Abstract
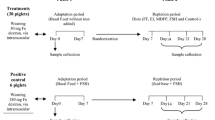
The present study was to evaluate the consequences of iron status across oral and parenteral iron administrations in prevention of iron deficiency anemia. A total of 24 one-day-old male neonatal piglets were allocated into three groups given non-iron supplementation (NON), intramuscular iron dextran injection (FeDex), and oral administration of ferrous glycine chelate (FeGly), respectively. At day 8, no significant differences in final body weight, average weight gain, and tissue coefficients were observed among three groups (P > 0.05). Both oral FeGly and FeDex injection significantly increased serum iron, ferritin, hemoglobin, and tissue iron deposition (P < 0.05). However, FeDex-injected supplementation resulted in rapidly rising hepcidin levels and hepatic iron deposition (P < 0.05). In addition, compared to parenteral iron supplementation, greater serum IgA level, SOD, and GSH-Px activities, lower expressions of IL-1β and TNF-α in the liver, and lower expressions of IL-6 and TNF-α in the spleen were found in oral iron piglets (P < 0.05). According to our results, oral administration of ferrous glycine chelate improved iron homeostasis, and oxidative and immune status in anemic neonatal pigs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beard JL (2001) Iron biology in immune function, muscle metabolism and neuronal functioning. J Nutr 131:568S–579S. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-277X.2001.00268.x
Black MM, Quigg AM, Hurley KM, Pepper MR (2011) Iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in the first two years of life: strategies to prevent loss of developmental potential. Nutr Rev 69:S64–S70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00435.x
Jonker FAM, van Hensbroek MB (2014) Anaemia, iron deficiency and susceptibility to infections. J Inf Secur 69:S23–S27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2014.08.007
Collard KJ (2009) Iron homeostasis in the neonate. Pediatrics 123:1208–1216. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-1047
Ziegler EE, Nelson SE, Jeter JM (2014) Iron stores of breastfed infants during the first year of life. Nutrients 6(5):2023–2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6052023
Svoboda M, Vanhara J, Berlinska J (2017) Parenteral iron administration in suckling piglets—a review. Acta Vet Brno 86:249–261. https://doi.org/10.2754/avb201786030249
Pineda O, Ashmead HD (2001) Effectiveness of treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children with ferrous bis-glycinate chelate. Nutrition 17:381–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-9007(01)00519-6
Bovell-Benjamin AC, Viteri FE, Allen LH (2000) Iron absorption from ferrous bisglycinate and ferric trisglycinate in whole maize is regulated by iron status. Am J Clin Nutr 71:1563–1569. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-2040(00)00065-5
Braude R, Chamberlain AG, Kotarbinska M, Mitchell KGJBJoN (1962) The metabolism of iron in piglets given labelled iron either orally or by injection. 16:427–449 doi:https://doi.org/10.1079/BJN19620043
Szabo P, Bilkei G (2002) Short communication—iron deficiency in outdoor pig production. J Vet Med Ser A-Physiol Pathol Clin Med 49:390–391. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0442.2002.00448.x
Knight LC, Dilger RN (2018) Longitudinal effects of iron deficiency anemia and subsequent repletion on blood parameters and the rate and composition of growth in pigs. Nutrients 10:17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10050632
Kruszewski M, Iwanenko T, Bartlomiejczyk T, Wolinski J, Starzynski RR, Gralak MA, Zabielski R, Lipinski P (2008) Hepatic iron content corresponds with the susceptibility of lymphocytes to oxidative stress in neonatal pigs. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 657:146–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.08.020
Kegley EB, Spears JW, Flowers WL, Schoenherr WD (2002) Iron methionine as a source of iron for the neonatal pig. Nutr Res 22:1209–1217. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0271-5317(02)00434-7
Maes D, Steyaert M, Vanderhaeghe C, Rodriguez AL, de Jong E, Sacristan RD, Vangroenweghe F, Dewulf J (2011) Comparison of oral versus parenteral iron supplementation on the health and productivity of piglets. Vet Rec 168:188–188. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.c7033
Ku PK, Miller ER, Ullrey DE (1983) Effect of parenteral iron on serum electrolytes of the baby pig. J Anim Sci 57:638–644. https://doi.org/10.1051/gse:19830408
Starzynski RR, Laarakkers CMM, Tjalsma H, Swinkels DW, Pieszka M, Stys A, Mickiewicz M, Lipinski P (2013) Iron supplementation in suckling piglets: how to correct iron deficiency anemia without affecting plasma hepcidin levels. PLoS One 8(7):e64022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064022
Anderson GJ, Frazer DM, Wilkins SJ, Becker EM, Millard KN, Murphy TL, McKie AT, Vulpe CD (2002) Relationship between intestinal iron-transporter expression, hepatic hepcidin levels and the control of iron absorption. Biochem Soc Trans 30:724–726. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0300724
Hansen SL, Nares T, Hsiao-Ching L, Moeser AJ, Spears JW (2009) Iron transporters are differentially regulated by dietary iron, and modifications are associated with changes in manganese metabolism in young pigs. J Nutr 139:1474–1479
Ji P, Lonnerdal B, Kim K, Jinno CN (2019) Iron oversupplementation causes hippocampal iron overloading and impairs social novelty recognition in nursing piglets. J Nutr 149:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxy227
Nemeth EJAH (2013) Targeting the hepcidin-ferroportin axis in the diagnosis and treatment of anemias. Adv Hematol 2010:750643 doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/750643, 1, 9
Kurtoglu E, Ugur A, Baltaci AK, Undar L (2003) Effect of iron supplementation on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in iron-deficiency anemia. Biol Trace Elem Res 96:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1385/bter:96:1-3:117
Koskenkorva-Frank TS, Weiss G, Koppenol WH, Burckhardt S (2013) The complex interplay of iron metabolism, reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen species: insights into the potential of various iron therapies to induce oxidative and nitrosative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 65:1174–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.09.001
Vieyra-Reyes P, Millan-Aldaco D, Palomero-Rivero M, Jimenez-Garces C, Hernandez-Gonzalez M, Caballero-Villarraso J (2017) An iron-deficient diet during development induces oxidative stress in relation to age and gender in Wistar rats. J Physiol Biochem 73:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0529-x
Knutson MD, Walter PB, Ames BN, Viteri FE (2000) Both iron deficiency and daily iron supplements increase lipid peroxidation in rats. J Nutr 130:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/130.3.621
Ma J, Wen XS, Mo FF, Wang XL, Shen ZL, Li M (2014) Effects of different doses and duration of iron supplementation on curing iron deficiency anemia: an experimental study. Biol Trace Elem Res 162:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0115-4
Lipinski P, Starzynski RR, Canonne-Hergaux F, Tudek B, Olinski R, Kowalczyk P, Dziaman T, Thibaudeau O, Gralak MA, Smuda E, Wolinski J, Usinska A, Zabielski R (2010) Benefits and risks of iron supplementation in anemic neonatal pigs. Am J Pathol 177:1233–1243. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2010.091020
Adham KG, Alkhalifa AA, Farhood MH, Aleisa NA, Daghestani MH (2014) Oxidative stress and antioxidant response to subacute and subchronic iron overload in Wistar rat. Biologia 69:817–824. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-014-0364-x
Bonaccorsi-Riani E, Danger R, Lozano JJ, Martinez-Picola M, Kodela E, Mas-Malavila R, Bruguera M, Collins HL, Hider RC, Martinez-Llordella M, Sanchez-Fueyo A (2015) Iron deficiency impairs intra-hepatic lymphocyte mediated immune response. PLoS One 10:16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136106
Ekiz C, Agaoglu L, Karakas Z, Gurel N, Yalcin I (2005) The effect of iron deficiency anemia on the function of the immune system. Hematol J 5:579–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.thj.6200574
Hassan TH, Badr MA, Karam NA, Zkaria M, El Saadany HF, Rahman DMA, Shahbah DA, Al Morshedy SM, Fathy M, Esh AMH, Selim AM (2016) Impact of iron deficiency anemia on the function of the immune system in children. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:5. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000005395
Sadeghian MH, Keramati MR, Ayatollahi H, Manavifar L, Enaiati H, Mahmoudi M (2010) Serum immunoglobulins in patients with iron deficiency anemia. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 26:45–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-010-0025-3
Ferrucci L, Semba RD, Guralnik JM, Ershler WB, Bandinelli S, Patel KV, Sun K, Woodman RC, Andrews NC, Cotter RJ, Ganz T, Nemeth E, Longo DL (2010) Proinflammatory state, hepcidin, and anemia in older persons. Blood 115:3810–3816. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-02-201087
Jason J, Archibald LK, Nwanyanwu OC, Bell M, Jensen RJ, Gunter E, Buchanan I, Larned J, Kazembe PN, Dobbie H, Jarvis WR (2001) The effects of iron deficiency on lymphocyte cytokine production and activation: preservation of hepatic iron but not at all cost. Clin Exp Immunol 126:466–473. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01707.x
Svoboda M, Drabek J, Krejci J, Rehakova Z, Faldyna M (2004) Impairment of the peripheral lymphoid compartment in iron-deficient piglets. J Vet Med Ser B-Infect Dis Vet Public Health 51:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0450.2004.00761.x
Toblli JE, Cao G, Oliveri L, Angerosa M (2012) Comparison of oxidative stress and inflammation induced by different intravenous iron sucrose similar preparations in a rat model. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 11:66–78. https://doi.org/10.2174/187152812798889358
Xiong HT, Gao YH, Liu D, Wang YZ, Du HH (2015) High level of hepcidin mRNA expression is associated with high production of immune factors in Tibetan pigs. Livest Sci 171:73–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2014.11.008
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFD0501201), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31702127), the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (2018QNRC001), and the Hunan Province Key Laboratory of Animal Nutritional Physiology and Metabolic Process (2018TP1031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 173 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Z., Wan, D., Li, G. et al. Comparison of Oral and Parenteral Iron Administration on Iron Homeostasis, Oxidative and Immune Status in Anemic Neonatal Pigs. Biol Trace Elem Res 195, 117–124 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01846-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01846-9