide precipitates in chemically complex steels processed by direct strip casting. Mater Charact, 2016, 112: 259–268
Sellamuthu P, Hodgson P, Stanford N. Effect of copper on microstructure, recrystallization and precipitation kinetics in strip cast low carbon steel. Mater Res Express, 2020, 6: 1265j5
Sellamuthu P, Stanford N, Hodgson P D. Recrystallization kinetic behavior of copper-bearing strip cast steel. Steel Res Int, 2013, 84: 1273–1280
Guan B, Hong S H, Schulz C, etal The microstructure, antimicrobial properties, and corrosion resistance of Cu-bearing strip cast steel. Adv Eng Mater, 2020, 22: 1901265
Wang W, Zhu C, Zeng J, et al. MnS precipitation behavior of high-sulfur microalloyed steel under sub-rapid solidification process. Metall Mater Trans B, 2019, 51: 45–53
Grydin O, Gerstein G, Nürnberger F, et al. Twin-roll casting of aluminum-steel clad strips. J Manuf Process, 2013, 15: 501–507
Münster D, Zhang B, Hirt G. Processing of clad steel strips consisting of a high manganese and stainless steel pairing produced by twin-roll casting. Steel Res Int, 2017, 88: 1600285
Stolbchenko M, Grydin O, Schaper M. Influence of surface roughness on the bonding quality in twin-roll cast clad strip. Mater Manufacturing Processes, 2017, 33: 727–734
Grydin O, Stolbchenko M, Schaper M. Deformation zone length and plastic strain in twin-roll casting of strips of Al-Mg-Si alloy. JOM, 2017, 69: 2648–2652
Haga T, Tkahashi K, Ikawaand M, et al. Twin roll casting of aluminum alloy strips. J Mater Process Tech, 2004, 153–154: 42–47
Sahoo S, Ghosh S. Microstructure evolution ofeutectic Al-Cu strips by high-speed twin-roll strip casting process. Appl Phys A, 2015, 121: 45–50
Wang H, Zhou L, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of twin-roll casting process parameters on the microstructure and sheet metal forming behavior of 7050 aluminum alloy. J Mater Process Tech, 2016, 233: 186–191
Kim M S, Kim S H, Kim H W. Deformation-induced center segregation in twin-roll cast high-Mg Al-Mg strips. Scripta Mater, 2018, 152: 69–73
Liu Y, Sun Y, Zhang L, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-5Mg-0.8Mn alloys with various contents of Fe and Si cast under near-rapid cooling. Metals, 2017, 7: 428
Song R, Harada Y, Kumai S. Influence of cooling rate on primary particle and solute distribution in high-speed twin-roll cast Al-Mn based alloy strip. Mater Trans, 2018, 59: 110–116
Al-Helal K, Patel J, Fan Z. Melt conditioning twin roll casting with thermo-mechanical treatment of recycled AA6111 alloy. JOM, 2018, 71: 1714–1721
Al-Helal K, Chang I, Patel J B, et al. Thermomechanical treatment of high-shear melt-conditioned twin-roll cast strip of recycled AA5754 alloy. JOM, 2019, 71: 2018–2024
He C, Li Y, Li J, et al. Effect of electromagnetic fields on microstructure and mechanical properties of sub-rapid solidification-processed Al-Mg-Si alloy during twin-roll casting. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2019, 766: 138328
Xu W, Birbilis N, Sha G, et al. A high-specific-strength and corrosion-resistant magnesium alloy. Nat Mater, 2015, 14: 1229–1235
Wang J, Wang L, Guan S, et al. Microstructure and corrosion properties of as sub-rapid solidification Mg-Zn-Y-Nd alloy in dynamic simulated body fluid for vascular stent application. J Mater Sci-Mater Med, 2010, 21: 2001–2008
Liang D, Cowley C B. The twin-roll strip casting of magnesium. JOM, 2004, 56: 26–28
Yang X, Patel J B, Huang Y, et al. Towards directly formable thin gauge AZ31 Mg alloy sheet production by melt conditioned twin roll casting. Mater Des, 2019, 179: 107887
Todaro C J, Easton M A, Qiu D, et al. Grain structure control during metal 3D printing by high-intensity ultrasound. Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 1–9
Kun Y, Hanqing X, Yilong D, et al. Mechanical properties and formability of ultrasonic treated twin roll casting magnesium alloy sheet. Rare Metal Mater Eng, 2017, 46: 622–626
Sorensen D, Hintsala E, Stevick J, et al. Intrinsic toughness of the bulk-metallic glass Vitreloy 105 measured using micro-cantilever beams. Acta Mater, 2020, 183: 242–248
Zhang L, Wu Y, Feng S, et al. Rejuvenated metallic glass strips produced via twin-roll casting. J Mater Sci Tech, 2020, 38: 73–79
Seki I, Kimura H, Inoue A. Thermal stability and mechanical properties of Ti47.4Cu42Zr5.3TM5.3(TM=Co, Fe) metallic glass sheets prepared by twin-roller casting method. Mater Trans, 2008, 49: 498–501
East D, Gibson M A, Liang D, et al. Production and mechanical properties of roll bonded bulk metallic glass/aluminum laminates. Metall Mat Trans A, 2013, 44: 2010–2020
Lee K S, Lee Y S. Fabrication of a Cu36Zr48Al8Ag8 bulk metallic glass sheet by atmosphere-controlled vertical twin roll strip casting. Int J Cast Met Res, 2018, 32: 78–84
Xu M, Liu G, Li T, et al. Microstructure characteristics of Ti-43Al alloy during twin-roll strip casting and heat treatment. Trans Non-ferrous Met Soc China, 2019, 29: 1017–1025
Wang W, Zhu C, Zeng J, et al. Microstructures and Nb-rich precipitation behaviors of inconel 718 superalloy under sub-rapid solidification process. Metall Mater Trans A, 2020, 51: 2306–2317
Shao C, Zhao S, Wang X, et al. Architecture of high-strength aluminum-matrix composites processed by a novel microcasting technique. NPG Asia Mater, 2019, 11: 69
Huang H, Wang J, Liu W. Mechanical properties and reinforced mechanism of the stainless steel wire mesh-reinforced Al-matrix composite plate fabricated by twin-roll casting. Adv Mech Eng, 2017, 9: 168781401771663
Morris J W. Making steel strong and cheap. Nat Mater, 2017, 16: 787–789
Bhadeshia H K D H, Edmonds D V. The bainite transformation in a silicon steel. Metall Mater Trans A, 1979, 10: 895–907
He B B, Hu B, Yen H W, et al. High dislocation density-induced large ductility in deformed and partitioned steels. Science, 2017, 357: 1029–1032
Jiang S, Wang H, Wu Y, et al. Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation. Nature, 2017, 544: 460–464
Ding R, Yao Y, Sun B, et al. Chemical boundary engineering: A new route toward lean, ultrastrong yet ductile steels. Sci Adv, 2020, 6: eaay1430
Liu L, Yu Q, Wang Z, et al. Making ultrastrong steel tough by grain-boundary delamination. Science, 2020, 368: 1347–1352
Wang Y, Sun J, Jiang T, et al. A low-alloy high-carbon martensite steel with 2.6 GPa tensile strength and good ductility. Acta Mater, 2018, 158: 247–256
Wang C, Chang Y, Zhou F, et al. M3 microstructure control theory and technology of the third-generation automotive steels with high-strength and high ductility (in Chinese). Acta Metall Sin, 2020, 56: 400–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1760202, 51904345), Hunan Provincial Key Research and Development Program (Grant No. 2018WK2051), and the State Scholarship Fund from the China Scholarship Council (Grant No. 201906370153).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, C., Zeng, J. & Wang, W. Twin-roll strip casting of advanced metallic materials. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 65, 493–518 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-020-1800-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-020-1800-8