Abstract
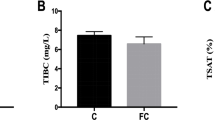
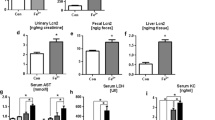
Iron overload often occurs during blood transfusion and iron supplementation, resulting in the presence of non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI) in host plasma and damage to multiple organs, but effects on the intestine have rarely been reported. In this study, an iron overload mouse model with plasma NTBI was established by intraperitoneal injection of iron dextran. We found that plasma NTBI damaged intestinal morphology, caused intestinal oxidative stress injury and reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, and induced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. In addition, plasma NTBI increased the relative abundance of Ileibacterium and Desulfovibrio in the cecum, while the relative abundance of Faecalibaculum and Romboutsia was reduced. Ileibacterium may be a potential microbial biomarker of plasma NTBI. Based on the function prediction analysis, plasma NTBI led to the weakening of intestinal microbiota function, significantly reducing the function of the extracellular structure. Further investigation into the mechanism of injury showed that iron absorption in the small intestine significantly increased in the iron group. Caco-2 cell monolayers were used as a model of the intestinal epithelium to study the mechanism of iron transport. By adding ferric ammonium citrate (FAC, plasma NTBI in physiological form) to the basolateral side, the apparent permeability coefficient (Papp) values from the basolateral to the apical side were greater than 3×10−6 cm s−1. Intracellular ferritin level and apical iron concentration significantly increased, and SLC39A8 (ZIP8) and SLC39A14 (ZIP14) were highly expressed in the FAC group. Short hairpin RNA (shRNA) was used to knock down ZIP8 and ZIP14 in Caco-2 cells. Transfection with ZIP14-specific shRNA decreased intracellular ferritin level and inhibited iron uptake. These results revealed that plasma NTBI may cause intestinal injury and intestinal flora dysbiosis due to the uptake of plasma NTBI from the basolateral side into the small intestine, which is probably mediated by ZIP14.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkhateeb, A.A., and Connor, J.R. (2010). Nuclear ferritin: a new role for ferritin in cell biology. Biochim Biophys Acta 1800, 793–797.
Andrews, N.C., and Schmidt, P.J. (2007). Iron homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol 69, 69–85.
Baek, J.H., Shin, H.K.H., Gao, Y., and Buehler, P.W. (2020). Ferroportin inhibition attenuates plasma iron, oxidant stress, and renal injury following red blood cell transfusion in guinea pigs. Transfusion 60, 513–523.
Biganzoli, E., Cavenaghi, L.A., Rossi, R., Brunati, M.C., and Nolli, M.L. (1999). Use of a Caco-2 cell culture model for the characterization of intestinal absorption of antibiotics. Farmaco 54, 594–599.
Camaschella, C. (2019). Iron deficiency. Blood 133, 30–39.
Camaschella, C., Nai, A., and Silvestri, L. (2020). Iron metabolism and iron disorders revisited in the hepcidin era. Haematologica 105, 260–272.
Chen, S., Wu, X., Wang, X., Shao, Y., Tu, Q., Yang, H., Yin, J., and Yin, Y. (2020). Responses of intestinal microbiota and immunity to increasing dietary levels of iron using a piglet model. Front Cell Dev Biol 8, 603392.
Chua, A.C.G., Olynyk, J.K., Leedman, P.J., and Trinder, D. (2004). Nontransferrin-bound iron uptake by hepatocytes is increased in the Hfe knockout mouse model of hereditary hemochromatosis. Blood 104, 1519–1525.
Das, N.K., Schwartz, A.J., Barthel, G., Inohara, N., Liu, Q., Sankar, A., Hill, D.R., Ma, X., Lamberg, O., Schnizlein, M.K., et al. (2020). Microbial metabolite signaling is required for systemic iron homeostasis. Cell Metab 31, 115–130.e6.
Ding, H., Yu, X., Chen, L., Han, J., Zhao, Y., and Feng, J. (2020a). Tolerable upper intake level of iron damages the intestine and alters the intestinal flora in weaned piglets. Metallomics 12, 1356–1369.
Ding, H., Yu, X., and Feng, J. (2020b). Iron homeostasis disorder in piglet intestine. Metallomics 12, 1494–1507.
Ding, H., Zhang, Q., Yu, X., Chen, L., Wang, Z., and Feng, J. (2021). Lipidomics reveals perturbations in the liver lipid profile of iron-overloaded mice. Metallomics 13, mfab057.
Dong, Z., Wan, D., Li, G., Zhang, Y., Yang, H., Wu, X., and Yin, Y. (2020). Comparison of oral and parenteral iron administration on iron homeostasis, oxidative and immune status in anemic neonatal pigs. Biol Trace Elem Res 195, 117–124.
Eady, J.J., Wormstone, Y.M., Heaton, S.J., Hilhorst, B., and Elliott, R.M. (2015). Differential effects ofbasolateral and apical iron supply on iron transport in Caco-2 cells. Genes Nutr 10, 14.
El-Sheikh, A.A., Ameen, S.H., and AbdEl-Fatah, S.S. (2018). Ameliorating iron overload in intestinal tissue of adult male rats: quercetin vs deferoxamine. J Toxicol 2018, 1–13.
Evans, R.W., Rafique, R., Zarea, A., Rapisarda, C., Cammack, R., Evans, P. J., Porter, J.B., and Hider, R.C. (2008). Nature ofnon-transferrin-bound iron: studies on iron citrate complexes and thalassemic sera. J Biol Inorg Chem 13, 57–74.
Ferro, E., Visalli, G., Civa, R., La Rosa, M.A., Randazzo Papa, G., Baluce, B., D’Ascola, D.G., Piraino, B., Salpietro, C., and Di Pietro, A. (2012). Oxidative damage and genotoxicity biomarkers in transfused and untransfused thalassemic subjects. Free Radic Biol Med 53, 1829–1837.
Fleming, R.E., and Ponka, P. (2012). Iron overload in human disease. N Engl J Med 366, 348–359.
Ganz, T. (2013). Systemic iron homeostasis. Physiol Rev 93, 1721–1741.
Gao, J., Yang, Z., Zhao, C., Tang, X., Jiang, Q., and Yin, Y. (2022). A comprehensive review on natural phenolic compounds as alternatives to in-feed antibiotics. Sci China Life Sci doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2246-4.
Golfeyz, S., Lewis, S., and Weisberg, I.S. (2018). Hemochromatosis: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management of hepatic iron overload with a focus on MRI. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 12, 767–778.
Gulec, S., Anderson, G.J., and Collins, J.F. (2014). Mechanistic and regulatory aspects of intestinal iron absorption. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 307, G397–G409.
Gunshin, H., Fujiwara, Y., Custodio, A.O., DiRenzo, C., Robine, S., and Andrews, N.C. (2005). SLC11A2 is required for intestinal iron absorption and erythropoiesis but dispensable in placenta and liver. J Clin Invest 115, 1258–1266.
Guthrie, G.J., Aydemir, T.B., Troche, C., Martin, A.B., Chang, S.M., and Cousins, R.J. (2015). Influence of ZIP14 (SLC39A14) on intestinal zinc processing and barrier function. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 308, G171–G178.
Haenen, G.R.M.M., and Bast, A. (2014). Glutathione revisited: a better scavenger than previously thought. Front Pharmacol 5, 260.
Hider, R.C., Silva, A.M.N., Podinovskaia, M., and Ma, Y. (2010). Monitoring the efficiency of iron chelation therapy: the potential of nontransferrin-bound iron. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1202, 94–99.
Hubatsch, I., Ragnarsson, E.G.E., and Artursson, P. (2007). Determination of drug permeability and prediction of drug absorption in Caco-2 monolayers. Nat Protoc 2, 2111–2119.
Knutson, M.D. (2019). Non-transferrin-bound iron transporters. Free Radic Biol Med 133, 101–111.
Koonyosying, P., Kongkarnka, S., Uthaipibull, C., Svasti, S., Fucharoen, S., and Srichairatanakool, S. (2018). Green tea extract modulates oxidative tissue injury in beta-thalassemic mice by chelation of redox iron and inhibition oflipid peroxidation. Biomed Pharmacother 108, 1694–1702.
La Carpia, F., Wojczyk, B.S., Annavajhala, M.K., Rebbaa, A., Culp-Hill, R., D’Alessandro, A., Freedberg, D.E., Uhlemann, A.C., and Hod, E.A. (2019). Transfusional iron overload and intravenous iron infusions modify the mouse gut microbiota similarly to dietary iron. NPJ Biofilms Microbio 5, 26.
La Carpia, F., Slate, A., Bandyopadhyay, S., Wojczyk, B.S., Godbey, E.A., Francis, K.P., Prestia, K., and Hod, E.A. (2022). Red blood cell transfusion-induced non-transferrin-bound iron promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in human sera and mortality in catheterized mice. Br J Haematol 196, 1105–1110.
Li, J., Wang, S., Duan, J., Le, P., Li, C., Ding, Y., Wang, R., and Gao, Y. (2021). The protective mechanism of resveratrol against hepatic injury induced by iron overload in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 424, 115596.
Li, Y., Han, Y., Zhao, Q., Tang, C., Zhang, J., and Qin, Y. (2022). Fermented soy and fish protein dietary sources shape ileal and colonic microbiota, improving nutrient digestibility and host health in a piglet model. Front Microbiol 13, 911500.
Li, Y., Ouyang, Q., Chen, W., Liu, K., Zhang, B., Yao, J., Zhang, S., Ding, J., Cong, M., and Xu, A. (2023). An iron-dependent form of non-canonical ferroptosis induced by labile iron. Sci China Life Sci 66, 516–527.
Light, S.H., Su, L., Rivera-Lugo, R., Cornejo, J.A., Louie, A., Iavarone, A. T., Ajo-Franklin, C.M., and Portnoy, D.A. (2018). A flavin-based extracellular electron transfer mechanism in diverse Gram-positive bacteria. Nature 562, 140–144.
Liu, B., Pan, X., Liu, Z., Han, M., Xu, G., Dai, X., Wang, W., Zhang, H., and Xie, L. (2020a). Fecal microbiota as a noninvasive biomarker to predict the tissue iron accumulation in intestine epithelial cells and liver. FASEB J 34, 3006–3020.
Liu, Y., Luo, L., Luo, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, X., Sun, K., and Zeng, L. (2020b). Prebiotic properties of green and dark tea contribute to protective effects in chemical-induced colitis in mice: a fecal microbiota transplantation study. J Agric Food Chem 68, 6368–6380.
Lopez, A., Cacoub, P., Macdougall, I.C., and Peyrin-Biroulet, L. (2016). Iron deficiency anaemia. Lancet 387, 907–916.
Luo, Q., Lao, C., Huang, C., Xia, Y., Ma, W., Liu, W., and Chen, Z. (2021). Iron overload resulting from the chronic oral administration of ferric citrate impairs intestinal immune and barrier in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 1027–1036.
Ma, Y., Deng, L., Ma, P., Wu, Y., Yang, X., Xiao, F., and Deng, Q. (2021). In vivo respiratory toxicology of cooking oil fumes: evidence, mechanisms and prevention. J Hazard Mater 402, 123455.
Mayneris-Perxachs, J., Moreno-Navarrete, J.M., and Fernández-Real, J.M. (2022). The role of iron in host-microbiota crosstalk and its effects on systemic glucose metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol 18, 683–698.
Muckenthaler, M.U., Rivella, S., Hentze, M.W., and Galy, B. (2017). A red carpet for iron metabolism. Cell 168, 344–361.
Pai, A.B., Boyd, A.V., McQuade, C.R., Harford, A., Norenberg, J.P., and Zager, P.G. (2007). Comparison of oxidative stress markers after intravenous administration ofiron dextran, sodium ferric gluconate, and iron sucrose in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Pharmacotherapy 27, 343–350.
Pai, A.B., Conner, T., McQuade, C.R., Olp, J., and Hicks, P. (2011). Non-transferrin bound iron, cytokine activation and intracellular reactive oxygen species generation in hemodialysis patients receiving intravenous iron dextran or iron sucrose. Biometals 24, 603–613.
Raffaniello, R.D., Lee, S.Y., Teichberg, S., and Wapnir, R.A. (1992). Distinct mechanisms of zinc uptake at the apical and basolateral membranes of Caco-2 cells. J Cell Physiol 152, 356–361.
Ren, W., Yu, B., Yu, J., Zheng, P., Huang, Z., Luo, J., Mao, X., He, J., Yan, H., Wu, J., et al. (2022). Lower abundance of Bacteroides and metabolic dysfunction are highly associated with the post-weaning diarrhea in piglets. Sci China Life Sci 65, 2062–2075.
Scheiber, I.F., Alarcon, N.O., and Zhao, N. (2019). Manganese uptake by A549 cells is mediated by both ZIP8 and ZIP14. Nutrients 11, 1473.
Shu, W., Baumann, B.H., Song, Y., Liu, Y., Wu, X., and Dunaief, J.L. (2019). Iron accumulates in retinal vascular endothelial cells but has minimal retinal penetration after IP iron dextran injection in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 60, 4378–4387.
Shindo, M., Torimoto, Y., Saito, H., Motomura, W., Ikuta, K., Sato, K., Fujimoto, Y., and Kohgo, Y. (2006). Functional role of DMT1 in transferrin-independent iron uptake by human hepatocyte and hepatocellular carcinoma cell, HLF. Hepatol Res 35, 152–162.
Silva, A.M.N., and Rangel, M. (2022). The (bio)chemistry of non-transferrin-bound iron. Molecules 27, 1784.
Sun, H., Chow, E.C., Liu, S., Du, Y., and Pang, K.S. (2008). The Caco-2 cell monolayer: usefulness and limitations. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4, 395–411.
Svoboda, M., Vanhara, J., and Berlinska, J. (2017). Parenteral iron administration in suckling piglets—a review. Acta Vet Brno 86, 249–261.
Tagliabue, A., Bowie, A.R., Boyd, P.W., Buck, K.N., Johnson, K.S., and Saito, M.A. (2017). The integral role of iron in ocean biogeochemistry. Nature 543, 51–59.
Tanaka, H., Espinoza, J., Fujiwara, R., Rai, S., Morita, Y., Ashida, T., Kanakura, Y., and Matsumura, I. (2019). Excessive reactive iron impairs hematopoiesis by affecting both immature hematopoietic cells and stromal cells. Cells 8, 226.
Tan, Z., Liu, Y., Liu, H., Yang, C., Niu, Q., and Cheng, J.J. (2021). Effects of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural on removal performance and microbial community structure of aerobic activated sludge treating digested swine wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 9, 106104.
Taylor, K.M., Morgan, H.E., Johnson, A., and Nicholson, R.I. (2005). Structure-function analysis of a novel member of the LIV-1 subfamily of zinc transporters, ZIP14. FEBS Lett 579, 427–432.
Venkataramani, V. (2021). Iron homeostasis and metabolism: two sides of a coin. Adv Exp Med Biol 1301, 25–40.
Wang, C.Y., and Babitt, J.L. (2019). Liver iron sensing and body iron homeostasis. Blood 133, 18–29.
Wang, C.Y., Jenkitkasemwong, S., Duarte, S., Sparkman, B.K., Shawki, A., Mackenzie, B., and Knutson, M.D. (2012). ZIP8 is an iron and zinc transporter whose cell-surface expression is up-regulated by cellular iron loading. J Biol Chem 287, 34032–34043.
Wongjaikam, S., Kumfu, S., Khamseekaew, J., Sripetchwandee, J., Srichairatanakool, S., Fucharoen, S., Chattipakorn, S.C., and Chattipakorn, N. (2016). Combined iron chelator and antioxidant exerted greater efficacy on cardioprotection than monotherapy in iron-overloaded rats. PLoS ONE 11, e0159414.
Xiao, X., Cheng, Y.Z., Fu, J., Lu, Z.Q., Wang, F.Q., Jin, M.L., Zong, X., and Wang, Y.Z. (2021). Gut immunity and microbiota dysbiosis are associated with altered bile acid metabolism in LPS-challenged piglets. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021, 6634821.
Yu, X., Chen, L., Ding, H., Zhao, Y., and Feng, J. (2019). Iron transport from ferrous bisglycinate and ferrous sulfate in DMT1-knockout human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Nutrients 11, 485.
Yu, X., Zhang, Q., Ding, H., Wang, P., and Feng, J. (2022). Plasma non-transferrin-bound iron could enter into mice duodenum and negatively affect duodenal defense response to virus and immune responses. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 786–799.
Zang, Z.S., Xu, Y.M., and Lau, A.T.Y. (2016). Molecular and pathophysiological aspects of metal ion uptake by the zinc transporter ZIP8 (SLC39A8). Toxicol Res 5, 987–1002.
Zeidan, R.S., Han, S.M., Leeuwenburgh, C., and Xiao, R. (2021). Iron homeostasis and organismal aging. Ageing Res Rev 72, 101510.
Zhang, J., Chen, X., Hong, J., Tang, A., Liu, Y., Xie, N., Nie, G., Yan, X., and Liang, M. (2021). Biochemistry of mammalian ferritins in the regulation of cellular iron homeostasis and oxidative responses. Sci China Life Sci 64, 352–362.
Zhang, J., Wang, X., Vikash, V., Ye, Q., Wu, D., Liu, Y., and Dong, W. (2016). ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016, 1–18.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32272886) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD1300500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Ding, H., Yu, X. et al. Plasma non-transferrin-bound iron uptake by the small intestine leads to intestinal injury and intestinal flora dysbiosis in an iron overload mouse model and Caco-2 cells. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 2041–2055 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2347-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2347-0