Abstract
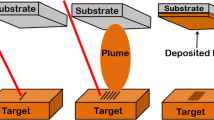
ZnO, as a wide-band gap semiconductor, has recently become a new research focus in the field of ultraviolet optoelectronic semiconductors. Laser molecular beam epitaxy (L-MBE) is quite useful for the unit cell layer-by-layer epitaxial growth of zinc oxide thin films from the sintered ceramic target. The ZnO ceramic target with high purity was ablated by KrF laser pulses in an ultra high vacuum to deposit ZnO thin film during the process of L-MBE. It is found that the deposition rate of ZnO thin film by L-MBE is much lower than that by conventional pulsed laser deposition (PLD). Based on the experimental phenomena in the ZnO thin film growth process and the thermal-controlling mechanism of the nanosecond (ns) pulsed laser ablation of ZnO ceramic target, the suggested effective ablating time during the pulse duration can explain the very low deposition rate of the ZnO film by L-MBE. The unique dynamic mechanism for growing ZnO thin film is analyzed. Both the high energy of the deposition species and the low growth rate of the film are really beneficial for the L-MBE growth of the ZnO thin film with high crystallinity at low temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rynolds D C, Look D C, Jogai B. Optically pumped ultraviolet lasing from ZnO. Solid State Commun, 1996, 99(12): 873–875
Sankur H, Cheung J T. Highly oriented ZnO films grown by laser evaporation. J Vac Sci Technol A, 1983, 1(4): 1806
Segawa Y, Ohtomo A, Kawasaki M, et al. Growth of ZnO thin film by laser MBE: Lasing of exciton at room temperature. Phy Stat Sol (b), 1997, 202: 669–672
He Y N, Zhu C C, Zhang J W. The study on mechanism of ultraviolet laser emission at room temperature from nanocrystal thin ZnO films grown on sapphire substrate by L-MBE. Microelectron J, 2004, 35(4): 389–392
Yu P, Tang Z K, Wong G K L, et al. Ultraviolet spontaneous and stimulated emissions from ZnO microcrystallite thin films at room temperature. Solid State Commun, 1997, 103(8): 459–463
Ohtomo A, Tsukazaki A. Pulsed laser deposition of thin films and superlattices based on ZnO. Semicond Sci Technol, 2005, 20: S1–S12
He Y N. Study of L-MBE of thin films and related nanostructures based on ZnO wide band-gap semiconductor (in Chinese). Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2005
He Y N, Zhu C C, Hou X, et al. Growth and characterization of ZnO films by laser molecular beam epitaxy. Vacuum Sci Tech (in Chinese), 2004, 24(6): 420–423
Craciun V, Elders J, Gardeniers J G E, et al. Characteristics of high quality ZnO thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Appl Phys Lett, 1994, 65(23): 2963–2965
Dang H J, Qin Q Z. Physical and chemical processes and mechanism of pulsed laser ablation of metal oxides. Chin J Quant Elect (in Chinese), 2004, 21(2): 217–223
Michel H. High-K gate dielectrics. Bristol, Philadelphia: Institute of Physics, c2004
Tsukazaki A, Ohtomo A, Onuma T, et al. Repeated temperature modulation epitaxy for p-type doping and light-emitting diode based on ZnO. Nat Mater, 2005, 5: 42–46
Cracium V, Craciun D, Bunescu M C, et al. Scanning electron microscopy investigation of laser ablated oxide targets. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 1999, 32: 1306–1312
Lu J, Ni X, He A. Physics of Interaction Between Laser and Materials (in Chinese). Bejing: China Machine Press, 1996. 66
Chrisey D B, Hubler G K. Pulsed Laser Deposition of Thin Film. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1994. 81
Kawasaki M. Ohtomo A, Ohkubo I., et al, Excitonic ultraviolet laser emission at room temperature from naturally made cavity in ZnO nanocrystal thin films. Mater Sci Eng B — Solid State Mater Adv Technol, 1998, 56: 239–245
Zhang J W, Xu Q A, Yang X D, et al. Study on the growth of the ZnO self-organized quantumn dots. In: Proceedings of 9th Chinese MOCVD Conference (in Chinese). Huangshan, Anhui Province, 2005, C-34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Xi’an Jiaotong University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Zhang, J., Yang, X. et al. Study on pulsed laser ablation and deposition of ZnO thin films by L-MBE. SCI CHINA SER E 50, 290–301 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-007-0035-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-007-0035-z