Abstract
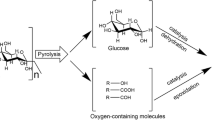
Catalytic conversion of sustainable cellulose to the value-added chemicals and high quality biofuel has been recognized as a perfect approach for the alleviation of the dependence on the non-renewable fossil resources. Previously, we successfully designed and explored novel and efficient cooperative ionic liquid pairs for this renewable material, which has advantages of high reactor efficiency than current technologies because of the dissolution and in situ catalytic decomposition mechanism. Here, the determinant of this process is further studied by the intensive investigation on the relationship between the cellulose conversion and the properties of ionic liquid catalyst and solvent. Scanning electron microscope (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TG) and elemental analysis were used for the comparative characterization of raw cellulose and the residues. The results demonstrate that this consecutive dissolution and in situ catalysis process is much more dependent on the dissolution capability of ionic liquid solvent, while comparatively, the effect of in situ acid catalysis is relatively insignificant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink HP, Bohn A. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2005, 44: 3358–3393
Klemm D, Schmauder HP, Heinze T. Cellulose. In: Vandamme E, De Beats S, Steinbüchel A, Eds. Biopolymers: Biology, Chemistry, Biotechnology, Applications, Polysaccharide II. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2002
Ummartyotin S, Manuspiya H. Renew Sust Energ Rev, 2015, 50: 204–213
Van de Vyver S, Geboers J, Jacobs PA, Sels BF. Chemcatchem, 2011, 3: 82–94
Zakrzewska ME, Bogel-Lukasik E, Bogel-Lukasik R. Chem Rev, 2011, 111: 397–417
Corma A, Iborra S, Velty A. Chem Rev, 2007, 107: 2411–2502
Zhao H, Holladay JE, Brown H, Zhang ZC. Science, 2007, 316: 1597–1600
Ryu S, Labbe N, Trinh CT. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2015, 99: 4237–4244
Ma H, Long JX, Wang FR, Wang LF, Li XH. Acta Phys Chim Sin, 2015, 31: 973–979
Deng W, Zhang Q, Wang Y. Sci China Chem, 2015, 58: 29–46
Jarvis M. Nature, 2003, 426: 611–612
Long JX, Yuan ZQ, Ma H, Shu RY, Li XH. Acta Phys Chim Sin, 2015, 31: 337–343
He H, Zheng Y, Chen H, Zhang X, Yao X, Zhang S. Sci China Chem, 2012, 55: 1548–1556
Lee SG. Chem Commun, 2006, 10: 1049–1063
Hallett JP, Welton T. Chem Rev, 2011, 111: 3508–3576
Swatloski RP, Spear SK, Holbrey JD, Rogers RD. J Am Chem Soc, 2002, 124: 4974–4975
Andanson JM, Padua AAH, Gomes MFC. Chem Commun, 2015, 51: 4485–4487
de Oliveira HFN, Rinaldi R. ChemSusChem, 2015, 8: 1577–1584
Long JX, Guo B, Li XH, Wang FR, Wang LF. Acta Phys Chim Sin, 2011, 27: 995–999
Long J, Li X, Wang L, Zhang N. Sci China Chem, 2012, 55: 1500–1508
Zhang S, Sun J, Zhang X, Xin J, Miao Q, Wang J. Chem Soc Rev, 2014, 43: 7838–7869
Long J, Guo B, Li X, Jiang Y, Wang F, Tsang SC, Wang L, Yu KMK. Green Chem, 2011, 13: 2334–2338
Long J, Li X, Guo B, Wang F, Yu Y, Wang L. Green Chem, 2012, 14: 1935–1941
Pinkert A, Marsh KN, Pang SS, Staiger MP. Chem Rev, 2009, 109: 6712–6728
Liu S, Tang L, Long J, Guan J, Li X. Catal Today, 2016, 264: 75–82
Zhao Y L, Liu XM, Wang JJ, Zhang SJ. Carbohydr Polym, 2013, 94: 723–730
Wen JL, Yuan TQ, Sun SL, Xu F, Sun RC. Green Chem, 2014, 16: 181–190
Zhang X, Wang T, Ma L, Zhang Q, Jiang T. Bioresour Technol, 2013, 127: 306–311
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, L. et al. Which is the determinant for cellulose degradation in cooperative ionic liquid pairs: dissolution or catalysis?. Sci. China Chem. 59, 557–563 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-016-5586-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-016-5586-z