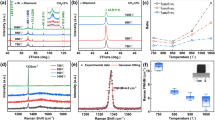
Abstract
Microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (MPCVD) is regarded as one of the most promising techniques for the preparation of large-scale and high-quality epitaxial single-crystal diamonds. This review paper provides an overview of recent advancements in MPCVD single-crystal diamond growth, including discussions on the growth mechanism, substrate holder design, and seed crystal screening and pretreatment for achieving homogeneous epitaxial single-crystal diamond. Key growth parameters such as temperature, methane concentration, power density, etc., are investigated to guide the attainment of optimal growth conditions. Furthermore, critical growth techniques like three-dimensional growth, repeated growth, and mosaic splicing are analyzed to enhance the area coverage of single-crystal diamonds. The work on achieving low defect and high purity growth is also elucidated. Additionally, this paper discusses the progress made in n-type and p-type doping of diamond materials. Finally, a summary is provided highlighting the challenges encountered during MPCVD single-crystal diamonds growth.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data were used for the research described in the article.
References
C.S. Yan, Y.K. Vohra, H.K. Mao, R.J. Hemley, Very high growth rate chemical vapor deposition of single-crystal diamond. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99, 12523–12525 (2002)
R.S. Balmer, J.R. Brandon, S.L. Clewes et al., Chemical vapour deposition synthetic diamond: materials, technology and applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 21, 364221 (2009)
C. Dang, A. Lu, H. Wang, H. Zhang, Y. Lu, Diamond semiconductor and elastic strain engineering. J. Semicond. 43, 021801 (2022)
C.T. Luo, L. Lindner, J. Langer, V. Cimalla, F. Hahl, Creation of nitrogen-vacancy centers in chemical vapor deposition diamond for sensing applications Creation of nitrogen-vacancy centers in chemical vapor deposition diamond for sensing applications. New J. Phys. 24, 033030 (2022)
T. Teraji, Chemical vapor deposition of homoepitaxial diamond films. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 203, 3324–3357 (2006)
Q. Liang, C.S. Yan, Y. Meng et al., Recent advances in high-growth rate single-crystal CVD diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 18, 698–703 (2009)
M. Schwander, K. Partes, A review of diamond synthesis by CVD processes. Diam. Relat. Mater. 20, 1287–1301 (2011)
F. Silva, J. Achard, O. Brinza et al., High quality, large surface area, homoepitaxial MPACVD diamond growth. Diam. Relat. Mater. 18, 683–697 (2009)
D.G. Goodwin, Scaling laws for diamond chemical-vapor deposition. I. Diamond surface chemistry. J. Appl. Phys. 74, 6888–6894 (1993)
D.G. Goodwin, Scaling laws for diamond chemical-vapor deposition. II. Atomic hydrogen transport. J. Appl. Phys. 74, 6895–6906 (1993)
T.R. Anthony, Metastable synthesis of diamond. Vacuum 41, 1356–1359 (1990)
Q. Yang, W. Chen, C. Xiao, A. Hirose, M. Bradley, Low temperature synthesis of diamond thin films through graphite etching in a microwave hydrogen plasma. Carbon NY. 43, 2635–2638 (2005)
J.C. Angus, H.A. Will, W.S. Stanko, Growth of diamond seed crystals by vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 39, 2915–2922 (1968)
O.A. Ivanov, A.B. Muchnikov, V.V. Chernov et al., Experimental study of hydrogen plasma etching of (1 0 0) single crystal diamond in a MPACVD reactor. Mater. Lett. 151, 115–118 (2015)
F.P. Bundy, H.T. Hall, H.M. Strong, R.H. Wentorf, Man-made diamonds. Nature 176, 51–55 (1955)
P. Bundy, The P-T phase and reaction diagram for elemental carbon. J. Geophys. Res. 85, 6930–6936 (1980)
J.E. Butler, Y.A. Mankelevich, A. Cheesman, J. Ma, M.N.R. Ashfold, Understanding the chemical vapor deposition of diamond: Recent progress. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 21, 364201 (2009)
A. Netto, M. Frenklach, Kinetic Monte Carlo simulations of CVD diamond growth-interlay among growth, etching, and migration. Diam. Relat. Mater. 14, 1630–1646 (2005)
R.S. Sussmann, CVD diamond for electronic devices and sensors (Wiley, London, 2009)
M. Jiang, C. Chen, Diamond formation mechanism in chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Sci. 119, 1–7 (2022)
Y. Mokuno, A. Chayahara, Y. Soda, Y. Horino, N. Fujimori, Synthesizing single-crystal diamond by repetition of high rate homoepitaxial growth by microwave plasma CVD. Diam. Relat. Mater. 14, 1743–1746 (2005)
A. Chayahara, Y. Mokuno, Y. Horino et al., The effect of nitrogen addition during high-rate homoepitaxial growth of diamond by microwave plasma CVD. Diam. Relat. Mater. 13, 1954–1958 (2004)
S. Nad, Y. Gu, J. Asmussen, Growth strategies for large and high quality single crystal diamond substrates. Diam. Relat. Mater. 60, 26–34 (2015)
H. Yamada, A. Chayahara, Y. Mokuno, Y. Horino, S. Shikata, Simulation of microwave plasmas concentrated on the top surface of a diamond substrate with finite thickness. Diam. Relat. Mater. 15, 1383–1388 (2006)
H. Yamada, A. Chayahara, Y. Mokuno, Y. Horino, S. Shikata, Simulation of temperature and gas flow distributions in region close to a diamond substrate with finite thickness. Diam. Relat. Mater. 15, 1738–1742 (2006)
A. Charris, S. Nad, J. Asmussen, Exploring constant substrate temperature and constant high pressure SCD growth using variable pocket holder depths. Diam. Relat. Mater. 76, 58–67 (2017)
M. Feng, P. Jin, X. Meng et al., One-step growth of a nearly 2 mm thick CVD single crystal diamond with an enlarged surface by optimizing the substrate holder structure. J. Cryst. Growth 603, 2–7 (2023)
H.D. Li, G.T. Zou, Q.L. Wang et al., High-rate growth and nitrogen distribution in homoepitaxial chemical vapour deposited single-crystal diamond. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25, 1803–1806 (2008)
C.J. Chu, R.H. Hauge, J.L. Margrave, M.P.D. Evelyn, Growth kinetics of (100), (110), and(111)homoepitaxial diamond films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 61, 1393–1395 (1992)
Y. Zhao, Y. Guo, L. Lin et al., Comparison of the quality of single-crystal diamonds grown on two types of seed substrates by MPCVD. J. Cryst. Growth 491, 89–96 (2018)
A. Tallaire, J. Achard, A. Boussadi et al., High quality thick CVD diamond films homoepitaxially grown on (111)-oriented substrates. Diam. Relat. Mater. 41, 34–40 (2014)
A. Tallaire, V. Mille, O. Brinza et al., Thick CVD diamond films grown on high-quality type IIa HPHT diamond substrates from new diamond technology. Diam. Relat. Mater. 77, 146–152 (2017)
X.C. Liu, X.G. Ge, Y.F. Li et al., Preparation of single-crystal diamond for small angle X-ray scattering in situ loading test. Diam. Relat. Mater. 121, 108719 (2022)
A. Tallaire, J. Achard, F. Silva et al., Oxygen plasma pre-treatments for high quality homoepitaxial CVD diamond deposition. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Res. 201, 2419–2424 (2014)
M. Naamoun, A. Tallaire, F. Silva et al., Etch-pit formation mechanism induced on HPHT and CVD diamond single crystals by H2/O2 plasma etching treatment: part of topical section on fundamentals and applications of diamond. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 209, 1715–1720 (2012)
J. Achard, A. Tallaire, R. Sussmann, F. Silva, A. Gicquel, The control of growth parameters in the synthesis of high-quality single crystalline diamond by CVD. J. Cryst. Growth 284, 396–405 (2015)
N. Derkaoui, C. Rond, K. Hassouni, A. Gicquel, Spectroscopic analysis of H2/CH4 microwave plasma and fast growth rate of diamond single crystal. J. Appl. Phys. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4883955
T. Teraji, T. Ito, Homoepitaxial diamond growth by high-power microwave-plasma chemical vapor deposition. J. Cryst. Growth 271, 409–419 (2014)
A. Tallaire, J. Achard, F. Silva, R.S. Sussmann, A. Gicquel, Homoepitaxial deposition of high-quality thick diamond films: Effect of growth parameters. Diam. Relat. Mater. 14, 249–254 (2005)
G. Lombardi, K. Hassouni, G.D. Stancu et al., Modeling of microwave discharges of H2 admixed with CH4 for diamond deposition. J. Appl. Phys. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2034646
J. Sierra Gómez, J. Vieira, M.A. Fraga, E.J. Corat, V.J. Trava-Airoldi, Surface morphology and spectroscopic features of homoepitaxial diamond films prepared by MWPACVD at High CH4 concentrations. Materials (Basel). 15, 7416 (2022)
F. Silva, K. Hassouni, X. Bonnin, A. Gicquel, Microwave engineering of plasma-assisted CVD reactors for diamond deposition. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 21, 364202 (2009)
A. Gicquel, F. Silva, C. Rond et al., Ultrafast deposition of diamond by plasma-enhanced CVD (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2014)
J. Achard, F. Silva, A. Tallaire et al., High quality MPACVD diamond single crystal growth: high microwave power density regime. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 6175–6188 (2007)
A.P. Bolshakov, V.G. Ralchenko, G. Shu et al., Single crystal diamond growth by MPCVD at subatmospheric pressures. Mater. Today Commun. 25, 101635 (2020)
J. Lu, Y. Gu, T.A. Grotjohn, T. Schuelke, J. Asmussen, Experimentally defining the safe and efficient, high pressure microwave plasma assisted CVD operating regime for single crystal diamond synthesis. Diam. Relat. Mater. 37, 17–28 (2013)
A. Tallaire, C. Rond, F. Bénédic et al., Effect of argon addition on the growth of thick single crystal diamond by high-power plasma CVD. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 208, 2028–2032 (2011)
A.P. Bolshakov, V.G. Ralchenko, V.Y. Yurov et al., High-rate growth of single crystal diamond in microwave plasma in CH4/H2 and CH4/H2/Ar gas mixtures in presence of intensive soot formation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 62, 49–57 (2016)
Y. Mokuno, A. Chayahara, Y. Soda et al., High rate homoepitaxial growth of diamond by microwave plasma CVD with nitrogen addition. Diam. Relat. Mater. 15, 455–459 (2006)
A. Tallaire, A.T. Collins, D. Charles et al., Characterisation of high-quality thick single-crystal diamond grown by CVD with a low nitrogen addition. Diam. Relat. Mater. 15, 1700–1707 (2006)
Q. Liang, C.Y. Chin, J. Lai et al., Enhanced growth of high quality single crystal diamond by microwave plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition at high gas pressures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 1–4 (2009)
A.M. Zaitsev, W. Wang, K.S. Moe, P. Johnson, Spectroscopic studies of yellow nitrogen-doped CVD diamonds. Diam. Relat. Mater. 68, 51–61 (2016)
J. Achard, F. Silva, O. Brinza, A. Tallaire, A. Gicquel, Coupled effect of nitrogen addition and surface temperature on the morphology and the kinetics of thick CVD diamond single crystals. Diam. Relat. Mater. 16, 685–689 (2007)
Y. Mokuno, A. Chayahara, H. Yamada, N. Tsubouchi, Improving purity and size of single-crystal diamond plates produced by high-rate CVD growth and lift-off process using ion implantation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 18, 1258–1261 (2009)
Y. Liou, A. Inspektor, R. Weimer, D. Knight, R. Messier, The effect of oxygen in diamond deposition by microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Mater. Res. Soc. 5, 2305–2312 (1990)
J. Liu, L. Lin, Y. Zhao et al., Homo-epitaxial growth of single crystal diamond in the purified environment by active O atoms. Vacuum 155, 391–397 (2018)
T. Teraji, High-quality and high-purity homoepitaxial diamond (100) film growth under high oxygen concentration condition. J. Appl. Phys. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4929962
M. Gong, Y. Chen, W. Yu et al., The effect of oxygen on the epitaxial growth of diamond. J. Semicond. 39, 123004 (2018)
C.J. Tang, A.J. Neves, A.J.S. Fernandes, Study the effect of O2 addition on hydrogen incorporation in CVD diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 13, 203–208 (2004)
G. Janssen, L.J. Giling, “Mosaic” growth of diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 4, 1025–1031 (1995)
A. Tallaire, J. Achard, F. Silva, O. Brinza, A. Gicquel, Growth of large size diamond single crystals by plasma assisted chemical vapour deposition: Recent achievements and remaining challenges. Comptes Rendus Phys. 14, 169–184 (2013)
H. Yamada, A. Chayahara, Y. Mokuno et al., Developments of elemental technologies to produce inch-size single-crystal diamond wafers. Diam. Relat. Mater. 20, 616–619 (2011)
H. Yamada, A. Chayahara, Y. Mokuno, Y. Kato, S. Shikata, A 2-in. mosaic wafer made of a single-crystal diamond. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4868720
C. Findeling-Dufour, A. Gicquel, Study for fabricating large area diamond single-crystal layers. Thin Solid Films 308–309, 178–185 (1997)
H. Yamada, A. Chayahara, Y. Mokuno, N. Tsubouchi, S.I. Shikata, Uniform growth and repeatable fabrication of inch-sized wafers of a single-crystal diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 33, 27–31 (2013)
P. Bergonzo, D. Tromson, C. Descamps et al., Improving diamond detectors: a device case. Diam. Relat. Mater. 16, 1038–1043 (2007)
K. Ikeda, H. Umezawa, K. Ramanujam, S.I. Shikata, Thermally stable schottky barrier diode by Ru/diamond. Appl. Phys. Express 2, 0112021–0112023 (2009)
A.T. Blumenau, M.I. Heggie, C.J. Fall, R. Jones, T. Frauenheim, Dislocations in diamond: core structures and energies. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 65, 2052051–2052058 (2002)
A. Tallaire, T. Ouisse, A. Lantreibecq et al., Identification of dislocations in synthetic chemically vapor deposited diamond single crystals. Cryst. Growth Des. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.6b00053
Y. Kato, H. Umezawa, S. Shikata, M. Touge, Effect of an ultraflat substrate on the epitaxial growth of chemical-vapor-deposited diamond. Appl. Phys. Express 6, 4–7 (2013)
Y. Mokuno, Y. Kato, N. Tsubouchi et al., A nitrogen doped low-dislocation density free-standing single crystal diamond plate fabricated by a lift-off process. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4885552
P.M. Martineau, M.P. Gaukroger, K.B. Guy et al., High crystalline quality single crystal chemical vapour deposition diamond. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 21, 364205 (2009)
Y. Mokuno, A. Chayahara, H. Yamada, N. Tsubouchi, Improvements of crystallinity of single crystal diamond plates produced by lift-off process using ion implantation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 19, 128–130 (2010)
N. Mizuochi, H. Watanabe, J. Isoya, H. Okushi, S. Yamasaki, Hydrogen-related defects in single crystalline CVD homoepitaxial diamond film studied by EPR. Diam. Relat. Mater. 13, 765–768 (2014)
A.M. Zaïtsev, Optical properties of diamond: a data handbook. Criminol. Crim. Justice. 11, 277–278 (2011)
S.J. Charles, J.E. Butler, B.N. Feygelson et al., Characterization of nitrogen doped chemical vapor deposited single crystal diamond before and after high pressure, high temperature annealing. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Res. 201, 2473–2485 (2004)
T. Teraji, High-quality and high-purity homoepitaxial diamond (100) film growth under high oxygen concentration condition. J. Appl. Phys. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4929962
B. Willems, A. Tallaire, J. Achard, Optical study of defects in thick undoped CVD synthetic diamond layers. Diam. Relat. Mater. 41, 25–33 (2014)
R. Rouzbahani, S.S. Nicley, D.E.P. Vanpoucke et al., Impact of methane concentration on surface morphology and boron incorporation of heavily boron-doped single crystal diamond layers. Carbon NY. 172, 463–473 (2021)
Y. Einaga, Boron-doped diamond electrodes: fundamentals for electrochemical applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 55, 3605–3615 (2022)
M. Werner, O. Dorsch, H.U. Baerwind et al., Charge transport in heavily B-doped polycrystalline diamond films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 64, 595–597 (1994)
E.A. Ekimov, V.A. Sidorov, Superconductivity in diamond. Nature 428, 542–545 (2004)
C. Tavares, F. Omnès, J. Pernot, E. Bustarret, Electronic properties of boron-doped {111}-oriented homoepitaxial diamond layers. Diam. Relat. Mater. 15, 582–585 (2006)
M.N.R. Ashfold, J.P. Goss, B.L. Green et al., Nitrogen in diamond. Chem. Rev. 120, 5745–5794 (2020)
R.G. Farrer, On the substitutional nitrogen donor in diamond. Solid State Commun. 7, 685–688 (1969)
M.A. Pinault, J. Barjon, T. Kociniewski, F. Jomard, J. Chevallier, The n-type doping of diamond: Present status and pending questions. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 401–402, 51–56 (2007)
S. Koizumi, M. Kamo, Y. Sato, H. Ozaki, T. Inuzuka, Growth and characterization of phosphorous doped 111 homoepitaxial diamond thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 1065–1067 (1997)
M.A. Pinault-Thaury, I. Stenger, R. Gillet et al., Attractive electron mobility in (113) n-type phosphorus-doped homoepitaxial diamond. Carbon N. Y. 175, 254–258 (2021)
M. Hasegawa, D. Takeuchi, S. Yamanaka et al., n-Type control by sulfur ion implantation in homoepitaxial diamond films grown by chemical vapor deposition. Japanese J. Appl. Phys. Part Lett. (1999). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.38.L1519
X. Sun, G. Wu, S. Shen et al., Insight into B-S ratio model and surface atom interactions of co-doping diamond: first-principles studies. Diam. Relat. Mater. 135, 109824 (2023)
D.Y. Liu, L.C. Hao, Z.A. Chen et al., Sulfur regulation of boron doping and growth behavior for high-quality diamond in microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0009615
Z. Lin, L. Ji, W. Wang, Precision machining of single crystal diamond cutting tool via picosecond laser irradiation. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 114, 106226 (2023)
G. Hemts, AlGaN / GaN high-electron mobility transistors with low thermal resistance grown on single-crystal diamond (111) substrates by metalorganic vapor-phase epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 1–4 (2011)
J. Fu, A. Hoffman, M.K. Kuntumalla et al., Investigation of the cooling enhancement of a single crystal diamond heat sink with embedded microfluidic channels. Diam. Relat. Mater. 130, 109470 (2022)
Z. Shi, Q. Yuan, Y. Wang et al., Optical properties of bulk single-crystal diamonds at 80–1200 K by vibrational spectroscopic methods. Materials (Basel). 14, 1–11 (2021)
A.K. Ratnikova, M.P. Dukhnovsky, Y.Y. Fedorov et al., Homoepitaxial single crystal diamond grown on natural diamond seeds (type IIa) with boron-implanted layer demonstrating the highest mobility of 1150 cm2/V·s at 300 K for ion-implanted diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 20, 1243–1245 (2011)
Wang XW. Research on single crystal diamond mosaic growth using HPHT diamond substrates. Dissertation of Master Degree. Shangdong University, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020
M. Schreck, S. Gsell, R. Brescia et al., Ion bombardment induced buried lateral growth: the key mechanism for the synthesis of single crystal diamond wafers. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–8 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Science and Technology Major Project of Henan Province (No. 231100230300), Science and Technology Major Project of Henan Province (No. 221100230300) and the Innovative Funds Plan of Henan University of Technology (No. 2021ZKCJ06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Project administration, Zhengxin Li and Xun Yang.; writing—original draft, Ying Ren; writing—review and editing, Xiaogang Li, Wei Lv and Haoyong Dong; synergistic effect, Feng Yue.; review and editing, Nicolas Wöhrl and Joana Catarina Mendes. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Prof. Zhengxin Li is the head of our research team and the funder of our research.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Y., Li, X., Lv, W. et al. Recent progress in homoepitaxial single-crystal diamond growth via MPCVD. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 525 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12267-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12267-3